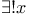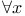|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Grimaldi R.P. — Discrete and combinatorial mathematics. An introduction |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Principia Mathematica 138 177
Principle of choice 5
Principle of cross classification 428
Principle of duality for a Boolean algebra 764
Principle of duality for Boolean functions 737 738
Principle of duality for Boolean variables 737 738
Principle of duality for logic 65
Principle of duality for set theory 161
Principle of inclusion and exclusion 261 403—412 418 424 428 433 683
Principle of Mathematical Induction 184 (see also “Mathematical induction” “Mathematical
Principle of Strong Mathematical Induction 196
probability 3 45 172—174 176 178 179 245 418 425 476 428 457 458 480 523 794
Probability Bernoulli trial 173
Probability Binomial distribution 173
Probability elementary event 173
Probability event 173
Probability experiment 172
Probability independent events 794
Probability independent outcome 173
Probability sample space 172
Problem of the 36 officers 858 872
Procedural language 618
Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society 589
Product of Boolean functions 737
Product of disjoint cycles 814
Product of maxterms 742
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) network 372 394
Program verification 194
Projection 271—273
Projective plane 867—869
proof 51 139 140 “Mathematical “Mathematical
Proof by contradiction 87 91 95 113 133 134 148 158 184 233 295
Proper coloring of a graph 588
Proper divisors of 0 213
Proper divisors of zero 703
Proper prefix 319
Proper subgroup 780
Proper subset 144—146
Proper substring 320
Proper suffix 319
Properties of exponents A-4
Properties of logarithms A-7
Properties of the integers 183—243
Properties of the integers Division Algorithm 213—218 225—227
Properties of the integers Euclidean Algorithm 226—229
Properties of the integers Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 183 232—236
Properties of the integers greatest common divisor 225—229 231
Properties of the integers least common multiple 230 231
Properties of the integers Mathematical induction 183—199 233
Properties of the integers primes 183 214 215 232—234
Properties of the integers Well-Ordering Principle 184
Proposition 51 (see also “Statement”)
Protons 42
push 502
q is necessary for p 52
Qnintilianus, Marcus Fabius 730
Quadratic equation 829
Quadratic time complexity 296 304
Quantifiers 100 102 103 120 138 145 146 166 185 295
Quantifiers 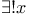 120 120
Quantifiers  100 100
Quantifiers 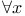 100 100
Quantifiers Bound variable 100
Quantifiers Connectives 100 101
Quantifiers Existential quantifier 100
Quantifiers Free variable 100
Quantifiers Implicit 102 103
Quantifiers Unique existential quantifier 120
Quantifiers Universal quantifier 100
quantum mechanics 43
Quartic equation 829
Quaternary sequence 245
QUEUE 626
Quick sort 638
Quine-McCluskey method 753 773
Quintic equation 830 872
Qume, W.V. 624 773
Quotient 215 216
r(C, x) 421
Ralston, Anthony 556 601 602
Ramsey theory 311
Ramsey, Frank Plumpton 311
Random walk 523
RANGE 252
Rate of a code 796 811
Reachability 350
Reachable state 340
Reactor 497
Read, R.C. 590 595 600 602 832
Received word 795 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Record 720
Recurrence relations 461—464 471—480 482—499 511 512 521 522
Recurrence relations, boundary conditions 462
Recurrence relations, characteristic equation 471
Recurrence relations, characteristic roots 471
Recurrence relations, Fibonacci relation 472 521
Recurrence relations, first-order linear relation 461—467
Recurrence relations, general solution 462
Recurrence relations, homogeneous relation 463
Recurrence relations, initial condition 462
Recurrence relations, linear relation 463
Recurrence relations, linearly independent solutions 471 477
Recurrence relations, method of generating functions 493—499
Recurrence relations, method of undetermined coefficients 482—484
Recurrence relations, nonhomogeneous relation 463 482—484
Recurrence relations, nonlinear relation 499—504
Recurrence relations, particular solution 483
Recurrence relations, second-order linear relations 471—480
Recurrence relations, system of recurrence relations 498 499
Recurrence relations, Table of particular solutions for the method of undetermined coefficients 490
Recurrent event 523
Recursion 202
Recursive algorithm 467 488 489
Recursive definition 202—204 206—208 254 284 316 318 324 325 461 620 622
Recursive function 260 468 469
Recursive procedure 637
Recursive process 202
Recursively defined set 209 249 250 323—325
Redei, L. 581
Redfield, J. Howard 832
Reducible polynomial 844
Reductio ad absurdum 87 148
Redundant state 388
Reed, M.B. 600 602
Reed, Robert D. 45 46
Refinement (of a partition) 391
Reflection principle 49 523
Reflections 782
Reflexive property (of a relation) 350 351 367 394 395
Region 563
Regular graph 551
Reingold, Edward Martin 523 524
Relation 202 245 248 249 251 284 309 349—362 364 366—368 372—379 382—386 388 394 395 397 399 400 529
Relation composition 357 358
Relation matrix 359 362 367
Relation reachability 350
Relation, 1-equivalence 350 388
Relation, antisymmetric relation 352 362 367
Relation, associative law of composition 358
Relation, binary relation 248
Relation, composite relation 358 360
Relation, converse of a relation 284
Relation, definition of a relation 248 349
Relation, divides relation 373
Relation, equivalence relation 355 368 382—386 394—396
Relation, equivalent states 350 388
Relation, first level of reachability 350
Relation, irreflexive relation 357
Relation, k-equivalent states 350 388
Relation, modulo n relation 350
| Relation, partial order 353—356 372—379 394
Relation, partial ordering relation 353 372
Relation, poset 372—374 376—379
Relation, powers of a relation 358 359
Relation, reflexive relation 350 351 362 367 394 395
Relation, relation composition 357 358
Relation, relation matrix 359—362 367
Relation, second level of reachability 350
Relation, subset relation 249 353 373 376 378
Relation, symmetric relation 351 362 367 394 395
Relation, transitive relation 352 362 367 373 394 395
Relation, zero-one matrix 357 359—362 395
Relational data base 272 311
Relative complement 159
Relatively prime integers 226
Relatively prime polynomials 845
Relativity theory 731
Remainder 215 216
Remainder theorem 841
Rencontre 420 428
Repeat-until loop 61 189
Repetition 146
Replication number 866
Representation Theorem for a finite Boolean algebra 768 773
Resek, Diane 140
Reserved words 14
Reset 330
Restriction of a function 257
Reversal of a string 325
Right child 617
Right coset 791
Right subtree 622 623
Right-cancellation property (in a group) 779
Rigid motions of a cube 826 827
Rigid motions of a regular hexagon 822 823
Rigid motions of a regular tetrahedron 827 828
Rigid motions of a square 814
Rigid motions of an equilateral triangle 781—783
Ring 735 778 779 835 846
Ring homomorphism 723—725 731
Ring isomorphism 723 726 728
Ring of matrices 702 703
Ring of polynomials 835 837
Ring theory 701—733 792 835 837 838 849
Ring theory Boolean ring 732
Ring theory cancellation law of addition 709 724
Ring theory cancellation law of multiplication 707 711
Ring theory center of a ring 733
Ring theory characteristic 849
Ring theory commutative ring 703
Ring theory congruence modulo n 717
Ring theory definition 701 702
Ring theory field 706 711 719 731
Ring theory group of units 792
Ring theory homomorphism 723—725 731
Ring theory ideal 714 725 731
Ring theory integers modulo n 717—721
Ring theory integral domain 706 711
Ring theory isomorphic rings 723
Ring theory isomorphism 723 726 728
Ring theory kernel of a homomorphism 729
Ring theory matrix rings 702 703 730
Ring theory multiplicative identity 703
Ring theory multiplicative inverse 706
Ring theory, 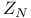 717 717
Ring theory, proper divisors of zero 703
Ring theory, ring of matrices 702 703
Ring theory, ring of polynomials 835 837
Ring theory, ring properties 709—714
Ring theory, ring with unity 703 837 838
Ring theory, subring 712—714 724 725
Ring theory, subtraction 709
Ring theory, unit 706
Ring theory, unity 703
Ring with unity 703 837 838
Ringel, Gerhard 599 602
Rings of Saturn 45
Rinnooy Kan, A. H. G. 585 600 602
Riordan, John 429 458
Roberts, Fred S. 45 46 600 602
Rook 420—422
Rook polynomial 421—425 429 434 683
Root of a binary ordered tree 500
Root of a polynomial 838 841 844
Root of a tree 614
Rooted binary tree 499 500
Rooted Fibonacci tree 653
Rooted ordered binary tree 505—507 523
Rooted tree 614 619 628 629
Rorres, Chris A-24
Rosen, Kenneth H. 45 46 241
Ross, Kenneth A. 139 140
Rota, Gian Carlo 429 458
Rotations 781 782
Rothman, Tony 872 873
Rothschild, Bruce L. 311 312
Round-robin tournament 582
Rouvray, Dennis H. 600 602
Row major implementation 253 259
Row matrix A-13
Row number 741
Row vector A-13
Roy, R.R. 45 46
Ruin problems 523
Rule for Proof by Cases 88
Rule of Conditional Proof 88
Rule of Conjunction 85 88
Rule of Conjunctive Simplification 88 108 157
Rule of Contradiction 86—88
Rule of Detachment 80 81 88
Rule of Disjunctive Amplification 88 157
Rule of Disjunctive Syllogism 86 88
Rule of Existential Generalization 136
Rule of Existential Specification 136
Rule of product 3 5—8 12 19—24 35 36 145 163 234 246 254 255 261 276 351 353 354 419 591 594
Rule of sum 3 4 6 20 23 145 151 170 263 265 276
Rule of the Constructive Dilemma 88
Rule of the Destructive Dilemma 88
Rule of Universal Generalization 128—132 147
Rule of Universal Specification 124—132 147
Rules of ad Absurdum 87
Rules of Inference 80—83 85 86 88 94 95 124—132 137 147
Rules of Inference, Law of the syllogism 82
Rules of Inference, Modus ponens 80
Rules of Inference, Modus tollens 83
Rules of Inference, Proof by (the method of) contradiction 87
Rules of Inference, Rule for proof by cases 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of conditional proof 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of conjunction 85 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of conjunctive simplification 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of detachment 80 81
Rules of Inference, Rule of disjunctive amplification 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of disjunctive syllogism 86 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of the constructive dilemma 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of the destructive dilemma 88
Rules of Inference, Rule of universal generalization 128—132 147
Rules of Inference, Rule of universal specification 124—132 147
Rules of Inference, Table of rules of inference 88
Russell, Lord Bertrand Arthur William 138 156 177
Russell’s paradox 156 177
Ryser, Herbert John 45 46 428 429 695 696 872 873
S(m, n) 264
S(x, k) 799
Saaty, Thomas L. 695
Sahni, Sartaj 668 670 694 696
Sample space 172 247 262 418 426
Samuel, Pierre 731 732 872 873
Sandier, R. 872 873
Saturated edge 673
Saturated hydrocarbons 598 607 610 611
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте