|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Katz V.J. Ч A History of Mathematics: An Introduction |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm 468 490 522Ч531 583 834Ч835
Leibniz, integrals 718
Leibniz, interchangeability theorem 550Ч552
Leibniz, limits 708
Leibniz, transmutation theorem 524Ч527
Leonardo da Vinci 393
Leonardo of Pisa 288 297Ч299 307Ч309
Leonardo of Pisa, biography 299
Lever, law of 103Ч107
Levi ben Gerson 299Ч300 302Ч306 329
Levi ben Gerson, biography 303
Li Ye 207Ч208
Limits, and  -adic numbers 825 -adic numbers 825
Limits, and nineteenth century analysis 706Ч709
Limits, defined 708
Limits, in Bolzano 712Ч713
Limits, in Cantor 732
Limits, in Cauchy 708Ч709 719Ч720
Limits, in eighteenth century mathematics 586
Limits, in Maclaurin 584Ч585
Limits, in Newton 511 515 520
Limits, in twentieth century mathematics 815Ч819
Lindemann, Ferdinand 664Ч665
Line integrals 742Ч743 747Ч748
Linear congruence 197Ч199 218Ч221 328
Linear equations, Chinese 197Ч202
Linear equations, Greek 175Ч176
Linear equations, in ancient mathematics 14Ч19
Linear equations, in medieval Europe 309 314
Linear equations, in Renaissance mathematics 350
Linear equations, solutions to 695Ч697
Linear equations, systems of 309 314 328 350 372 612Ч613 615Ч617 687-697
Liouville, Joseph 656Ч657 664 669 805
Liu Hui 193Ч195
Lobachevsky, biography 775
Lobachevsky, Nikolai 789
Lobachevsky, non Ч Euclidean geometry 767 774Ч779 782Ч785
Loci see Analytic geometry; Three- and four-line locus problem
Logarithms 418Ч420 493 614
Logarithms, in Euler 567 568
Logarithms, in Leibniz 528Ч529
Logarithms, in Newton 508Ч509
Logarithms, in Renaissance mathematics 416Ч420
Logarithms, in seventeenth century mathematics 535
Logarithms, invention of 416Ч418 834
Logic, Aristotelian 50Ч51 54Ч56
Logic, Boolean 686Ч687
Logic, in Euclid 63Ч65 (see also Proof)
Longitude, astronomy 142 154Ч156
Longitude, geography 394Ч397 (see also Coordinate systems)
Lovelace, Lady (Ada Byron King) 807 837Ч838 845
Lovelace, Lady (Ada Byron King), biography 838
Lunes 52
LТHospital, Guillaume 532Ч534 575 612
M r r , Chevalier de 431 448 452 158 599 601Ч602 , Chevalier de 431 448 452 158 599 601Ч602
M ller, Johannes 398Ч401 ller, Johannes 398Ч401
Mac Lane, Saunders 806 833
Maclaurin,    611Ч613 611Ч613
Maclaurin,    562Ч565 583Ч585 562Ч565 583Ч585
Maclaurin, Colin, biography 563 708
Madhava 494
Mah v v ra 228 ra 228
Manifolds 780Ч783 791Ч792
Map-making 393Ч397
Mapping 833
Maseres, Francis 678
Mathematical games 338Ч339
Mathematical model 127Ч129
Mathematical model, in Archimedes 103
Matrices 687Ч695
Matrices, and canonical forms 694Ч695
Matrices, and eigenvalues 691Ч694
Matrices, defined 651 689
Matrices, in ancient mathematics 17Ч19
Maxima and minima 468Ч469 473Ч475 819
Maxima and minima, in eighteenth century mathematics 561 566 572
Maxima and minima, in Lacroix 706
Maxima and minima, in Leibniz 528
Maxima and minima, in lТHospital 533
Maxima and minima, in Newton 512
Maxwell, James Clerk 685Ч686 747Ч748 750 752
Mayan mathematics 332Ч334
Mayer, Walther 832Ч833
Mazzinghi, Antonio de 346
Mean speed rule 319 320Ч321 421
Mean value theorem 717 719
Medieval mathematics, European 288Ч321
Medieval mathematics, European, algebra 307Ч314
Medieval mathematics, European, and Greek mathematics 289Ч291 297 299Ч300 310 312 314Ч316
Medieval mathematics, European, and Indian and Chinese mathematics 299 307
Medieval mathematics, European, and Islamic mathematics 289Ч291 299Ч300 307 312 314
Medieval mathematics, European, combinatorics 300Ч306
Medieval mathematics, European, cultural influences 327Ч331
Medieval mathematics, European, geometry 292Ч299
Medieval mathematics, European, kinematics 314Ч321
Medieval mathematics, European, probability 449
Medieval mathematics, European, summary 326
Medieval mathematics, European, trigonometry 293 296 298Ч300
Menabrea, L. F. 838
Menaechmus 116 134
Menelaus 136 152Ч153
Meray, Charles 731
Mercator, Gerard 397
Mercator, Nicolaus 493 505
Mersenne, Marin 306 436 458
Mesopotamia see Babylonian mathematics
Method of analysis 115Ч116 127Ч128 183Ч185 187 369Ч370 432
Method of exhaustion 91
Method of exhaustion, in Archimedes 113 114
Method of exhaustion, in Islamic mathematics 273Ч274
Method of least squares 753Ч758
Method of least squares, in Gauss 755Ч757
Method of least squares, in Legendre 753Ч755
Metric 780Ч781 784
Metric system 639
Metric, functional spaces 817Ч818
Metric, projective 789Ч791
Monge, and education 637Ч639
Monge, and projective geometry 785
Monge, Gaspard 597 633Ч635 721
Moon see Astronomy
Moore, Eliakim H. 822
Moscow Mathematical Papyrus 3 14Ч15 23Ч25
Multiple integration 574Ч578
Multiplication see Arithmetic computations
MUSIC 48Ч49 53 86Ч87 171 173 411Ч412
Napier, John 416Ч420
Natural numbers 734 807 814
Natural numbers, axioms 735Ч736
Navigation 393Ч394
negative numbers 677Ч678
Negative numbers, Chinese 19
Negative numbers, in Euler 614
Negative numbers, in Hamilton 682Ч684
Negative numbers, in Maclaurin 612
Negative numbers, in medieval mathematics 329
Negative numbers, in Peacock 678Ч680
Negative numbers, in Renaissance mathematics 353Ч354 364
Negative numbers, Indian 226
Negative numbers, Islamic 245 252
Nehemiah, Rabbi 136 163Ч164
Neile, William 496
Neiuwentijdt, Bernard 528
Netto, Eugen 674
Newton,     515Ч516 520Ч522 515Ч516 520Ч522
Newton, and  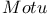 516Ч519 516Ч519
Newton, and Berkeley 582Ч585
Newton, and Cambridge University 678Ч679
Newton, and Leibniz 510 591
Newton, and Maclaurin 613
| Newton, and nineteenth century analysis 705
Newton, and probability 610Ч611
Newton, biography 468 504
Newton, differential equations 547
Newton, fluxions and fluents 509Ч514
Newton, Isaac 503Ч522
Newton, limits 708
Newton, power series 505Ч506
Nicomachus 170Ч173
Nicomedes 110Ч111 134
Nilakantha, Kerala Gargya 494
Nineteenth-century mathematics 650Ч804
Nineteenth-century mathematics,  -dimensional geometry 792Ч797 -dimensional geometry 792Ч797
Nineteenth-century mathematics, algebraic equations 662Ч670
Nineteenth-century mathematics, analysis 704Ч760
Nineteenth-century mathematics, complex analysis 737Ч746
Nineteenth-century mathematics, differential geometry 768Ч771
Nineteenth-century mathematics, groups and fields 670Ч677
Nineteenth-century mathematics, HilbertТs axioms 797Ч800
Nineteenth-century mathematics, matrices 687Ч697
Nineteenth-century mathematics, non Ч Euclidean geometry 772Ч785
Nineteenth-century mathematics, number theory 652Ч661
Nineteenth-century mathematics, probability and statistics 753Ч760
Nineteenth-century mathematics, projective geometry 785Ч792
Nineteenth-century mathematics, summary 703 765 804
Nineteenth-century mathematics, symbolic algebra 677Ч687
Nineteenth-century mathematics, vector analysis 746Ч752
Noether, biography 830
Noether, Emmy 805Ч806 829Ч832
Noetherian ring 829Ч832
Non-Euclidean geometry 767 772Ч785
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Bolyai 778Ч779
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Helmholtz and Clifford 781Ч783
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Islamic mathematics 271
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Klein 789Ч792
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Lambert 628Ч630
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Lobachevsky 774Ч779 782Ч785
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Riemann 779Ч781
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Saccheri 624Ч628
Non-Euclidean geometry, in Taurinus 772Ч774
Non-Euclidean geometry, metrics in 789Ч791
Non-Euclidean geometry, models 783Ч785
Normal curve 604Ч605 758Ч760
Normal set 817
Normals 124 472Ч473
North American Indians 336Ч337
Notation see Algebraic symbolism
Nu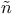 es, Pedro 357Ч358 396Ч397 es, Pedro 357Ч358 396Ч397
Number symbols, ancient 5Ч8
Number symbols, European 308
Number symbols, Mayan 333
Number symbols, origin of 230Ч231
Number theory, algebraic 659Ч661 677Ч678
Number theory, in Euclid 84Ч88
Number theory, in Euler 617Ч619
Number theory, in Fermat 458Ч460
Number theory, in Gauss 652Ч655
Number theory, in Leonardo of Pisa 310
Number theory, in Nicomachus 171Ч173
Number theory, Islamic 266
Number theory, Pythagorean 48Ч51 73
Number vs. magnitude 56 85Ч86
Number vs. magnitude, in Islamic mathematics 272Ч273
Number vs. magnitude, in medieval Europe 314 327 329
Number vs. magnitude, in Nicomachus 171
Number vs. magnitude, in Renaissance mathematics 349 377Ч378 386Ч388
Number words 5
Olbers, Heinrich 766
Oldenburg, Henry 468 531
Oracle 46
Oresme, Nicole 317Ч318 502
Ostrogradsky, Mikhail 705 748Ч749 792
Oughtred, William 504 834
Oxford University 316 318 695
Pacific Island mathematics 339Ч340
Pacioli, Luca 342 345Ч346 348 357 451
Pandrosian 183
Pappus 170 183Ч187
Pappus and analytic geometry 432
Pappus and Renaissance mathematics 368
parabola 119 122
Parabolic geometry 790
Parallel postulate 62 720
Parallel postulate, in eighteenth century geometry 624Ч630
Parallel postulate, in Islamic mathematics 269Ч271
Parallel postulate, in non-Euclidian geometry 772 775Ч776 785
PARAMETER 119
Parmenides 54
Pascal, adding machine 834
Pascal, and Desargues 462
Pascal, and Fermat 482Ч484
Pascal, and Leibniz 522
Pascal, biography 452
Pascal, Blaise 431Ч432 490
Pascal, probability 448 451 156
Pascal, projective geometry 785
PascalТs triangle 329Ч330 452 156
PascalТs triangle, and probability 599
PascalТs triangle, Chinese 202Ч203 205Ч206
PascalТs triangle, in Fermat 482
PascalТs triangle, in Leibniz 522Ч524
PascalТs triangle, in medieval Europe 311
PascalТs triangle, in Newton 507Ч508
PascalТs triangle, in Renaissance mathematics 354Ч355
PascalТs triangle, in Wallis 488
PascalТs triangle, Islamic 258Ч259 266
Peacock, and Boole 686
Peacock, and Lagrange 706
Peacock, biography 680
Peacock, George 651 677Ч680
Peano, Giuseppe 736Ч737 795
Peano, vector spaces 767 827
Pearson, Karl 759
Peirce, Benjamin 828
Peirce, Charles 850
Pell equation 221Ч225 615
Pentagon construction 76Ч77
Perfect numbers 88 458
Perfect set 817
Perigee 141
permutations 651 665 669Ч670
Permutations, in Lagrange 619Ч621
Permutations, in medieval Europe 305Ч306 (see also Combinatorics)
Perspective 389Ч393 (see also Projective geometry )
Pi ( ), ancient 18 ), ancient 18
Pi ( ), and probability 604 ), and probability 604
Pi ( ), in Archimedes 110Ч111 ), in Archimedes 110Ч111
Pi ( ), in Leibniz 526Ч527 ), in Leibniz 526Ч527
Pi ( ), in Wallis 488 ), in Wallis 488
Pi ( ), Islamic 268 ), Islamic 268
Pitiscus, Bartholomew 401Ч402
Pl cker, Julius 767 787 cker, Julius 767 787
Place-value system, and logarithms 418
Place-value system, and money 640
Place-value system, Hindu Ч Arabic 230Ч232
Place-value system, in ancient mathematics 6Ч8
Place-value system, in medieval Europe 290 302 307
Place-value system, in Renaissance mathematics 342Ч343 349 375Ч378
Place-value system, Islamic 240Ч243
Place-value system, Mayan 333
Plane numbers 172
Plane triangle 149Ч152 399 101
Planet see Astronomy
Plato 52Ч54 135
Plato of Tivoli 288 290Ч291
Plutarch 104 107
Poincar , and Stokes 752 , and Stokes 752
Poincar , biography 821 , biography 821
Poincar , Henri 784 785 , Henri 784 785
Poincar , homology 820Ч821 , homology 820Ч821
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



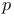 -adic numbers
-adic numbers  r
r ller, Johannes
ller, Johannes 
 v
v ra
ra 
 -dimensional geometry
-dimensional geometry  es, Pedro
es, Pedro  ), ancient
), ancient