|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Katz V.J. Ч A History of Mathematics: An Introduction |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 79 89 79 89
   295Ч296 295Ч296
  (House of Wisdom) 239 (House of Wisdom) 239
 of Euclid 58Ч95 of Euclid 58Ч95
 of Euclid, Book I 63Ч67 71 of Euclid, Book I 63Ч67 71
 of Euclid, Book II 67Ч73 124 249Ч250 of Euclid, Book II 67Ч73 124 249Ч250
 of Euclid, Book III 73Ч76 of Euclid, Book III 73Ч76
 of Euclid, Book IV 76Ч77 of Euclid, Book IV 76Ч77
 of Euclid, Book IX 86Ч88 458 of Euclid, Book IX 86Ч88 458
 of Euclid, Book V 77Ч82 of Euclid, Book V 77Ч82
 of Euclid, Book VI 71Ч72 82Ч84 116 of Euclid, Book VI 71Ч72 82Ч84 116
 of Euclid, Book VII 84Ч86 of Euclid, Book VII 84Ч86
 of Euclid, Book VIII 86Ч87 of Euclid, Book VIII 86Ч87
 of Euclid, Book X 88Ч90 of Euclid, Book X 88Ч90
 of Euclid, Book XI 90Ч91 117 of Euclid, Book XI 90Ч91 117
 of Euclid, Book XII 91Ч94 of Euclid, Book XII 91Ч94
 of Euclid, Book XIII 94Ч95 of Euclid, Book XIII 94Ч95
 of Euclid, Definitions and Postulates 60Ч62 of Euclid, Definitions and Postulates 60Ч62
 of Euclid, structure of 59Ч60 (see also Euclid) of Euclid, structure of 59Ч60 (see also Euclid)
  4 4
  , geometry 20Ч23 , geometry 20Ч23
  , linear equations 14Ч18 , linear equations 14Ч18
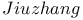 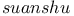 , square root 29 (see also Chinese mathematics) , square root 29 (see also Chinese mathematics)
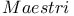 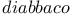 (abacists) 343Ч348 (abacists) 343Ч348
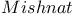 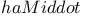 163Ч164 268 163Ч164 268
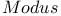 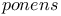 55Ч56 55Ч56
  55Ч56 55Ч56
 -dimensional geometry 792Ч797 -dimensional geometry 792Ч797
      see see  
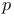 -adic numbers 824Ч825 829 -adic numbers 824Ч825 829
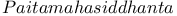 212 212
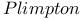 322 30Ч32 322 30Ч32
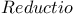 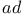  , in Archimedes 105 107 , in Archimedes 105 107
   , in eighteenth century mathematics 585 , in eighteenth century mathematics 585
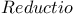 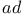 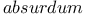 , in Euclid 64Ч65 , in Euclid 64Ч65
 4 21 28Ч29 4 21 28Ч29
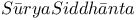 214 214
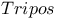 exam 679 816 exam 679 816
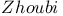 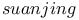 4 4
 cole Polytechnique 637Ч639 668 683 692 706Ч707 cole Polytechnique 637Ч639 668 683 692 706Ч707
 cole Polytechnique, and Cauchy 719 720 cole Polytechnique, and Cauchy 719 720
 cole Polytechnique, and Germain 656 cole Polytechnique, and Germain 656
 cole Polytechnique, and Monge 633 635 cole Polytechnique, and Monge 633 635
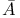 ryabhata 212Ч213 215Ч218 231 ryabhata 212Ч213 215Ч218 231
Ab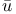 K K mil ibn Aslam 250Ч251 293 mil ibn Aslam 250Ч251 293
Ab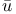 Nasr Mans Nasr Mans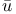 r 277Ч281 r 277Ч281
Abacists 343Ч348
Abel, and Fourier series 720 723
Abel, and Jordan 670
Abel, and Kronecker 671Ч672
Abel, and Weber 675
Abel, biography 666
Abel, Niels Henrik 638 651 665Ч667 704 715
Abraham bar Hiyya 288 290Ч291 292Ч293
Abraham ibn Ezra 301Ч302
Absolute geometry 778
Abstract algebra, Boolean algebra 686Ч687 842Ч844
Abstract algebra, categories and functors 806 833
Abstract algebra, division algebra 682
Abstract algebra, equations 662Ч670
Abstract algebra, equivalence classes 671Ч672 732
Abstract algebra, fields 651 667 676Ч677 797 806 822Ч826
Abstract algebra, groups 339 617 620Ч621 651 662 667Ч676 791Ч792 797Ч799 832Ч833
Abstract algebra, ideals and ideal numbers 659Ч661 671Ч672
Abstract algebra, integral domain 831
Abstract algebra, matrices 687Ч695
Abstract algebra, number theory 652Ч661
Abstract algebra, rings 617 806 828Ч829
Abstract algebra, set theory 812
Abstract algebra, symbolic 677Ч687
Abstract algebra, vector spaces 763 794Ч795 833
Abu-lЧWaf , Muhammad 277Ч281 , Muhammad 277Ч281
Acarya Jayadeva 223
Acceleration 318Ч319 421Ч423
Acrostic 1 46 102 135 168 192 238 288 342 385 431 468 544 596 650 704 766 805
Addition see Arithmetic computations
Adelard of Bath 290Ч291
African mathematics 337Ч339 (see also Egyptian mathematics)
Agnesi, Maria Gaetana 565Ч567
al Ч Din, Sadr 271
al Ч Karaj , Ab , Ab Bakr 186 251Ч252 255 258 Bakr 186 251Ч252 255 258
al Ч Khal l ibn Ahmad 263Ч264 l ibn Ahmad 263Ч264
al Ч Khayy m m , СUmar 238 269Ч271 437 624 , СUmar 238 269Ч271 437 624
al Ч Khayy m m , СUmar, biography 260 , СUmar, biography 260
al Ч Khayy m m , СUmar, cubic equations 259Ч262 , СUmar, cubic equations 259Ч262
al Ч Khw rizml rizml , Muhammad 240Ч241 244Ч249 , Muhammad 240Ч241 244Ч249
al Ч Khw rizml rizml , Muhammad, biography 245 , Muhammad, biography 245
al Ч SamawТal, ibn Yahy 252Ч255 258Ч259 376 252Ч255 258Ч259 376
al Ч SamawТal, ibn Yahy , biography 253 , biography 253
al Ч Uql d d s s , Abu-lЧHasan 241Ч243 , Abu-lЧHasan 241Ч243
al-B r r n n , Abu-l-Rayh , Abu-l-Rayh n 238 275Ч277 281 330 n 238 275Ч277 281 330
al-Batt n n , Abu СAbdall , Abu СAbdall h 275 h 275
al-F ris ris , Kam , Kam l al-D l al-D n 266 n 266
al-K sh sh , Ghiy , Ghiy th al Ч D th al Ч D n 243 281Ч282 n 243 281Ч282
al-K h h , Ab , Ab Sahl 273 Sahl 273
al-Khw rizml rizml , Muhammad, and European mathematics 293 350 , Muhammad, and European mathematics 293 350
al-SamawТal, ibn Yahy , combinatorics 264 , combinatorics 264
al-SamawТal, ibn Yahy , number system 243 , number system 243
al-Tus , Nas , Nas r al Ч D r al Ч D n 270Ч271 405 n 270Ч271 405
al-Tus , Sharaf al Ч D , Sharaf al Ч D n 262Ч263 363 437 n 262Ч263 363 437
Alberti, Leon Battista 389Ч390
Alcuin of Yor 289
Aleksandrov, Pavel Sergeiivich 832
Alexander, James W. 821Ч822
Alexandria Museum and Library 58Ч59 96 168 187 188
Algebra, and trigonometry 371Ч372
Algebra, Babylonian 16 35Ч39
Algebra, boolean 686Ч687
Algebra, Chinese 15Ч19 35 197Ч210
Algebra, Diophantine 173Ч183
Algebra, Egyptian 14Ч15
Algebra, etymology 244
Algebra, French 349Ч351
Algebra, geometric 67Ч73 95Ч96 122-125
Algebra, in Euler 614Ч619
Algebra, in Lagrange 619Ч621
Algebra, in Maclaurin 611Ч613
Algebra, in Newton 610Ч611
Algebra, in Vi te 370Ч375 (see also Abstract algebra; Equations) te 370Ч375 (see also Abstract algebra; Equations)
Algebra, Indian 225Ч228
Algebra, Islamic 243Ч263 343Ч346 348
Algebra, Italian 343Ч348 358Ч367
Algebra, linear 14Ч19 755
Algebra, medieval European 282Ч290 293 307Ч314 328Ч329
Algebra, polynomials 251Ч254 346Ч348
Algebra, quadratic equations 35Ч39
Algebra, symbolic 677Ч687
Algebra, twentieth century 822Ч833
Algebra, vectors 794Ч795
Algebraic symbolism 370Ч371 445Ч446
Algebraic symbolism, in Descartes 438
Algebraic symbolism, in Diophantus 174Ч175
Algebraic symbolism, in Fermat 432 435
Algebraic symbolism, in medieval Europe 312
Algebraic symbolism, in Renaissance mathematics 345Ч346 350Ч352 356 365
algorithm, defined 8
Algorithm, etymology 241
American Mathematical Society 805
American mathematics, computers 839Ч851
American mathematics, eighteenth century 640Ч642
American mathematics, twentieth century 823 828 830
Amicable numbers 266
Analysis, complex analysis 737Ч746
Analysis, eighteenth century 544Ч590
Analysis, nineteenth century 704Ч760
Analysis, probability and statistics 753Ч760
Analysis, summary 595 765
Analysis, vector analysis 746Ч752
Analytic geometry 431Ч434 633Ч635
Anasazi mathematics 336Ч337
| Angle of parallelism 775
Apogee 141
Apollonius 102Ч103 134 678
Apollonius,  117Ч129 184 117Ч129 184
Apollonius, and astronomy 140Ч141
Apollonius, and Renaissance mathematics 368
Apollonius, and seventeenth century mathematics 432Ч433 435 438 460
Apollonius, biography 118
Appel, Kenneth 805 851
Approximation methods 214Ч215
Arabia see Islamic mathematics
Arabic names 241
Arc length 293 469 496Ч498
Archimedes 55 102Ч117 134 368
Archimedes,    108 108
Archimedes,   114Ч115 114Ч115
Archimedes,      105Ч106 105Ч106
Archimedes, 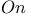 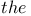 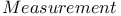 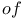   108Ч111 187 108Ч111 187
Archimedes,   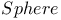  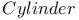 115 115
Archimedes,     113Ч114 113Ч114
Archimedes,   111Ч113 111Ч113
Archimedes, and Islamic mathematics 259 262Ч263 273
Archimedes, and Leibniz 531
Archimedes, and Renaissance mathematics 368
Archimedes, biography 102 107 111 116
Archimedes, engineering 107Ч108
Archimedes, geometry 111Ч116
Archimedes, HilbertТs axioms 799
Archimedes, law of the lever 103Ч107
Archimedes, method of discovery 111Ч113
Archimedes, principle of insufficient reason 105
Archimedes, sums of series 113Ч115
Archimedes, velocity 160Ч161
Archytas 86Ч87
Area of circle 19Ч22 162 268 488
Area of polygon 161 296
Area of rectangle 622
Area of region bounded by curves 468Ч469 487Ч488 499-503 513Ч514 623 717Ч718
Area of segment of a circle 22 162 273 293 297
Area of segment of a parabola 113Ч115
Area of segment of a spiral 114Ч115
Area of surface 574Ч575
Area of surface of a sphere 115Ч116
Area of triangle 19Ч20 160Ч161 269
Argand, Jean Ч Robert 738
Aristaeus 117 134 184 186
Aristarchus 137 368
Aristotle 54Ч58 159
Aristotle, and astronomy 140
Aristotle, HilbertТs axioms 800
Aristotle, in medieval Europe 314Ч316 319
Aristotle, logic 54Ч56
Arithmetic computations 349
Arithmetic computations, Babylonian 12Ч14
Arithmetic computations, Chinese 14
Arithmetic computations, Egyptian 8Ч12
Arithmetic computations, Greek 175
Arithmetic computations, in medieval Europe 307Ч308
Arithmetic computations, Indian 226
Arithmetic computations, Islamic 240 242
Arithmetic computations, Mayan 333
Arithmetic computations, with decimals 376Ч377
Arithmetization of analysis 683 729Ч737
Associative law 81 823
Astrolabe 294
Astrology 301Ч302
Astronomy, ancient 25Ч27
Astronomy, and logarithms 416Ч420
Astronomy, Babylonian 136 138 142
Astronomy, Chinese 195Ч197
Astronomy, early Greek 135Ч145
Astronomy, in Brahe 408
Astronomy, in Copernicus 404Ч408
Astronomy, in Kepler 409Ч416
Astronomy, in Newton 516Ч522
Astronomy, Indian 212 218 221
Astronomy, Islamic 274 277
Astronomy, Mayan 332
Astronomy, Ptolemaic 145Ч157
Astronomy, Renaissance 398Ч416
Astronomy, summary 167 (see also Trigonometry) )
Asymptote 122Ч123
Augustine 289
Autolycus 137 160 368
Axioms 55
Axioms, algebraic 822Ч823
Axioms, Boolean 686Ч687
Axioms, completeness 806
Axioms, for group theory 674Ч676
Axioms, for natural numbers 735Ч737
Axioms, for non Ч Euclidean geometry 781
Axioms, for set theory 810Ч814
Axioms, for topology 817Ч818
Axioms, for vector spaces 826Ч827 (see also Proof)
Axioms, HilbertТs 767Ч768 797Ч800
Axioms, in Peacock 678Ч680
Axioms, of choice 809Ч810
B rgi, Jobst 416 rgi, Jobst 416
Babbage, Charles 678 707 807
Babbage, difference and analytical engines 835Ч838 844
Babylonia 2
Babylonian mathematics 1Ч3
Babylonian mathematics, and Chinese mathematics 206
Babylonian mathematics, and Greek mathematics 67Ч68 70 72Ч73 96 176Ч177 181Ч182 188
Babylonian mathematics, and Islamic mathematics 239 240 243 244 263
Babylonian mathematics, arithmetic computations 12Ч14
Babylonian mathematics, astronomy 136 138 142 156
Babylonian mathematics, calendars 26Ч27
Babylonian mathematics, geometry 19Ч25
Babylonian mathematics, number symbols 6Ч8
Babylonian mathematics, place value system 230
Babylonian mathematics, quadratic equations 35Ч39
Babylonian mathematics, square roots 27Ч28
Babylonian mathematics, summary 45
Bakhsh l l manuscript 231 manuscript 231
Banach space 827
Banach Ч Tarski paradox 812Ч813
Banach, Stefan 806
Banneker, Benjamin 641
Barrow, Isaac 498 500Ч503
Barrow, Isaac, biography 502
Bartels, Martin 654 775
Bayes, Thomas 605Ч608 755Ч756
Beltrami, Eugenio 783Ч784 789
Berkeley, George 582Ч583
Berkeley, George, response to 583Ч585
Bernoulli, Daniel 555 578 580Ч582 705 837
Bernoulli, Jakob (Jacques, James) 458 545 549 575
Bernoulli, Jakob (Jacques, James),   597Ч601 597Ч601
Bernoulli, Jakob (Jacques, James), biography 546
Bernoulli, Johann (Jean, John) 519 528 531Ч535 556Ч557 575
Bernoulli, Johann (Jean, John), biography 546
Bernoulli, Johann (Jean, John), differential equations 545Ч549
Bernoulli, Johann (Jean, John), orthogonal trajectories 551Ч552
Bernoulli, Nicolaus 552Ч553
Bessel, Friedrich Wilhelm 738 757
Betti number 820Ч821 833
Betti, Enrico 819Ч820
Bh skara I 214Ч215 skara I 214Ч215
Bh skara II 218Ч226 skara II 218Ч226
Bh skara II, and combinatorics 229Ч230 skara II, and combinatorics 229Ч230
Bh skara II, biography 192 224 skara II, biography 192 224
Billingsley, Henry 386
binary number 844
Binomial theorem 506Ч509
Boethius 173 289
Bolyai, J nos 785 nos 785
Bolyai, J nos, biography 779 nos, biography 779
Bolyai, J nos, non Ч Euclidean geometry 767 774 778Ч779 nos, non Ч Euclidean geometry 767 774 778Ч779
Bolzano Ч Weierstrass property 814Ч815
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 (House of Wisdom)
(House of Wisdom)  of Euclid
of Euclid 
 (abacists)
(abacists) 
 -dimensional geometry
-dimensional geometry 
 -adic numbers
-adic numbers 
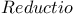
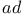
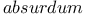 , in Archimedes
, in Archimedes 
 exam
exam 
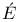 cole Polytechnique
cole Polytechnique 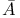 ryabhata
ryabhata 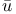 K
K mil ibn Aslam
mil ibn Aslam  , Ab
, Ab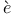 te
te 
 rgi, Jobst
rgi, Jobst 
 nos
nos