|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lakowicz J.R. Ч Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Quenching, advanced topics, probe accessibility to waterЧand lipid-soluble quenchers 267Ч270
Quenching, advanced topics, quenching efficiency 278Ч280
Quenching, advanced topics, transient effects 280Ч285
Quenching, advanced topics, transient effects, proteins, distance-dependent quenching in 285
Quenching, bimolecular quenching constant 241
Quenching, chloride probes 540
Quenching, collisional, theory of 239Ч242
Quenching, collisional, theory of, bimolecular quenching constant, interpretation of 241Ч242
Quenching, collisional, theory of, Stern Ч Volmer equation, derivation of 240Ч241
Quenching, energy transfer,  changes from 420 changes from 420
Quenching, fractional accessibility 247Ч249
Quenching, fractional accessibility, experimental considerations 249
Quenching, fractional accessibility, Stern Ч Volmer plots, modified 248Ч249
Quenching, intramolecular 257Ч258
Quenching, molecular information from fluorescence 17
Quenching, proteins, anisotropy decays 360Ч361
Quenching, proteins, anisotropy decays, tryptophan position and 467
Quenching, proteins, applications to 249Ч257
Quenching, proteins, applications to, colicin  folding 251Ч252 folding 251Ч252
Quenching, proteins, applications to, conformational changes and tryptophan accessibility 250
Quenching, proteins, applications to, effects of quenchers on proteins 251
Quenching, proteins, applications to, endonuclease III 249Ч250
Quenching, proteins, applications to, multiple decay time qnenching 250Ч251
Quenching, quenchers 238Ч239
Quenching, quenching-resolved emission spectra 252Ч255
Quenching, quenching-resolved emission spectra, fluorophore mixtures 252Ч253 254
Quenching, quenching-resolved emission spectra, Tet repressor 253Ч255
Quenching, simulated intensity decay 99
Quenching, sphere of action 244Ч245
Quenching, static and dynamic, examples of 243Ч244
Quenching, static, theory of 242
Quenching, steric shielding and charge effects 245Ч247
Quenching, steric shielding and charge effects, DMA-bound probe accessibility 246Ч247
Quenching, steric shielding and charge effects, ethenoadenine derivatives 247
Quenching, Stern Ч -Vblmer equation, deviations from 244Ч245 248Ч249
Quenching, tryptophan fluorescence, by phenylalanine 503Ч504
Quin-2 165 557 558 559
Quinidine 4
Quinine 2
Quinine sulfate 52 637 638 639 640 641 642
Quinine, chloride sensors 539
Quinine, energy transfer 374
Quinine, quantum yield standards 53
Quinolinium 238
Quinones 238 538
R6G laser 105 106
Radiation boundafy condition (RBC) model 280Ч284
Radiationless energy transfer effects 302
Radiative decay rate 453
Radio-frequency amplifiers, frequency-domain lifetime measurements 150
Radiometric probes, MLCs 587Ч588 589
Raman scatter 39Ч40 41 249
Ravin adenine dinuckotide see УFADФ
Ravine mononucleotide 15
Raylcigh scatter 40 41 249
Reactive Blue 4 586 587 588
Red and near-IR dyes 74Ч75
Red shift, solvent effects 449Ч450
Red-edge excitation shifts 231Ч233
Refractive index 53 187 188
Relaxation 12
Relaxation dynamics 212Ч233
Relaxation dynamics, continuous and two-state spectral relaxation 212Ч213
Relaxation dynamics, continuous versus two-state 226Ч230
Relaxation dynamics, continuous versus two-state, experimental distinction 227
Relaxation dynamics, continuous versus two-state, phase modulation studies of solvent relaxation 227Ч229
Relaxation dynamics, continuous versus two-state, solvent relaxation versus rotational isomer formation 229Ч230
Relaxation dynamics, hfetime-resolved emission spectra 222Ч224
Relaxation dynamics, perspectives of solvent dynamics 233
Relaxation dynamics, picosecond relaxation in solvents 224Ч226
Relaxation dynamics, picosecond relaxation in solvents, multiexponential relaxation in water 225Ч226
Relaxation dynamics, picosecond relaxation in solvents, theory of time-dependent solvent relaxation 224Ч225
Relaxation dynamics, red-edge excitation shifts 231Ч233
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES) measurement 213Ч215
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES) measurement, direct recording 213
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES) measurement, from wavelength-dependent decays 213Ч215
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES), biochemical examples 215Ч222
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES), biochemical examples, analysis 218Ч220
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES), biochemical examples, apomyoglobin 215Ч217
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES), biochemical examples, labeled membranes 217Ч218 219
Relaxation dynamics, time-resolved emission spectra (TRES), biochemical examples, proteins, spectral relaxation in 220Ч222
Relaxation dynamics, TRES versus DAS 230Ч231
Resonance energy transfer (RET) 11 367 409 515
Resonance energy transfer (RET) and diffusive motions in biopolymers 416
Resonance energy transfer (RET), applications 420Ч421
Resonance energy transfer (RET), molecular information from fluorescence 19
Resonance energy transfer (RET), principles 13Ч14
Resorufin 548
Restricted geometries, energy transfer 434Ч435
Restriction fragments 604
RET see УResonance energy transferФ
Retinal 438Ч439
Reversible two-state model 518Ч519
Reversible two-state model, steady-state fluorescence of 518
Reversible two-state model, time-resolved decays for 518Ч519
Rhenium MLCs 578 584 585 590
Rhodamine 2
Rhodamine 6G dye laser 480
Rhodamine 800 76
Rhodamine B. 3 16 50 51
Rhodamine derivatives 74
Rhodamine derivatives, Forster distances 388
Rhodamine derivatives, structures of 70Ч72
Rhodamine, anisotropy decay 364
Rhodamine, DMA energy transfer reactions 381
Rhodamine, DNA technology 608
Rhodamine, glucose sensor 543
Rhodamine, quantum yield standards 52
Rhodopsin disk membranes, retinal in 438Ч439
RhodЧ2 553
Ribonuclease  453 462 493Ч496 453 462 493Ч496
Ribonuclease  , anisotropy decays, FD 498 , anisotropy decays, FD 498
Ribonuclease  , spectral relaxation 221 Ч222 , spectral relaxation 221 Ч222
Ribonuclease A 416
Ribose binding protein (RBP) 474Ч475
Rigid rotor 334Ч336
Rigid versus flexible hexapeptide, distance distributions 397Ч399
Rihozyme substrate binding 256Ч257
ro see УForster distanceФ
Room-temperature phosphorescence of proteins 509
Rose Bengal 646 648 649
Rotamers (rotational isomers) 229Ч230 445 488Ч489
Rotational correction times, ellipsoids 253Ч255
Rotational correlation time 98Ч99 100 304
Rotational diffusion 12Ч13 151Ч152
Rotational diffusion, amsotropy decay, ellipsoids, theory 354
Rotational diffusion, amsotropy decay, frequency-domain studies of 355Ч357 358
Rotational diffusion, amsotropy decay, nonspherical molecules 347Ч348
Rotational diffusion, amsotropy decay, stick versus slip rotational diffusion 353
Rotational diffusion, amsotropy decay, time-domain studies of 354Ч355
Rotational diffusion, membranes, hindered 331 Ч333
Rotational diffusion, oxytocin 336Ч337
Rotational diffusion, Perrin equation 303Ч306
Rotational diffusion, Perrin equation, examples of Perrin plots 306
Rotational diffusion, Perrin equation, rotational motions of proteins 304Ч306
Rotational isomer formation 229Ч230 445 488Ч489
Rotational motion, measurement of 98
Rotational motion, transition metal-ligand complexes 416
Rotors, hindered 329
Rotors, rigid 334Ч336
Row cytometry 85
Row cytometry, DNA fragment siring by 607
Row cytometry, literature references 655Ч656
ROX 599 600
Ruthenium MLCs 34 87 88
Ruthenium MLCs, amsotropy properties 338 575Ч576
Ruthenium MLCs, blood gas measurement 546
Ruthenium MLCs, electronic states 573Ч575
Ruthenium MLCs, frequency-domain lifetime measurements 175
Ruthenium MLCs, oxygen sensors 536Ч538
| Ruthenium MLCs, pH probes 548
Sample geometry effects 53Ч55
Sample preparation, common errors in 55Ч56
SBFI (sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate) 555 556
Scattered light effect, frequency-domain lifetime measurements 154Ч155
Scattering, qtieaching considerations 249
Second-order transmission, monochromator 35
Segmental mobility, biopolymer-bound fluoropbore 329Ч330
Segmental mobility, DNA 340 341
Seminaphthofluoresceins (SNAFLS) 548 549Ч551
Seminaphthorhodofluors (SNARFS) 548 549Ч551
Sensing and sensors 79 531Ч565
Sensing and sensors by coltisional quenching 536Ч541
Sensing and sensors by coltisional quenching, chloride 539Ч541
Sensing and sensors by coltisional quenching, miscellaneous 541
Sensing and sensors by coltisional quenching, oxygen 536Ч538 539
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes 552Ч560
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes, calcium and magnesium 556Ч559 565
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes, cardiac markers 564
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes, cation probe specificity 552Ч553
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes, chloride 539
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes, glucose 559Ч560
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes, sodium and potassium 554Ч556
Sensing and sensors, analyte recognition probes, theory of 553Ч554
Sensing and sensors, clinical chemistry 531Ч532
Sensing and sensors, energy-transfer 541Ч545
Sensing and sensors, glucose 542Ч543
Sensing and sensors, glucose, ion 543Ч544 545
Sensing and sensors, glucose, pH and 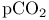 541Ч542 541Ч542
Sensing and sensors, glucose, theory for 545
Sensing and sensors, immunoassays 560Ч565
Sensing and sensors, immunoassays, ELISA 560
Sensing and sensors, immunoassays, energy-transfer 562Ч563
Sensing and sensors, immunoassays, fluorescence polarization 563Ч565
Sensing and sensors, immunoassays, time-resolved 560Ч562
Sensing and sensors, lanthanide 560
Sensing and sensors, literature references 656
Sensing and sensors, mechanisms of sensing 535Ч536
Sensing and sensors, metal-hgand complexes see УMetal-ligand complexesФ
Sensing and sensors, molecular information from fluorescence 19Ч21
Sensing and sensors, pH, two-stale sensors 545Ч551
Sensing and sensors, pH, two-stale sensors, blood gases, optical detection of 545Ч546
Sensing and sensors, pH, two-stale sensors, pH sensors 546Ч551
Sensing and sensors, phosphorescence 538
Sensing and sensors, photoinduced electron-transfer (PET) probes for metal ions and anions 551Ч552
Sensing and sensors, probes 78 79
Sensing and sensors, proteins as sensors 88Ч89
Sensing and sensors, spectral observables for 532Ч535
Sensing and sensors, spectral observables for, lifetime-based sensing 534Ч535
Sensing and sensors, spectral observables for, optical properties of tissues 534
Serotonin 480
Serum albumin 13 71Ч72 75 255 256 462 503Ч504
Serum albumin, anisotropy decay 362Ч363
Serum albumin, intensity decay of 493
Serum albumin, rotational correlation time 304
Silicone, oxygen sensor support materials 536 537 538
Silver 238 239
Simulated intensity decay 99
Single-channel anisotropy measurement method 298Ч299 300
Single-exponential decay 619Ч620
Single-exponential decay law 282
Single-exponential decay, spherical molecules 304
Single-exponential decay, time-dependent intensity 179
Single-exponential fit, FD intensity decay approximation 396 397
Single-particle detection 85
Single-pboton excitation, green fluorescent protein 166
Single-photon counting 100 (see also УTime-correlated aingle-photon countingФ)
Site-directed mutagenesis, azurins 454Ч455 (see also УGenetically engineered proteinsФ)
Skeletal muscle troponin C 407Ч409
Skeletal protein 4.1 386
Smoluchowski model 241 280Ч281 282 284
SNAFL 174 548 549Ч551
SNARF 548 549Ч551
Sodium analyte recognition probes 554Ч556
Sodium Green 555 556
Sodium metibisulfite 249
Sodium probes 16 78 543 544 552 554Ч556
Sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate (SBFI) 554
Soleil Ч Babinet compensator 149
SoleilletТs rule, depolarization factor multiplication 311Ч312
Solvent effects on emission spectra 185Ч208 233 452 501
Solvent effects on emission spectra, biochemical examples with Prodan 201Ч202
Solvent effects on emission spectra, biochemical examples with solvent-sensitive probes 202Ч205
Solvent effects on emission spectra, biochemical examples, calmodulin, hydrophobic surface exposure 202Ч203
Solvent effects on emission spectra, biochemical examples, cyclodextrin binding using dansyl probe 203
Solvent effects on emission spectra, biochemical examples, membrane binding site polarity 203Ч205
Solvent effects on emission spectra, development of advances solvent-sensitive probes 205Ч206
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Lippert equation 187Ч194
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Lippert equation, application of 191Ч193
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Lippert equation, derivation of 187Ч191
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Lippert equation, polarity scales 193Ч194
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Lippert plots, specific solvent effects 196Ч198
Solvent effects on emission spectra, mixtures, effects of 206Ч208
Solvent effects on emission spectra, overview 185Ч187
Solvent effects on emission spectra, polarity surrounding membrane-bound fluorophore 186
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Prodan, fatty acid binding proteins 202
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Prodan, LE and 1CT states 200Ч201
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Prodan, phase transition in membranes 201Ч202
Solvent effects on emission spectra, Prodan, protein association 202
Solvent effects on emission spectra, specific 194Ч198
Solvent effects on emission spectra, spectral shift mechanisms 186Ч187
Solvent effects on emission spectra, summary of 208
Solvent effects on emission spectra, temperature effects 198Ч201
Solvent relaxation 12 (see also УSolvent effects on emission spectraФ УRelaxation
Solvent relaxation, excited-state reactions 515
Solvent relaxation, versus rotational isomer formation 229Ч230
Solvent-sensitive probes 71 202Ч205
SPA (N-sulfopropylacridiruum) 539Ч541
Species-associated spectra (SAS) 519 527
Spectral karyotyping 614
Spectral observables, sensors 532Ч535
Spectral overlap, two-state model 519
Spectral properties, metal-hgand complexes 576Ч578
Spectral relaxation 498Ч499 (see also УRelaxation dynamicsФ)
Spectral response, PMTs 42Ч43
Spectral shift mechanisms, solvent effects on emission spectra 186Ч187
Spectrofluorometer 26
Spectrofluorometer, ideal 28Ч32
Spectroscopy, general principles see УPrinciples of fluorescenceФ
Spectroscopy, literature references 654
Sperm whale myoglobin 493
Sphere of action 244Ч245
Spin labeled naphthalene derivative 257
Spin-labeled PC 273
Spin-orbit coupling, quenching 239
SPQ [6-methoxy-N-(3-sulfopropyl)quinolinium], chloride sensors 539 540 541
SPQ [6-methoxy-N-(3-sulfopropyl)quinolinium], quenching 165 238
Stains, DNA 604Ч607
Stains, DNA, Bis DNA stains 605Ч606
Stains, DNA, energy-transfer stains 606Ч607
Stains, DNA, fragment sizing by flow cytometry 607
Standard lamp, correction factors obtained with 51Ч52
Standards,  -carbotine derivatives 637Ч638 -carbotine derivatives 637Ч638
Standards, corrected emission spectra 51
Standards, emission spectra correction 51
Standards, lifetime 645Ч649
Standards, long-wavelength 639 640 641 642
Standards, quantum yield 52Ч53
Standards, ultraviolet 639 642
Staphylococcal nuclease 163 221 282 283 453 462 473Ч474
Staphylococcal nuclease, anisotropy decay of 496
Staphylococcal nuclease, emission center of gravity 499
Staphylococcal nuclease, intensity decay of 493
Staphylococcal nuclease, phosphorescence 509
Staphylococcus aureus metalloprotease 464Ч465
Static quenching 240 (see also УQuenchingФ)
Static quenching, combined with dynamic quenching 243
Static quenching, examples of 243Ч244
Static quenching, theory of 242
Steady-state amsotropy, calculation of 304
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 changes from
changes from 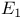 folding
folding 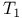
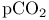
 -carbotine derivatives
-carbotine derivatives