|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lakowicz J.R. Ч Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Diroethylindole 649
Distance distribution functions 409Ч410
Distance distributions 395Ч397 (see also УEnergy transfer time-resolvedФ)
Distance distributions from steady-state data 419Ч420
Distance distributions in glycopeptide 410Ч411
Distance distributions in nucleic acids 416Ч418
Distance distributions in nucleic acids, DNA, double-helical 416Ч418
Distance distributions in nucleic acids, DNA, four-way Holliday junction in 417Ч418
Distance distributions in peptides 397Ч401
Distance distributions in peptides, concentration of D-A pairs and 401
Distance distributions in peptides, cross-fitting data to exclude alternative models 399Ч400
Distance distributions in peptides, donor decay without RET 400Ч401
Distance distributions in peptides, rigid versus flexible hexapeptide 397Ч399
Distance distributions in proteins 401Ч410
Distance distributions in proteins from time-domain measurements 409
Distance distributions in proteins, analysis with frequency domain data 404Ч406
Distance distributions in proteins, distance distribution functions 409Ч410
Distance distributions in proteins, domain motion in 409
Distance distributions in proteins, melittin 401Ч404
Distance measurements, resonance energy transfer 374Ч378
Distance measurements, resonance energy transfer, melittin, alpha helical 374Ч375
Distance measurements, resonance energy transfer, orientation factor effects on possible range of distances 375Ч376
Distance measurements, resonance energy transfer, orientation of protein-bound peptide 377Ч378
Distance measurements, resonance energy transfer, protein folding measured by RET 376
Distance-dependent quenching (DDQ) model 280Ч284
Disulfides, quenching by 238
DM-Nerf 548
DMANCN 200 201
DMANS (4-Dimethylamino-4-nitrostilbene) 639Ч642
DMPC (dimyristoyl-1- -phosphatidyl-cholme) 197 -phosphatidyl-cholme) 197
DMPC (dimyristoyl-1- -phosphatidyl-cholme), cholesterol membranes 223Ч224 -phosphatidyl-cholme), cholesterol membranes 223Ч224
DMPC (dimyristoyl-1- -phosphatidyl-cholme), hilayers 275 -phosphatidyl-cholme), hilayers 275
DMPC (dimyristoyl-1- -phosphatidyl-cholme), vesicles, DPH anisotropics in 316 -phosphatidyl-cholme), vesicles, DPH anisotropics in 316
DMPC (dimyristoyl-1- -phosphatidyl-cholme), vesicles, quasi-three-dimensional diffusion 276Ч278 -phosphatidyl-cholme), vesicles, quasi-three-dimensional diffusion 276Ч278
DMPP (dimethyldiazaperopyrenium) 432Ч433
DMS (dimethylamino-4-methoxystilbene) 646Ч648
DNA base analogs 77Ч78
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe 380 608Ч610
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, energy transfer mechanisms 19
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, Forster distances 388
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, linked, diffusion effects 411Ч416
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, linked, diffusion effects, apparent distance distribution 415Ч416
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, linked, diffusion effects, experimental measurement 412Ч413
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, linked, diffusion effects, goodness of fit surfaces und parameter resolution 413Ч415
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, linked, diffusion effects, RET and diffusive motions in biopolymers 416
DNA hybridization, one donorЧund acceptor-labeled probe, linked, diffusion effects, simulations of RET for flexible pair 411Ч412
DNA oligomer association kinetics 380Ч381
DNA probes 76Ч78 87 88
DNA sequencing 595Ч604
DNA stains 3
DNA technology 595Ч614
DNA technology, hybridization 607Ч612
DNA technology, hybridization, excimer formation 610
DNA technology, hybridization, imagers 612
DNA technology, hybridization, in situ 613Ч614
DNA technology, hybridization, light-generated probe arrays 612Ч613
DNA technology, hybridization, one donorЧand acceptor-labeled probe 608Ч610
DNA technology, hybridization, PCR 612
DNA technology, hybridization, polarization assays 610Ч612
DNA technology, hybridization, RET applications 416Ч418 420Ч421
DNA technology, sequencing 595Ч604
DNA technology, sequencing, energy-transfer dyes 598Ч601
DNA technology, sequencing, lifetime-based 604
DNA technology, sequencing, NIR probes 601Ч604
DNA technology, sequencing, nucleotide labeling methods 598
DNA technology, stains, high-sensitivity 604Ч607
DNA technology, stains, high-sensitivity, energy-transfer stains 606Ч607
DNA technology, stains, high-sensitivity, fragment sizing by flow cytometry 607
DNA technology, stains, high-sensitivity, his DNA stains 605Ч606
DNA, anisotropy decay, time-dependent 361Ч362
DNA, anisotropy decay, time-dependent, oligomer hydrodynamics 339Ч340
DNA, anisotropy decay, time-dependent, segmental mobility 340 341
DNA, distance distributions, double-hetical 416Ч417
DNA, distance distributions, double-hetical, four-way Holliday junction in 417~418
DNA, energy transfer 425
DNA, energy transfer, energy transfer in one dimension 432Ч433
DNA, energy transfer, FD lifetime measurements 164Ч165
DNA, energy transfer, metal-ligand complex dynamics 578Ч580
DNA, energy transfer, Trp repressor binding anisotropy 309
DNA-B helicase 257
DNA-bound probe accessibility, quenching 246Ч247
DNBS (dimtrobenzenesulfenyl) 388
Domain motion 334Ч335 409
Donor decay without RET in peptides 400Ч401
Donor-acceptor pairs see also УEnergy transferФ
Donor-acceptor pairs and distance distribution in peptides 401
Donor-acceptor pairs, acceptor decays 418
Donor-acceptor pairs, distance distribetions from steady-state data with different fto values 419Ч420
Donor-acceptor pairs, distance distribetions from steady-state data, quenching, changing fto by 420
DOPC (dioleolyl-1- -phosphatidylcholine) 201 -phosphatidylcholine) 201
DOPC (dioleolyl-1- -phosphatidylcholine), quenching 269Ч270 -phosphatidylcholine), quenching 269Ч270
DOPC (dioleolyl-1- -phosphatidylcholine), red-edge excitation 232 -phosphatidylcholine), red-edge excitation 232
DOS (trans-4-dimethylamino-4-(1-oxybutyl)-stilbene 186
DOTCI 73
DPA (diphenylanthracene) 52 155
DPH(1, 6-diphenyl-1,3, 5-hexatriene) 15 72
DPH(1, 6-diphenyl-1,3, 5-hexatriene) in film 313
DPH(1, 6-diphenyl-1,3, 5-hexatriene), anisotropic rotational diffusion 356Ч357
DPH(1, 6-diphenyl-1,3, 5-hexatriene), anisotropy decays, time-dependent 329 331 332
DPH(1, 6-diphenyl-1,3, 5-hexatriene), Forster distances 388
DPH(1, 6-diphenyl-1,3, 5-hexatriene), membrane probes 268
DPH(1, 6-diphenyl-1,3, 5-hexatriene), quenching-resolved spectra 253 254
DPO (2,5-diphenyloxazole) 205
DPPC (dipalmitolyl+ -phosphatidylcholine) systems 201 275 -phosphatidylcholine) systems 201 275
DPPC (dipalmitolyl+ -phosphatidylcholine) systems, energy transfer in two dimensions 430Ч432 -phosphatidylcholine) systems, energy transfer in two dimensions 430Ч432
DPPC (dipalmitolyl+ -phosphatidylcholine) systems, Patman-laibled, TRES 217Ч218 219 -phosphatidylcholine) systems, Patman-laibled, TRES 217Ч218 219
DPPG vesicles 581 582
DPS (4-dimethylamino-4-fluorostilbene) 172 646Ч648
DTAC micelles 246
Dye lasers 104Ч107 480
Dyes 2 3
Dyes, energy-transfer 598Ч601 606Ч607
Dyes, red and near IR 74Ч75
Dyes, solvent relaxation 229
Dynamic quenching see УCollisional quenchingФ УQuenchingФ
Dynamics of relaxation see УRelaxation dynamicsФ
Dynode chains 43Ч44
Dynorphin 497
E1A [(5-(iodoacetamido)eosin] 388
Efficiency, quenching 241
Electro-optic modulator 149Ч150
Electron scavengers, quenching by 239
Electron transfer, photoinduced (PET) 536 551Ч552
Electronic state resolution from polarization spectra 297Ч298
Electronic states 5Ч6
Electronics, frequency-domain fluorometers 147 149Ч150
Electronics, photomultiplier tube 41
Electronics, time-correlated single-photon counting 109Ч111
Electrophoresis 109
ELISA 3 560
Elongation factor (Ta-GDP) 462
Emission spectra 3Ч4 5Ч6
Emission spectra, corrected 637Ч649
Emission spectra, corrected,  -carbolene derivatives as fluorescence standards 637Ч638 -carbolene derivatives as fluorescence standards 637Ч638
Emission spectra, corrected, 9, 10-diphenyianthracene, quinine sulfate and fluorescein 637 638
Emission spectra, corrected, additional spectra 642 643
Emission spectra, corrected, instrumentation 51Ч52
Emission spectra, corrected, instrumentation, comparison with known emission spectra 51
Emission spectra, corrected, instrumentation, conversion between wavelength and wavenumber 52
Emission spectra, corrected, instrumentation, correction factors obtained with standard lamp 51Ч52
Emission spectra, corrected, instrumentation, quantum counter and scatterer use 52
Emission spectra, corrected, long-wavelength standards 639 640 641 642
Emission spectra, corrected, ultraviolet standards 639 642
Emission spectra, decay-associated 490Ч491 499Ч501
Emission spectra, instrumentation 25Ч28
Emission spectra, instrumentation, distortions in 28
Emission spectra, instrumentation, ideal spectrofluorometer 28Ч32
Emission spectra, molecular information from fluorescence 17
Emission spectra, quenching-resolved 252Ч255
Emission spectra, quenching-resolved, fluorophore mixtures 252Ч253 254
| Emission spectra, quenching-resolved, Tet repressor 253Ч255
Emission spectra, representative, literature references 653Ч654
Emission spectra, through optical filters 40Ч41
Emission spectra, tryptophan decay-associated 490Ч491
Emission spectra, two-component mixture 621Ч623
Emission wavelength, and anisotropy 312
Emylenediamine, dansylated 206
Endonucleases 249Ч250 381
Energy transfer efficiency from enhanced accepter fluorescence 381Ч382
Energy transfer in membranes 382Ч386
Energy transfer in membranes, distance of closest approach in 385Ч386
Energy transfer in membranes, lipid distributions around Gramicidin 384Ч385
Energy transfer in membranes, membrane fusion and lipid exchange 386
Energy transfer in solution 386Ч388
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions 425Ч440
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, diffusion effects on RET with unlinked donors and acceptors 428Ч429
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, dimensionality effect on RET 429Ч434
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, dimensionality effect on RET, one dimension 432Ч433
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, dimensionality effect on RET, two dimensions 430Ч432
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, restricted geometries 434Ч435
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, RET in rapid-diffusion limit 435Ч440
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, RET in rapid-diffusion limit, acceptor location in lipid vesicles 437
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, RET in rapid-diffusion limit, Forster transfer versos exchange interactions 439Ч440
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, RET in rapid-diffusion limit, retinal location in rhodopsin disk membranes 438Ч439
Energy transfer to multiple acceptors in one, two, or three dimensions, three dimensions 425Ч429
Energy transfer, acceptor emission 381
Energy transfer, data analysis 405
Energy transfer, diffusion-enhanced 387
Energy transfer, distance measurements using RET 13 374Ч378
Energy transfer, distance measurements using RET, melittin, a helical 374Ч375
Energy transfer, distance measurements using RET, orientation factor effects on possible range of distances 375Ч376
Energy transfer, distance measurements using RET, orientation of protein-buund peptide 377Ч378
Energy transfer, distance measurements using RET, protein folding measured by RET 376
Energy transfer, DNA hybridization, one donorЧand acceptor-labeled probe 380 608Ч610
Energy transfer, excited-state reactions 515
Energy transfer, Forster distances 388
Energy transfer, homotransfer 373
Energy transfer, macromolecular associations, RET for measurement of 378Ч382
Energy transfer, macromolecular associations, RET for measurement ofcalcium indicators 379Ч380
Energy transfer, macromolecular associations, RET for measurement ofDNA oligomer association kinetics 380Ч381
Energy transfer, macromolecular associations, RET for measurement ofenergy transfer efficiency from enhanced acceptor fluorescence 381Ч382
Energy transfer, macromolecular associations, RET for measurement ofprotein kinase subonit dissociation 378Ч379
Energy transfer, orientation factor 371
Energy transfer, proteins 374Ч377 456Ч461
Energy transfer, proteins, anisotropy decreases, detection of ET by 459
Energy transfer, proteins, interferon- , tyrosine-to-tryptophan energy transfer in 456Ч457 , tyrosine-to-tryptophan energy transfer in 456Ч457
Energy transfer, proteins, phenylalanine-to-tyrosme 459Ч461
Energy transfer, proteins, RET efficiency quantitation 457Ч458
Energy transfer, radrationless, anisotropy measurement 302
Energy transfer, representative  values 388 values 388
Energy transfer, sensor mechanisms 541Ч545
Energy transfer, sensor mechanisms, glucose 542Ч543
Energy transfer, sensor mechanisms, ion 543Ч544 545
Energy transfer, sensor mechanisms, pH and 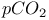 541Ч542 541Ч542
Energy transfer, sensor mechanisms, theory for 545
Energy transfer, theory of 368Ч374
Energy transfer, theory of transfer rate dependence on distance, overlap integral, and orientation factor 373
Energy transfer, theory ofhomotransfer und heterotransfer 373Ч374
Energy transfer, theory oforientation factor 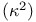 371 Ч373 371 Ч373
Energy transfer, time-resolved 395Ч421
Energy transfer, time-resolved, acceptor decays 418
Energy transfer, time-resolved, applications of RET 420Ч421
Energy transfer, time-resolved, diffusion effects for linked D-A pairs 411Ч416
Energy transfer, time-resolved, diffusion effects for linked D-A pairs, apparent distance distribution 415Ч416
Energy transfer, time-resolved, diffusion effects for linked D-A pairs, experimental measurement 412Ч413
Energy transfer, time-resolved, diffusion effects for linked D-A pairs, goodness of fit surfaces and parameter resolution 413Ч415
Energy transfer, time-resolved, diffusion effects for linked D-A pairs, RET and diffusive motions in biopolymers 416
Energy transfer, time-resolved, diffusion effects for linked D-A pairs, simulations of RET for flexible pair 411Ч412
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distribotions in glycopeptide 410Ч411
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions 395Ч397
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions from steady-state data 419Ч420
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions from steady-state data, D-A pairs with different  values 419Ч420 values 419Ч420
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions from steady-state data, quenching, changing Ro by 420
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in nucleic acids 416Ч418
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in nucleic acids, DNA, double-helical 416Ч417
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in nucleic acids, DNA, four-way Holliday junction in 417Ч418
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in peptides 397Ч401
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in peptides, concentration of D-A pairs and 401
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in peptides, cross-fitting data to exclude alternative models 399Ч400
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in peptides, donor decay without RET 400Ч401
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in peptides, rigid versus flexible hexapeptide 397Ч399
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in proteins 401Ч410
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in proteins, analysis with frequency domain data 404Ч406
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in proteins, distance distribution functions 409Ч410
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in proteins, domain motion in 409
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in proteins, from tune-domain measurements 409
Energy transfer, time-resolved, distance distributions in proteins, melittin 401Ч404
Energy transfer, time-resolved, DNA hybridization 420Ч421
Energy transfer, time-resolved, incomplete labeling effects 418Ч419
Energy transfer, time-resolved, orientation factor effects 419
Energy transfer, time-resolved, terbium 420Ч421 438
Energy-gap law 577Ч579 588
Energy-transfer immunoassays 562Ч563
Energy-transfer stains and dyes, DNA 598Ч601 606Ч607
Enzyme cofactors 15
Enzyme cofactors, intrinsic fluorescence 63Ч65
Enzyme cofactors, time-domain lifetime measurement 134Ч135
Eosin 20
Eosin-labeled ethanolamine 372
ERITC (erytbrosynЧ5-isothincyanate) 337
ErvthrosinB 20 133Ч134
Escherichia coli maltose receptor protein 466
Escherichia coli ribose binding protein 474Ч475
Escherichia coti lac repressor 514
Ethanetiuol 285
Ethanol, indole emission spectra in cyclohexane-ethanol mixtures 449Ч450
Ethanol, indole lifetime in 452
Ethanol, polarizability properties 188
Ethanol, rotational diffusion in 304
Ethanol, tryptophan anisotropy spectra in 449
Ethenoadernine and derivatives 15 239 347 248 256 388
Ethers 188 238
Ethidium bromide 76 77 246
Ethidium bromide, anisotropy decay 361Ч362
Ethidium bromide, DNA technology 605
Ethidium bromide, energy transfer in one dimension 432 433
Ethidium homodimer 77 605
Ethoxyocoumarin 205
Ethyl acetate 189
Etnanolamine 372
Europium, energy transfer studies 416
Europium, immunoassays 561
Europium, qneaching by 239
Europium, Raster distances 388
Europrum probes 87
Exchners 9 515
Exchners, DNA hybridization 610
Exchners, phenylalanine 452
Exchners, quasi-three-diniensional diffusion in membranes 276Ч278
Exciplex formation 9 238Ч239 515
Excitation anisotropy spectra 295Ч298 447Ч449
Excitation anisotropy, two-photon and multiphoton 315Ч316
Excitation pfaotoselection of fluorophores 294Ч295
Excitation spectra, anisotropy 295Ч298 447Ч449
Excitation spectra, instrumentation 25Ч28
Excitation spectra, instrumentation, corrected spectra 50Ч51
Excitation spectra, instrumentation, distortions in 28
Excitation spectra, instrumentation, ideal spectrofluorometer 27Ч28
Excitation spectra, polarization, tyrosine and tryptophan 447Ч449
Excitation wavelength independence of fluorescence 7Ч8
Excited charge-transfer complex (exciplex) 238Ч239 515
Excited-state distribution, one, two, and three photon excitation 315
Excited-state reactions 515Ч528
Excited-state reactions, analysis by phase-modulation fluorometry 521Ч526
Excited-state reactions, analysis by phase-modulation fluorometry, apparent phase and modulation lifetimes, effects on 523
Excited-state reactions, analysis by phase-modulation fluorometry, wavelength-dependent phase and modulation values 524Ч525
Excited-state reactions, biochemical examples 527Ч528
Excited-state reactions, biochemical examples, 7-azaindole tautomerization 527
Excited-state reactions, biochemical examples, membrane-bound cholesterol exposure 527Ч528
Excited-state reactions, differential-wavelength methods 520Ч521
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -phosphatidyl-cholme)
-phosphatidyl-cholme)  -carbolene derivatives as fluorescence standards
-carbolene derivatives as fluorescence standards  , tyrosine-to-tryptophan energy transfer in
, tyrosine-to-tryptophan energy transfer in  values
values