Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Barrow J.D., Tipler F.J. — Anthropic Cosmological Principle
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Anthropic Cosmological PrincipleАвторы: Barrow J.D., Tipler F.J. Аннотация: Ever since Copernicus, scientists have continually adjusted their view of human nature, moving it further and further from its ancient position at the center of Creation. But in recent years, a startling new concept has evolved that places it more firmly than ever in a special position. Known as the Anthropic Cosmological Principle, this collection of ideas holds that the existence of intelligent observers determines the fundamental structure of the Universe. In its most radical version, the Anthropic Principle asserts that "intelligent information-processing must come into existence in the Universe, and once it comes into existence, it will never die out."
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1986Количество страниц: 726Добавлена в каталог: 08.04.2009Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Closed universes, lifetime calculation 376 Closed universes, long-lived, cosmological expansion of 650 Closed universes, long-lived, timescales of 653—654 Closed universes, small, near final singularity, timescales of 647 Closed universes, telelogical prediction 153 Closed universes, time-evolution of expansion scale factor in 376 Closure of Universe, teleological arguments for 153 675 Clustering 377—378 415 Co-operative behaviour 100—102 Cocke-Wheeler cosmological model 674 Coincidences, elemental properties 124 143 252—253 Coincidences, large number 11 219—231 246—247 Cold bodies, planets as 328 340 Coleman-Weinberg interaction potential 432 435 Collins, C.B., on isotropy of Universe 419 423 426 Collins, C.B., on special initial conditions for evolution of Universe 250 Colonization (of space) 580 584—586 Colonization theories/models, diffusion model 585 Colonization theories/models, MacArthur-Wilson colonization theory 584 585 Colonization, motivations for 593—600 Colour charge (of quarks) 355 356 Communications region, far future of Universe 668 Communications, interstellar 577 Communications, motivations for 590—593 Comparative Advantage, (economic) Theory of 596 Complexity theory (of ecologists) 141 Compton scattering 299 Computer hardware, human brain compared with 136 137 Computer hardware, living body compared to 75 659 Computer program, human being as 659 Computer program, self-reproducing 522 Computer program, telelogical explanation 75 Computer program, Universe as 9 125 Computer speeds 136 206n 662 Computer technology, necessary for interstellar communication/exploration 577 578 Conformal diagrams see “Penrose diagrams” Conformal time 442 491 Confucianism 98—99 Confucius, quoted 98 Consciousness, collapsing wave functions 468 469 Consciousness, meaning of word 469 507n Consciousness, necessary to bring Cosmos into existence 471 Consequences, as coincidences 12 Constants of nature 5 see Constants of Nature, constrainted by self-selection effect 5 Constants of Nature, effects of small changes 254 Constants of Nature, statistical basis 253—254 257 Contingency argument 104—106 Continuous creation theories, of Jordan 235 Convergent evolution 132 Cooke, Josiah 88—89 118n Copenhagen interpretation 458 459 Copenhagen Interpretation, contrary-to-common-sense nature highlighted by EPR experiment 463 Copenhagen Interpretation, von Neumann's axioms for 464—465 Copenhagen Interpretation, wave function collapse required by 459 466 467 496 Copernican system 496 Copernician Principle 1 501 502 503 Copernician Principle, ETI justified by 600—601 Copernician Principle, Weak Anthropic Principle resulting in 4 Copernicus satellite/probe 379 Copernicus, Nicolas 49—50 Copleston, F. C, debate with Bertrand Russell 103 107—108 Cosmic epochs concept, of A.N. Whitehead 192 Cosmic teleology, defended by Peacocke and Mascall 183 Cosmic teleology, developed by Tennant 181—182 Cosmic teleology, notion introduced by Pringle-Pattison 181 Cosmogonic Philosophy 158 Cosmological arguments, and design arguments 103—109 Cosmological constant 225 234 412—424 Cosmological constant, anthropic limit for 414 Cosmological constant, effects on information processing 668—669 Cosmological models, closed universe 622 Cosmological models, cyclic models 616 Cosmological models, ever-expanding universe 623 Cosmological models, evolving models 616 Cosmological models, open universe 622 Cosmological models, recollapsing universe 623 Cosmological models, unchanging models 616 Cosmology, anthropic principles in 367—449 Costs, interstellar exploration 581—583 Costs, von Neumann probes 582—583 591—592 Covalent bonds 300 301 526 Cowper, William, quoted 220 Crane, S., quoted 166 Creation 'out of nothing' 440—444 Creation interpretation, Second Law of Thermodynamics 176 177 Croll, James, estimate of Earth's age 163 Crucial steps, in evolution of Man 562—564 Cudworth's 'plastic nature' concept 59 Cultural imperialism 596 Cummings, E. E., quoted 497 Cyclops project 577 D'Alembert, Jean 65 D'Alembert, quoted 103 D'Alembert, wave equation solution in one dimension 267 Daedalus project 581—582 Daedalus project, cost 582 Daedalus project, payload size 584 Daedalus project, rocket power 644 Dark material, galaxy groups/clusters 377 Dark material, possible particles for 390—391 Darwin, Charles 83—84 Darwin, concession on rate of evolutionary change 162 Darwin, Erasmus 72 Darwin, on Heat Death 167 Darwin, Origin of Species 9 161 162 615 Darwin, progress-to-perfection optimism 166 Darwin, quoted 166 167 180 Darwin, telelogical interpretation 85 86 Dawkins, R., idea-complexes as living organisms 522 Day length, calculation of 309—310 de Sitter space-time 433 434 435 668 De Sitter, W., quoted 430 Deceleration, of expanding Universe 375 Definitions, Anthropic Principle 15—23 Definitions, biology 512 Degeneracy pressure 303 Deity, and pantheism 107 121 Deity, contrasting evidence for, in Newton's time 30 Delayed choice experiments 469—470 Democritus 36—37 Density contrast, conformal time relationship 416 Density contrast, limited range for 417 418 Density enhancement 378 Density irregularities, adiabatic 388 390 Density irregularities, as possible formation processes for galaxies 388 Density irregularities, condensation growth of 415 Density irregularities, isothermal 388 Density parameter 376 377 626 Density parameter 376 Density parameter 375 Density parameter 411 Density parameter 627 Density parameter 501 503 Density parameter 377 Density, atomic weight relationship 299 Derham, W. 67—68 Descartes, Rene 53—54 Descartes, teleology dismissed by 54 Design arguments 27—109 Design arguments, and cosmological arguments 103—109 Design arguments, chronology of 46 54 92 Design arguments, critical developments 68—83 Design arguments, Darwin's rejection of 84 Design arguments, devolution 83—92 Design arguments, historical prologue 27—31 Design arguments, Kant's discussion 73—74 Design arguments, Medieval 46—49 Design arguments, non-Western philosophy/religion 92—102 Design arguments, of ancients 31—46 Design arguments, Renaissance 49—54 Design arguments, scepticism against 29 Designed Universe, Aristotelian view 37 Designed Universe, Design Argument for 22 Determinate natural teleology 134 Determinism, and chaos 90—91 118—129 Determinism, classification of 138—139 Determinism, Teilhard's use of weak form 200 Determinism, Thomas Huxley's view 86—87 Deterministic system, world viewed as 459—460 Deuterium oxide, biological effects 541 Deuterium, abundance relative to hydrogen 379 Deuterium, formation at beginning of Universe 371 Deuterons, formation reactions 321 Deuterons, nuclear potential as function of radius 319 Deuterons, triplet state 321 Dewdney, A. K., two-dimensional world 266 DeWitt boundary condition 497 DeWitt's Postulate of Complexity 473 DeWitt, Bryce S., quoted, on WAP selection effect in MWI 482—483 Dicke, Robert H., anthropomorphic explanation 16 219 Dicke, Robert H., gravitation theory (with Carl Brans) 245 Dicke, Robert H., on large numbers coincidences 246—247 Dicke, Robert H., quoted, on cosmological coincidences 243 Dicke, Robert H., Weak Anthropic Principle developed by 16 125 Dielectric constants, of various liquids, plotted against dipole moments 538 Dielectric constants, of various substances 537 Diffusion models (of exploration/colonization) 585 589—590 Dimensional analysis, first used 289 Dimensional analysis, unreasonable effectiveness of 270 Dimensionality 258—276 see also “Three-dimensional space” Dimensionality, additional-dimension effects 274—275 Dimensionality, effect on fundamental constants 269 Dineutrons 321 322 Dingle, H., quoted 224 Dinosaurs, size of 313 Diogenes 36 Diprotons, non-existence of 322 Diprotons, nuclear binding energies 322 Diprotons, singlet state 321 Dirac, P.A.M., criticisms of 233—234 Dirac, P.A.M., influenced by Milne's gravitational theory 238 Dirac, P.A.M., large number hypothesis 231—234 276 Dirac, P.A.M., time-varying Newtonian gravitation constant 11 20—21 Discreteness (of apparatus/system) 485 Dispersal phase, behaviour pattern in colonization 593—594 DNA replication 304—305 DNA, computer program analogy 75 Dobzhansky, T., on Teilhard 199 Dobzhansky, T., teleological nomenclature 134 Dog colours, as design argument 92 Dolphins, encephalization of 131 Dominant energy condition 423 Doyle, Arthur Conan, quoted 310 354 Drake equation 586 589 Drake equation, probabilities not varying with Galactic age 587 Dual timescales, effect on evolutionary biology 244—245 Duhem, Pierre, Heat Death of Universe criticized by 617 Dyson, Freeman, closed-universe life ruling 637 Dyson, Freeman, first paper on study of far future 658 Dyson, Freeman, quoted 318 Dyson, Freeman, quoted on cosmic key times 385 Dysteleology 126 166—173 Earth information content of 661—662 Earth's age, biological constraints on 159—165 Earth's atmosphere, composition 542 543 544 549 Earth's atmosphere, marginal stability of 543—544 567 569 614 Earth's future, in presence of monopoles 657 Earth's future, Weak Anthropic Principle constraints on 556—570 Eco, U., quoted 511—522 548 Economics, interstellar travel 581—583 Economics, nuclear weapons 599 Economics, relative materials/wages 172 644 Eddington luminosity 350 Eddington number 225 Eddington, Arthur S., 'spoofs' of his methodology 227—228 Eddington, Arthur S., calculation of fundamental constants of Nature 224—227 Eddington, Arthur S., credibility damaged 227 Eddington, Arthur S., on age of Universe 385 Eddington, Arthur S., on cosmological constant 412 Eddington, Arthur S., on existence of global time 195 Eddington, Arthur S., on redshifts 237 Eddington, Arthur S., quoted 613 Eddington, Arthur S., quoted, on end of Universe 618 Eddington, Arthur S., quoted, on number of protons in Universe 219 Eddington, Arthur S., quoted, on Second Law of thermodynamics 658 Eddington-Lemaltre-Bondi universe 638 639 Edsall, J. T., quoted, on carbon dioxide 548 Egerton, Francis, bequest for (Bridgewater) Treatises 82 Egyptian creation myth 94 Egyptian text, quoted, on creation 440 Ehrenfest, P., on dimensionality 260 261—262 Ehrlich, Paul R., criticism of Julian Simon 21 In Ehrlich, Paul R., on energy requirements 169—170 Ehrlich, Paul R., single political and economic goal proposed 141 Einstein's cosmological constant 225 234 415 450n Einstein's cosmological equations, ensemble solutions 250 Einstein's cosmological model 616 Einstein's cosmological model, quasi-Penrose diagram for 635 Einstein's general relativity equations 138 409 Einstein's gravitational equations, quantization of 492 Einstein's gravitational theory, Action Principle in 490 Einstein's special theory of relativity 384 Einstein, Albert, criticism of quantum mechanics 476 Einstein, Albert, definition of physical reality 461 Einstein, Albert, on magnitude of dimensionless factors of proportionality 270 Einstein, Albert, quoted 430 Einstein, Albert, unsuccessful in simultaneous-measurement experiment 461 Einstein-de Sitter universe 425 Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) experiment 461—463 Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) experiment and Copenhagen Interpretation 463 Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) experiment as delayed choice experiment 470 Electromagnetic interaction 293 Electromagnetic interaction in unified theories 355 357 Electromagnetic interactions 370—371 Electron charge, time variation of 240—241 Electron orbitals 297 Electron orbitals velocities of 297 Electron spin, measured in EPR experiment 462 463 Electron spin, memory states of apparatus to measure 473 Electron-positron plasma 664 665 Electron-positron plasma, as information storage device 669 Electron-positron plasma, as remaining matter 649 650 Electron-to-proton mass ratio (B), as controlling physical parameter 293 296 Electron-to-proton mass ratio (B), importance in DNA replication 304—305 Electron-to-proton mass ratio (B), uncertainty relationship 304 Elements, quirks in properties 22 143 Elements, relative abundance 542 Ellis cosmological model 249 434 601 Ellis cosmological model, Davies' SAP argument against 602 Empedocles of Argigentum 34 Empirical theologians 180—184 Encephalization 130 Encephalization, increase in humans 130 Encephalization, increase in marine species 131 End (telos) 33 End (telos), Aristotelian view 38 End of Universe 677 Endoskeleton, development necessary as crucial step in Man's evolution 564 Energy requirements 169—171 Energy sources, far future 663—664 665 675 Energy-time uncertainty relation, information-processing restricted by 671 Entropy per baryon 381—382 383 Entropy per baryon, value of 401—408 Entropy per baryon, weak anthropic limits on 407—408 Entropy, black holes 353 Entropy, maximization 166—173 Entropy, reversal from maximum 178 Epicurus of Samos 41 Epiglottis, Paley's discussion 78
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



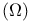 age of Universe expressed in terms of
age of Universe expressed in terms of