|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Katz V.J. Ч A History of Mathematics: An Introduction |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Descartes, normal lines 472Ч473
Descartes, Rene 129 368Ч369 496 613
Descartes, theory of equations 447Ч448
Determinants 612 651 689Ч690
Dickson, Leonard Eugene 823
Diez, Juan 642
Differential equations, exact 554 751Ч752
Differential equations, in Bernoulli, Daniel 580Ч582
Differential equations, in Bernoulli, Jakob 545 549
Differential equations, in Bernoulli, Johann 545Ч549
Differential equations, in Bernoulli, Nicolaus 552Ч553
Differential equations, in Cauchy 719Ч720
Differential equations, in DТAlembert 578Ч580 692
Differential equations, in eighteenth century mathematics 545Ч560
Differential equations, in Euler 545 553Ч558 570Ч574 580-582 692
Differential equations, in Leibniz 527Ч531 546Ч547
Differential equations, in Newton 509 512
Differential equations, linear 547Ч549 553Ч554 556-558
Differential equations, partial 573 578Ч582 635 721Ч722
Differential form 795Ч797
Differential geometry, in Clairaut 630Ч632
Differential geometry, in Euler 632Ч633
Differential geometry, in Gauss 768Ч770
Differential geometry, in Monge 633Ч635
Differential geometry, of curves 630Ч632
Differential geometry, of surfaces 632Ч633 768Ч771
Differential triangle 499 502Ч503
Differential triangle, in Leibniz 524Ч527
Differential triangle, in Newton 512
Differential triangle, in seventeenth century mathematics 490
Diodes 126Ч127 134
Diophantus 168 187
Diophantus, and Euler 615
Diophantus, and Renaissance mathematics 365 372
Diophantus, Arithmetica 173Ч183
Dirichlet, and continuity 710
Dirichlet, Peter Lejeune 655 659 705 725Ч726
Distributive law 81 226 823
Ditton, Humphry 532 534Ч535
Divergence theorem 748Ч749
Division see Arithmetic computations
Dodgson, Charles L. 696
Domingo Gundisalvo 290Ч291
Donnolo, Shabettai 301
Double difference, method of 194
Doubling the cube 51Ч52 128 662Ч663
Duality 785Ч787
Durer, Albrecht 390Ч393
Dyck, Walther von 651 674Ч675
DТAlembert, and Lacroix 706
DТAlembert, and limits 708
DТAlembert, biography 579
dТAlembert, Jean le Rond 578Ч581 585Ч586 692 695
Eccenter 141 402
Eccentricity 141
Ecliptic 137Ч139
Edgeworth, Francis 759
Education, eighteenth century 637 678
Education, medieval 316 330Ч331
Education, nineteenth century 678 679 720
Education, Renaissance 359
Education, seventeenth century 704Ч705 (see also Textbooks)
Egypt 3
Egyptian Mathematical Leather Roll 10
Egyptian mathematics 1 188
Egyptian mathematics, algebra 13Ч14
Egyptian mathematics, and Greek mathematics 93 100 122 184 188
Egyptian mathematics, arithmetic computations 8Ч12
Egyptian mathematics, calendars 26Ч27
Egyptian mathematics, counting 5Ч6
Egyptian mathematics, geometry 20Ч21
Egyptian mathematics, square root 27
Egyptian mathematics, summary 45
Eigenvalues 691Ч694
Eighteenth century mathematics 544Ч642
Eighteenth century mathematics, algebra 610Ч621
Eighteenth century mathematics, analysis 544Ч590
Eighteenth century mathematics, differential equations 545Ч560
Eighteenth century mathematics, education 637Ч640
Eighteenth century mathematics, geometry 621Ч637
Eighteenth century mathematics, number theory 617Ч619
Eighteenth century mathematics, probability 597Ч609
Eilenberg, Samuel 806 833
Eisenstein, Ferdinand Gotthold 689
Elliptic geometry 790
Epicycle 140 402 413
Equations, abstract algebra 662Ч670
Equations, construction of solutions of 437Ч438 447Ч448
Equations, cubic see Cubic equations
Equations, cyclotomic 620 657Ч659 661Ч667 669
Equations, differential see Differential equations
Equations, indeterminate 175 197Ч202 218Ч225 284 308Ч309 615-616
Equations, linear see Linear equations
Equations, polynomial see Polynomial equations
Equations, quadratic see Quadratic equations
Equations, systems see Linear equations
Equations, theory of 373Ч375 445Ч448 667-670
Equinox 138
Eratosthenes 55 104 186
Error-correcting codes 846Ч847
Ethnomathematics 332Ч340
Euclid 58Ч59 184
Euclid,  186 186
Euclid,  157 157
Euclid, analysis 185Ч186
Euclid, and Apollonius 118 122 124 129
Euclid, and Archimedes 107 108 111 114
Euclid, and Diophantus 177
Euclid, and education 678
Euclid, and eighteenth century mathematics 582 621Ч637
Euclid, and Heron 159Ч161
Euclid, and Islamic mathematics 241 249Ч250 262 269
Euclid, and medieval Europe 297 299 302 327 328
Euclid, and Nicomachus 171Ч173
Euclid, and Nicomedes 111
Euclid, and nineteenth century mathematics 659
Euclid, And Ptolemy 146
Euclid, and Renaissance mathematics 368 377Ч378 385Ч386
Euclid, and seventeenth century mathematics 437Ч439 504
Euclid, application of areas 71
Euclid, basic propositions 63Ч67
Euclid, circles and pentagons 73Ч77
Euclid, conic sections 116 117
Euclid, constructions 61Ч62
Euclid, geometric algebra 67Ч73 95Ч96
Euclid, HilbertТs axioms 799Ч800
Euclid, irrational magnitudes 90
Euclid, number theory 84Ч88
Euclid, parallel postulate 62 (see also Parallel postulate )
Euclid, probability 601
Euclid, ratio and proportion 77Ч84
Euclid, similarity 67 77 82Ч84
Euclid, solid geometry 90Ч95 (see also Elements of Euclid)
Euclidean algorithm 78
Euclidean algorithm, and Chinese mathematics 201
Euclidean algorithm, and Indian mathematics 218
Euclidean algorithm, in Nicomachus 171
Euclidean constructions 66Ч69
Euclidean Domain 660
Eudemus 48
Eudoxus 46 50 91
Eudoxus, and astronomy 136 139Ч140
Eudoxus, biography 81
Euler,   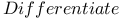 570Ч573 585 570Ч573 585
Euler,    573Ч574 573Ч574
Euler,     567Ч570 567Ч570
Euler,  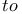 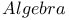 614Ч615 614Ч615
Euler, and nineteenth century analysis 706 739 744
Euler, biography 553
Euler, calculus of variations 558
| Euler, continuity 709Ч710
Euler, curves 630 632Ч633
Euler, derivatives 715Ч718
Euler, differential equations 553Ч558 570Ч574 580Ч582 692
Euler, differential geometry 630 632Ч633
Euler, double integrals 575Ч578
Euler, Fourier series 720
Euler, functions 724
Euler, Leonhard 544
Euler, linear equations 615Ч617 695
Euler, matrices 692
Euler, multiple integration 577Ч578
Euler, number theory 617Ч619 652Ч653 655
Euler, primes 459
Euler, theory of surfaces 767
Euler, topology 635Ч637 848
Expectation 457Ч458
Exponents, rules of, in Diophantus 179
Exponents, rules of, in medieval Europe 317
Exponents, rules of, in Renaissance mathematics 346 350 370 416
Exponents, rules of, Islamic 252Ч253
Extensive quantity 793
Exterior derivative 796
Factor Theorem 448
Factorial rule 301
False position, in Egypt 15
False position, in Greece 181Ч182
False position, in medieval Europe 307 344
False position, in Renaissance mathematics 344
Faulhaber, Johann 482
Fermat, analytic geometry 431Ч436 442
Fermat, and Diophantus 182
Fermat, areas 481Ч485
Fermat, biography 433
Fermat, Last Theorem 459Ч460 655Ч657 659
Fermat, little theorem 459 617Ч618
Fermat, maxima and minima 470Ч472
Fermat, number theory 458Ч460 617Ч618 655
Fermat, Pierre de 129 182
Fermat, probability 448 451
Fermat, tangents 471
Ferrari, Lodovico 360Ч361 364 613
fibonacci see Leonardo of Pisa
Fibonacci sequence 309
Fields 651
fields, defined 676Ч677
Fields, in nineteenth century mathematics 667 676Ч677
Fields, in twentieth century mathematics 823Ч826
Figurate numbers 49
Finck, Thomas 401
Finzi, Mordecai 306
Fisher, Ronald 760
Fluxions and fluents, in Agnesi 566
Fluxions and fluents, in Berkeley 582Ч583
Fluxions and fluents, in Dixon and Hayes 534Ч535
Fluxions and fluents, in Maclaurin 562Ч565
Fluxions and fluents, in Newton 509Ч514
Fluxions and fluents, in Simpson 560Ч562
foci 125Ч127
Forcadel, Pierre 386
Four-color theorem 805 850
Fourier, biography 720
Fourier, Charles 847
Fourier, Joseph 705 720Ч726
Fr chet, Maurice 816Ч819 chet, Maurice 816Ч819
Fractions, Babylonian 13
Fractions, Chinese 14
Fractions, decimal 242Ч243 375Ч378
Fractions, Egyptian 9Ч12
Fractions, Greek 78
Fractions, in Chuquet 349Ч351
Fractions, in exponents 317 446 485Ч488
Fractions, in Gerardi 345
Fractions, in medieval Europe 302 307
Fractions, in Renaissance mathematics 375Ч378
Fractions, in Richard of Wallingford 315Ч317
Fraenkel, Abraham 812
Franklin, Benjamin 641Ч642
Frege, Gottlob 736Ч737
French Revolution 637Ч640 707 721 775
Frend, William 678 838
Frobenius, Georg 651Ч652 674 691 695Ч697
Functions, and graphs 319Ч321
Functions, and wave equation 578Ч582 (see also Trigonometry)
Functions, continuous 581 709Ч711 715 723Ч726 817 819
functions, defined 567 587 723 724
Functions, in Euler 567Ч570
Functions, in Greece 143Ч145 157
Functions, integrable 726Ч727
Functions, representable as trigonometric series 722Ч726
Functions, spaces of 816Ч818
Functions, symmetric 375 446
Functions, uniformly continuous 727Ч729
functor 833
Fundamental theorem of algebra 447 738
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 86
Fundamental theorem of calculus 498Ч503 719
Fundamental theorem of calculus, in Lagrange 589Ч590
Fundamental theorem of calculus, in Leibniz 529Ч531
Fundamental theorem of calculus, in Maclaurin 564Ч565
Fundamental theorem of calculus, in Newton 514
Fundamental theorem of calculus, in Ostrogradsky 749
Fundamental theorem of calculus, in Riemann 745
G del, Kurt 806 813Ч814 del, Kurt 806 813Ч814
Galilei, 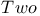 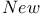 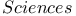 421Ч425 421Ч425
Galilei, biography 422
Galilei, Galileo 321 385 420Ч425 502
Galois, Evariste 651 667Ч669 676Ч677 694
Galton, Francis 758Ч759
Gauss Ч Jordan elimination 755
Gauss, 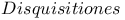 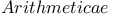 652Ч653 662Ч664 670-671 652Ч653 662Ч664 670-671
Gauss, 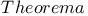  770Ч771 770Ч771
Gauss, and Abel 666
Gauss, and Dedekind 659Ч660
Gauss, biography 654
Gauss, Carl Friedrich 651
Gauss, complex analysis 738Ч739 744
Gauss, cyclotomic equations 662Ч664
Gauss, fields 678
Gauss, geometry 766Ч771 774 778Ч780 781
Gauss, integrals 748Ч749
Gauss, least squares 755Ч757
Gauss, number theory 652Ч655
Gauss, primes 657
Gauss, quadratic forms 670Ч671 677 688
Gaussian elimination 17Ч19 755
Gaussian integers 654Ч655
Geography 393Ч397
Geometric algebra 100 117
Geometric progression 86Ч87 416
Geometrical product 792
Geometry, absolute 778
Geometry, analytic 431Ч444
Geometry, and complex analysis 737Ч746
Geometry, Babylonian 19Ч25
Geometry, Chinese 20Ч23 193Ч197 207
Geometry, Egyptian 20Ч21
Geometry, eighteenth century 621Ч637
Geometry, Euclidean 58Ч96 776
Geometry, foundations of 797Ч800
Geometry, groups in 791Ч792
Geometry, in  dimensions 780 792Ч797 dimensions 780 792Ч797
Geometry, in African weaving 338
Geometry, in Archimedes 111Ч116
Geometry, in Clairaut 621Ч623 630Ч632
Geometry, in Dee 385Ч389
Geometry, in Euler 632Ч633 635Ч637
Geometry, in Monge 633Ч635
Geometry, in Plato 52Ч54
Geometry, in Saccheri 624Ч628 (see also Analytic geometry; Differential geometry; Non-Euclidean geometry; Projective geometry)
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




 chet, Maurice
chet, Maurice  del, Kurt
del, Kurt 
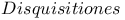
 dimensions
dimensions