|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Grimaldi R.P. — Discrete and combinatorial mathematics. An introduction |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
d(a, b) 658
d(x,y) 798 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Dantzig, G.B. 695
Data structures 245 362 395 396 499 607 620 626 651 720
Date, C.J. 311 312
Dauben, Joseph Warren 311 312
David, Florence Nightingale 179
De Arte Combinatoria 137
de Fermat, Pierre 239 240 730
de Laplace, Pierre Simon 173 457
de Montmort, Pierre Remond 428
DeBruijn, Nicolaas Govert 832
DEC (Digital Equipment Corporation) 5
Decision structure 55
Decision tree 630 631
Decoding algorithm 804 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Decoding function 796 804
Decoding table 807 808
Decoding table with syndromes 809 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Decoding with coset leaders 809 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Decomposition (of a permutation) 815
Decomposition theorem for chromatic polynomials 592
Dedekind domain 731
Dedekind, Richard 240 309 731 831
Deductive reasoning 137
Deficiency of a graph 689
Deficiency of a set of vertices 689
Definition 56 121 123
Deg  550 550
Deg (R) 566
Degree of a polynomial 835
Degree of a region 566
Degree of a table 273
Degree of a vertex 550
Delays 343
Delong, Howard 139 140
Delta function 606
DeMoivre, Abraham 310 428 456 522
DeMoivre’s Theorem 199 477
DeMorgan, Augustus 138 176 239 241 589
DeMorgan’s Laws for a Boolean algebra 764
DeMorgan’s Laws for Boolean functions 737
DeMorgan’s Laws for Boolean variables 737
DeMorgan’s Laws for logic 63 64 66
DeMorgan’s Laws for set theory 160 162 163 172
DeMorgan’s Laws for set theory (extended) 205 206
Denumerable set 309 A-29
Deo, Narsingh 523 524 599—601
Depth-first index 645
Depth-first search 624 625 628 651
Depth-first search algorithm 624
Depth-first spanning tree 645—647
Derangement 418 419 429
Descendant 615
Design of experiments 853 856 872
Determinant 478 479 A-19-A-21
Dfi  645 645
Dick, Auguste 731 732
Dickson, Leonard Eugene 240 241
dictionary order 617
Dierckman, Jeffrey S. 651 652
Difference equations 461 523
Differential equations 461
Digital Equipment Corporation 5
Digraph 363 530
Dijkstra, Edsger Wybe 658 694 695
Dijkstra’s Shortest-Path Algorithm 657 665
Dinitz, Jeffrey H. 873
Diophantine equation 230 240
Diophantus 230 239
Direct argument 133
Direct block 17
Direct product of groups 783
Direct proof 133 134
Directed cycle 365 373 532
Directed edge 330 363
Directed Euler circuit 554 555
Directed graph 333 349 357 363—368 372 373 394 395 530 533 657
Directed graph, arcs 330 363
Directed graph, associated undirected graph 364 533
Directed graph, edges 363 530
Directed graph, loop 363 530
Directed graph, nodes 363 530
Directed graph, strongly connected 365 558
Directed graph, vertices 363 530
Directed path 532
Directed tree 614
Directed walk 532
Dirichlet drawer principle 309 (see also “Pigeonhole principle”)
Dirichlet, Peter Gustav Lejeune 309 310 730
Disconnected graph 366 533
Disjoint (sets) 158 171
Disjoint collection of sets A-34
Disjoint subboards 421
Disjunction 52
Disjunctive normal form (d.n.f.) 740 772
Distance (in a graph) 535 653
Distance (in algebraic coding theory) 798 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Distance function 799 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Distinguishing string 391—393
Distributions 33 35 36 43
Distributive Law of multiplication over addition for integers 132
Distributive Law of multiplication over addition for real numbers 63
Distributive Law of scalar multiplication over matrix addition A-15
Distributive Laws for a Boolean algebra 762
Distributive Laws for a ring 702
Distributive Laws for Boolean functions 737
Distributive Laws for Boolean variables 737
Distributive Laws for logic 64 65
Distributive Laws for matrix multiplication over matrix addition A-24
Distributive Laws for set theory 160
div 60 302
Divide-and-conquer algorithms 511—520 523 634
Dividend 216
Divides (for integers) 213
Divides (for polynomials) 839
Divides relation 373 766
Division algorithm, for integers 215—218 225 226 231 253 276 278 293 717 788 789
Division algorithm, for polynomials 839—841 845—847
Division method (for hashing) 720
Divisor for integers 213 216
Divisor for polynomials 839
Divisors of zero; see Proper divisors of zero d.n.f. 740
Doctrine of Chances 428
dodecahedron 568 578 599
Domain (of a function) 252
Domain (of a relational data base) 273
Dombowski, Peter 872 873
Dominance (for functions) 294
Dominance Laws for a Boolean algebra 764
Dominance Laws for Boolean functions 737
Dominance Laws for Boolean variables 737
Dominating set 603 757
Domination Laws for logic 65 67
Domination Laws for set theory 160
Domination number of a graph 630
Don’t care conditions 758—760
Dornhoff, Larry L. 343 344 811 831 832
Dorwart, Harold L. 872 873
Double indirect block 17
Double induction 313
Double Negation 64
Double sum 32
Double summation 32
Doubly linked lists 395
Doubly stochastic matrix 697
Dual code 805 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Dual graph 568 569 571
Dual network 572 573
Dual of a statement 65 161 737 764
| Duality in a Boolean algebra 737 764
Duality in logic 65
Duality in set theory 161
Dyck, Walther Franz Anton von 830
Economics 523
Edges 363 530
Edmonds, J. 679
Efficiency of a coding scheme 796 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Eider’s phi function 409—411 720 779
Einstein, Albert 731
Electrical engineering 333
Electrical network 572 573 598 600 607 650
Electron 43
Element argument 147 158 160 161
Elementary event 173
Elementary subdivision 562
Elements 215 232 233 238
Elements of a set 143
Elsayed, E.A. 585 600 601
Embedding 397 560
Empty language 320
Empty set 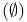 148 148
Empty string 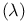 316 316
Encoding 795 801 804
Encoding function 795 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Enderton, Herbert B. 179 A-37
Energy state 43
ENIGMA 345
Enumeration 3 23 44 179 403 409 428 433
Epp, Susanna S. 139 140
Equality of Boolean functions 736
Equality of functions 281
Equality of matrices 702 A-14
Equality of polynomials 835
Equality of real numbers 61
Equality of sets 145 146
Equality of strings 317
Equality relation 355 356 382
Equivalence class 383 384 395
Equivalence problem 396
Equivalence relation 349 355 356 368 382—386 388 394—396 717 816 845 871
Equivalence relation, block 382
Equivalence relation, cell 382
Equivalence relation, equivalence class 383 384 395
Equivalence relation, partition 382—386 395
Equivalence relation, Stirling numbers of the second kind 386
EQUIVALENCE statement (in ANSI FORTRAN) 384 385
Equivalent codes 811 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Equivalent finite state machines 336
Equivalent states  350 388 350 388
Eratosthenes 239
Erdos, Paul 599
Erlanger Programm 831
Error correction (in a code) 800 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Error detection (in a code) 800 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Error pattern 794 (see also “Algebraic coding theory”)
Euclid 45 215 226 232 233 238 239
Euclidean algorithm, for integers 226—229 293 468 469 522 719
Euclidean algorithm, for polynomials 845
Euclidean geometry 859
Euler circuit 552 578 579
Euler trail 552 553 578 579
Euler, Leonard 309 396 456 457 505 529 551 563 598 730 830 858 872
Euler’s conjecture (Latin squares) 858
Euler’s Theorem on congruence 793
Euler’s Theorem on connected planar graphs 564 598
Even integer 131
Even parity string 342
Even, Shimon 502 523
Event 173
Event Bernoulli trial 173
Event elementary event 173
Eves, Howard 139 140 311 312
Exclusive OR 52 62 434 824
Exclusive or 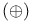 for Boolean functions 745 746 for Boolean functions 745 746
EXCLUSIVE-OR gate 754
Existential generalization 136
Existential quantifier  100 107 100 107
Existential specification 136
Expansion by minors A-23
Experiment 172 247
Explicit formula 201 202
EXPONENT A-1—A-4 A-6
Exponential function 418 A-1 A-4—A-6
Exponential generating function 449—453 457 458
Exponential time complexity 296 489
Exponentiation algorithm 302
Extension of a function 257
f is dominated by g 294
f is dominated by g on S 513
f(A) 252
f(x) is congruent to g(x) modulo s(x) 846
Factor of a polynomial 839 841
Factor Theorem 841 842
Factorial 7 206 298
Factorial time complexity 296
Factorization of a polynomial 842
Fallacy 85 128
Fano, Gino 859 872
Feedback network 774
Feit, Walter 831
Feller, William 458 523
Fendel, Daniel 140
Fermat’s Last Theorem 730 731
Fermat’s theorem on congruence 793
Fermi-Dirac model 43
fermions 43
Ferrers, Norman Macleod 457
Ferrer’s graph 448 457
Fibonacci numbers 183 207—209 299 300 456 461 472 476 481 488 489 522 526
Fibonacci relation 472 521
Fibonacci sequence 522
Fibonacci trees 653
Field 706 711 719 731 778 830 839 850 871
Fields (in a record) 720
FIFO structure 626
File structure 17
Filius Bonaccii 456
Finite affine plane 859—864
Finite field 835 840 843 847 849 850 851 871 872
Finite function 245 254 255 262 290 308 343
Finite geometry 835 859 862 865 871 872
Finite induction principle 181 (see also “Mathematical induction”)
Finite induction principle—alternative form 196—199 (see also “Mathematical induction—alternative form”)
Finite projective geometry 872
Finite projective plane 867 872 873
Finite sequence of n terms A-30
Finite set 144 149 A-28
Finite state machine 315 329—332 335—341 343 349 350 388—393 396 712 746
Finite state machine, 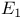 388 388
Finite state machine, 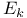 388 388
Finite state machine, 1-equivalent states 350 388
Finite state machine, arc 330
Finite state machine, definition 329
Finite state machine, directed edge 330
Finite state machine, E 388 389
Finite state machine, equivalent machines 336
Finite state machine, equivalent states 350 388
Finite state machine, first level of reachability 350
Finite state machine, input 328
Finite state machine, input alphabet 328 329
Finite state machine, internal states 328 329 388
Finite state machine, k-equivalent states 350 388
Finite state machine, k-unit delay machine 339 343
Finite state machine, Mealy machine 343
Finite state machine, minimal distinguishing string 391—393
Finite state machine, minimization process 388—393
Finite state machine, next state 328
Finite state machine, next state function 329
Finite state machine, one-unit delay machine 339
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте




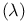

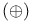 for Boolean functions
for Boolean functions