|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Katz V.J. Ч A History of Mathematics: An Introduction |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Bolzano, Bernhard 705 710Ч711 814Ч815
Bolzano, Bernhard, biography 711
Bombelli, Rafael 182 364Ч367
Bombelli, Rafael, biography 365
Boole, George 651 686Ч687 842
Borel, Emile 814Ч815
Bosse, Abraham 461
Boundary line 776
Bourbaki, Nicolas 812Ч813
Brachistochrone problem 547Ч549 562
Bradwardine, Thomas 315Ч316 318
Brahe, Tycho 408Ч409
Brahmagupta 214Ч215 218Ч223 226-227
Brahmagupta, biography 218
Brauer, Richard 829
Briggs, Henry 420
Brunelleschi, Filippo 389
Buddhism 196
Byron King, Ada (Lady Lovelace) 807 837Ч838 845
Byron King, Ada (Lady Lovelace), biography 838
Calculus 468Ч543
Calculus, and Leibniz 522Ч531
Calculus, and Newton 503Ч522
Calculus, and nineteenth century analysis 706Ч708
Calculus, areas and volumes 475Ч492
Calculus, differential 469Ч475 502 509Ч514 522Ч524 527Ч531 570-573 585Ч590 632Ч633 715-717
Calculus, foundations of 582Ч590
Calculus, Fundamental Theorem of 498Ч503 (see also Fundamental theorem of calculus) )
Calculus, integral 475Ч492 496Ч498 514Ч515 522Ч524 529Ч531 573-574 717Ч720 726Ч727
Calculus, inventor of 485 503 521
Calculus, of exponential and logarithmic functions 416 492Ч496 528Ч529 535 554Ч558 567 571
Calculus, of functions of several variables 550Ч554 561Ч562 572 575-578
Calculus, of trigonometric functions 493Ч495 533 554Ч558 572-573
Calculus, of variations 558Ч560
Calculus, of vectors 746Ч752
Calculus, summary 543
Calculus, texts 532 534 560Ч574 706
Calendar, Babylonian 26Ч27
Calendar, Chinese 197
Calendar, Christian 289
Calendar, Egyptian 26Ч27
Calendar, French revolutionary 637Ч638 640
Calendar, Jewish 26Ч27
Calendar, Julian 404
Calendar, Mayan 333Ч334
Cambodia 231Ч232
Cambridge University 502 678 679 840
Cambridge University, professors 502 566 707 750Ч751
Cambridge University, students 388 504 673 681 685 690 816
Camorano, Rodrigo 386
Canonical forms 694Ч695
Cantor, connectedness 815
Cantor, fundamental sequences 731Ч735
Cantor, Georg 705
Cantor, Georg, biography 732
Cantor, infinite sets 806
Cantor, real numbers 814
Cantor, set theory 807Ч812
Cardano,   360Ч367 360Ч367
Cardano, and probability 449Ч451
Cardano, biography 360
Cardano, Gerolamo 342 359Ч367 445 613
Cartan, Elie 767 795Ч797 828
Cartan, Henri 813
Cartography 393Ч397
Cauchy criterion 712 719 729
Cauchy sequence 711Ч712 817Ч818 825
Cauchy Ч Riemann equations 739 743 745
Cauchy,   707Ч708 720 707Ч708 720
Cauchy,  dimensions 792 dimensions 792
Cauchy,     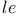   708 715Ч716 708 715Ч716
Cauchy, Augustin Ч Louis 651 705 707Ч720
Cauchy, biography 707
Cauchy, complex analysis 739Ч742
Cauchy, continuity 657Ч658 709Ч711 715 725
Cauchy, convergence 711Ч715 720 729
Cauchy, derivatives 715Ч717
Cauchy, determinants 688Ч689
Cauchy, differential equations 719Ч720
Cauchy, eigenvalues 692Ч694
Cauchy, integrals 717Ч720 726
Cauchy, irrational numbers 729
Cauchy, limits 708Ч709
Cauchy, permutations 665
Cavalieri, Bonaventura 477Ч478
Cayley,  dimensions 792 dimensions 792
Cayley, and Jordan 695
Cayley, Arthur 651 672Ч674 689Ч691 789
Cayley, biography 673
Cayley, graphs 849Ч850
Celestial equator 138 143 154Ч155
Center of gravity 105Ч107
Champollion, Jean 3
Chasles, Michel 767 788Ч789
Chevalier, August 668
China 3Ч4 192Ч193
Chinese mathematics 3Ч4 15Ч19
Chinese mathematics, algebra 35
Chinese mathematics, and Babylonian mathematics 206
Chinese mathematics, and European mathematics 307
Chinese mathematics, and Gaussian elimination 755
Chinese mathematics, and Indian mathematics 196 220Ч221
Chinese mathematics, and Islamic mathematics 206 220
Chinese mathematics, arithmetic calculations 14
Chinese mathematics, astronomy 195Ч197
Chinese mathematics, counting board 6Ч7 13
Chinese mathematics, cultural influences 327Ч330
Chinese mathematics, geometry 20Ч23
Chinese mathematics, indeterminate analysis 197Ч202
Chinese mathematics, linear equations 687
Chinese mathematics, medieval 192Ч210
Chinese mathematics, place value system 230
Chinese mathematics, polynomial equations 202Ч210
Chinese mathematics, Pythagorean theorem 32Ч35
Chinese mathematics, summary 45 237
Chinese mathematics, surveying 193Ч195
Chinese remainder problem and number theory 652 653
Chinese remainder problem in Indian mathematics 221
Chinese remainder problem in medieval mathematics 328
Chinese remainder problem in Qin Jiushao 199Ч202
Chinese remainder problem in Sun Zi 197Ч199
Chords in Hipparchus 143Ч145
Chords in Indian astronomy 212
Chords in Islamic mathematics 275
Chords in medieval Europe 297Ч299
Chords in Ptolemy 146Ч149 (see also Trigonometry)
Christianity and medieval mathematics 331
Christianity and Renaissance mathematics 402Ч404 407Ч408
Chrysippus 55
Chuquet, Nicolas 349Ч351 416
Church, Alonzo 840
Chutan Hsita 196
Circle, area of, in   163 163
Circle, area of, in al Ч Khwarizml 268
Circle, area of, in Archimedes 108Ч109
Circle, area of, in Babylonia 19Ч22
Circle, area of, in China 20Ч22
Circle, area of, in Egypt 20Ч21
Circle, area of, in Euclid 91Ч92
Circle, area of, in Heron 162
Circle, area of, in India 21
Clairaut, Alexis Ч Claude 554 575 597 621Ч623 630Ч632
Clairaut, and Stokes 751
Clifford, William 781Ч783
Closed set 817
Cohen, Paul 814
Cohomology group 832
Collins, John 493
Combinatorial topology 806
Combinatorics, in medieval Europe 300Ч306
| Combinatorics, Indian 228Ч230
Combinatorics, Islamic 263Ч267
Combinatory multiplication 794
Commandino, Federigo 368
Compactness 815 817Ч818
Complex analysis 737Ч746
Complex analysis, derivatives 743
Complex analysis, functions 742Ч746
Complex analysis, in Cauchy 718
Complex analysis, in Riemann 743Ч746
Complex analysis, integration 738Ч742
Complex analysis, residues 741Ч742
complex numbers 364Ч367 446Ч447 659-660
Complex numbers, in eighteenth century mathematics 557Ч558
Complex numbers, in Euler 614
Complex numbers, in Gauss 654Ч655
Complex numbers, in Hamilton 682Ч684
Complex numbers, in Peacock 678Ч679
Compounding 315Ч317
Computers 807 834Ч851
Computers, and von Neumann 844Ч845
Computers, BabbageТs engines 835Ч838 844
Computers, early developments 834Ч835
Computers, switching circuits for 841Ч844
Computers, Turing machine 839Ч841
Cone 91Ч94 (see also Conic sections) )
Congruences, higher order 652 653
Congruences, linear 197Ч199 218Ч221 328 617Ч618 651
Congruences, quadratic 618Ч619 652Ч653
Conic sections 116Ч129
Conic sections, analytic geometry of 433Ч434 438Ч444
Conic sections, asymptotes 122Ч123
Conic sections, conjugate diameters 132
Conic sections, construction of 392Ч393
Conic sections, directrix 127
Conic sections, foci 125Ч127
Conic sections, in projective geometry 460Ч462 785Ч787 790-791
Conic sections, Islamic 259
Conic sections, normals 124
Conic sections, symptoms 119Ч122
Conic sections, tangents 123Ч125
Connectedness 748 815 819
Continuity, defined 710
Continuity, in Cauchy 709Ч711
Continuous function 817
Continuum Hypothesis 734Ч735 814
Convergence 819
Convergence, Cauchy criterion for 729
Convergence, in Cauchy 711Ч715 719
Convergence, in Euler 614Ч615
Convergence, in Newton 509
Convergence, tests 713Ч714
Convergence, uniform 715 727Ч729
Coordinate systems, analytic geomety 435
Coordinate systems, astronomy 142Ч143 154Ч156
Coordinate systems, geography 394Ч397
Coordinate systems, geometry 438
Coordinate systems, graphs 319Ч321
Coordinate systems, non Ч Euclidean geometry 780Ч781 787 790
Coordinate systems, quaternions 685
Copernicus,   406Ч408 406Ч408
Copernicus, Nicolaus 145 404Ч408 782
Copernicus, Nicolaus, biography 403
Cosines, Law of 152 300 772 778
Cossists 351
Cotes, Roger 561
Counting 4Ч8 50
Counting board 6Ч7 13
Counting board, and place value system 230 232
Counting board, and polynomial equations 204Ч205 208 210
Counting board, and Qin 201
Counting board, in Renaissance mathematics 344
Counting the colors problem 264Ч266
CramerТs Rule 597 612 690 755
Crelle, August 666 672 727 735 805
Cross ratio 787Ч790
Cube root calculations 202 216
Cubic equations, al Ч Khayy m m 259Ч262 259Ч262
Cubic equations, al Ч T s s 262Ч263 262Ч263
Cubic equations, Chinese 202
Cubic equations, in Archimedes 115
Cubic equations, in Bombelli 366Ч367
Cubic equations, in Cardano 359Ч367
Cubic equations, in Dardi 347Ч348
Cubic equations, in del Ferro 350 358Ч359
Cubic equations, in Descartes 447Ч448
Cubic equations, in Diophantus 179Ч180
Cubic equations, in Lagrange 619Ч620
Cubic equations, in medieval mathematics 328
Cubic equations, in Renaissance mathematics 350 353 358Ч367
Cubic equations, in Tartaglia 359Ч361
Cubic equations, in Vi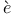 te 372Ч375 te 372Ч375
Cubic equations, trigonometric solution of 373Ч374
Cubic numbers 172
Curvature, defined 632
Curvature, differential geometry 768Ч771
Curvature, in Newton 513Ч514
Curvature, in seventeenth century mathematics 533Ч534
Curvature, non Ч Euclidean geometry 780Ч783
Curve, in analytic geometry 435Ч436 438Ч442
Curve, in Bernoulli 549
Curve, in calculus 468Ч469 487Ч488 499Ч503 513Ч514 623
Curve, in medieval Europe 320
Curve, in space 392Ч393 630Ч633
Curve, statistical 758Ч760
Cycloid, in Bernouli 545 548Ч549
Cycloid, in Gauss 662Ч664
Cycloid, in Wallis 489Ч490
Cyclotomic equations 620 657Ч659 661Ч667 669
da Cunha, Jos Anast Anast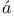 cio 705 712Ч713 cio 705 712Ч713
da Cunha, Jos Anast Anast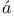 cio, biography 713 cio, biography 713
Dantzig, George 848
Dardi, Maestro 346Ч348
De Mere see Mere Chevalier
De Moivre, Abraham 601Ч605 609
De Moivre, biography 602
De Morgan, and Boole 686
de Morgan, Augustus 651 680Ч681 682 838 850
de Witt, Jan 442Ч444
Debeaune, Florimond 442
Decimal system, and logarithms 418
Decimal system, and money 640
Decimal system, Hindu Ч Arabic 230Ч232
Decimal system, in medieval Europe 302 307
Decimal system, in Renaissance mathematics 342Ч343 349 375Ч378 376Ч377
Decimal system, Islamic 240Ч243
Decimal-binary conversion 844
Dedekind, algebraic number theory 659Ч661 676Ч677 826 828
Dedekind, Axiom of Choice 809Ч810
Dedekind, cuts 729Ч731
Dedekind, functions 724
Dedekind, Richard 651 704 795
Dedekind, set theory 734
Dee, astronomy 398
Dee, geometry 386Ч389
Dee, John 385
Dee, kinematics 420Ч421
Dee, mapmaking 393 397
Deferent 141
del Ferro, Scipione 358Ч361
Delamain, Richard 834
Delaunay, Charles 747
della Francesca, Piero 347Ч348 390
della Nave, Annibale 359
Democritus 92Ч94 112
derivatives 715Ч717
Derived set 817
Desargues, Girard 432 460Ч462 785
Descartes, analytic geometry 431Ч432 436Ч442 504
Descartes, biography 437
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 dimensions
dimensions 
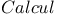
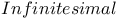
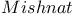
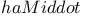
 m
m
 s
s te
te  Anast
Anast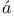 cio
cio