|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Shu F.H. Ч The Physical Universe: An Introduction to Astronomy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
"Radius" of closed universe 372Ч373
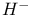 negative ion 95 negative ion 95
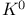 meson 404 meson 404
Absolute magnitude 160Ч161
Absolute zero 62
Absorption lines, scattering 85Ч86
Absorption lines, true absorption 85Ч86
Absorption of photons 45Ч46
Acceleration 14
Accretion 193 251Ч252 320 475 477
Accretion disks in active galactic nuclei 320 325
Accretion disks in close binary stars 193Ч196 199Ч200 204
ACID 73 512
Acoustic wave, sound 68Ч70
Action at a distance 40 107
Active galaxies 306Ч315 320Ч321 327Ч331
Adaptation 501Ч503 526
Adenine (A) 514 516 520 531 533
Adenosine 516 520
Adenosine triphosphate see "ATP"
Adiabatic fluctuation 294
Advance of perihelion of Mercury 204
Aerobic 529
Age of universe 11 360Ч361 462Ч463
ALCOR 180Ч181
Algae 493Ч495
Algol 182 191Ч193
Alleles 507
Allende meteorite 481
Allowed (permitted) transitions 53
Alpha Centauri 54Ч56
Alpha decay 116 444 460
Alpha helix 514
Alpha particle 41 116 460
Altruistic behavior 543
Amalthea 431
Ambipolar diffusion 253
Ameba (amoeba) 539 540
Amino acid 512Ч513 515 519 529 539
Amino acid chains (polypeptides) 513 517
Ammonia 234
Anaerobic 537 539
Ancient astronauts 547
Andromeda galaxy (M31) 291
Anemic spirals 295
Angular resolution 27Ч28
Anisotropic random velocities in disk of Galaxy 263
Anisotropic random velocities in elliptical galaxies 293
Anisotropy of cosmic microwave background 386
Annihilation (destruction) 61 113 132 140Ч141 323 389Ч390 400Ч401
Antibiotics 525
Antibodies 525
Anticyclonic motion 448 453Ч454
Antimatter 61 105Ч107 400Ч402
Antiparticles, antielectron (positron) 105 389 402Ч403
Antiparticles, antineutrino 107 389 402Ч403
Antiparticles, antineutron 107 389
Antiparticles, antiproton 105 389
Aperture synthesis 30
Apollo objects 424Ч425 545
Apollo-Soyuz 237
Apparent magnitude 160
Apsides 204Ч205
Area of a circle 569
Arecibo radio telescope 29
artificial intelligence 557Ч560
Asteroids 415 420 421 475
Astrology 3Ч4
Astronomical constants 567Ч568
Astronomical unit (AU) 32 83 567
Asymptotic giant 151Ч152
Atmosphere (as unit of pressure) 89
Atmosphere of planets 433Ч448 451Ч454
atom 41Ч42 44Ч47 50Ч53
Atomic hydrogen, distribution in external galaxies 283Ч285
Atomic hydrogen, distribution in Galaxy 246 267Ч273
Atomic hydrogen, energy level diagram and spectrum 45Ч47 218 221
Atomic hydrogen, hyperfine structure and 21Чcm line 52 227Ч230 302
Atomic nuclei 41 110Ч117
Atomic spectroscopy 45Ч57 52Ч53
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) 515Ч516 520Ч521 533 537 539 554
AU (astronomical unit) 32 83 567
Aurora australis 455
Aurora borealis 455
Australopithecus 545
BackЧtoЧfront evolution of metabolic chains 532 534Ч535
bacteria 524 536Ч537
Baimer photons 46Ч47 218Ч221
Balmer decrement 221
Barlike instabilities 277Ч278
Baroclinic 448 451 453
Barotropic 447 451 453
Barred spiral galaxies 292Ч295 305Ч306
Baryon number 104 109 401
Base 73 512
Base pairs 514Ч515 521
Baseline 30 31 311
Beam model for radio jets 313Ч315
Beam model for SS433 207
Becklin Ч Neugebauer object 235Ч236
Bending (deflection) of light 365Ч366 398
Beta decay 110Ч112 116 460
big bang 354 362 376Ч402 410
Big Burp 483
Big Dipper 3
Big Squeeze 362 410
BigЧBang nucleosynthesis 385 389Ч391
Binary galaxies 305 332Ч337
Binary pulsar 204Ч206
Binary stars 179Ч208
Binary stars, evolution of orbit 185 204Ч205
Binary stars, formation of 184Ч185 475Ч476
Binary stars, frequency of 184Ч185
Binary stars, influence in star clusters 177Ч178
Binary stars, light curves of 182Ч183 189Ч190 196 199
Binary stars, measurement of masses of 182Ч183
Binary stars, measurement of radii of 183Ч184
Binary stars, observational classification of 179Ч182
Binary stars, velocity curves of 181Ч182 204
Binary XЧray sources 198Ч204 325Ч326
Binding energy, electric 45Ч46
Binding energy, gravitational 37 157 200 202 204 281
Binding energy, nuclear 115Ч116
Biological evolution 499Ч503 525 528 532
Birkhoff's rule 358
BL Lacertae objects 306 308Ч310
Black holes 126 134Ч143 203Ч204 208 320Ч321 325 330Ч331 410
Blackbody radiation 77Ч80
Blue stragglers 173 193
BlueЧgreen algae 494 495 539
Bohr radius 44 88 426
Bok globules 216
Bolometric corrections 159 162
Bolometric magnitude 162
Boltzmann's constant (k) 65 67 567
Bose condensation 77
Boson 42 50 407Ч409 see
Bottom quark 103 407 see
Bound 37
Bound Universe 358Ч362
Bow shock 71 456
Brackett photons 218
Brain 550Ч551 554Ч556
Bridges between galaxies 332 333 335
Brightness see also "Magnitude"
Brightness, apparent brightness (energy flux) 32 37
Brightness, intrinsic brightness (luminosity) 32 37
Broken symmetries 402Ч412
Brownian motion 344
Bulk velocity 66 77
| Butcher Ч Oemler effect 348
Calcium as chemical element 51Ч52
Calcium in condensation sequence 477
Calcium in interstellar clouds 214Ч215
Callisto 415
Cambrian period 497 503 543
Cancer 524 526
Carbohydrate metabolism 530 535
Carbohydrates 494 506
Carbon as basis of organic life 52 547
Carbon as chemical element 51 52
Carbon catalyst in hydrogen burning 114
Carbon dioxide (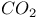 ) 434 436 437 440 494 530 ) 434 436 437 440 494 530
Carbon in carbohydrates 494
Carbon in condensation sequence 477
Carbon in organic chemistry 512
Carbon monoxide (CO) 234 269
Carbon stars 152 164 245
Carbon, radioactive isotope (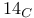 ) 112 ) 112
Carbon, role in grain formation in cool stellar atmospheres 245
Carbon, synthesis from helium 117Ч118
Carbonaceous chondrites 423 529
Cascade 46Ч47
Cassini's division 470Ч472
Cassiopeia A 239
Cataclysmic variables 194Ч198
Catalysts in cell 520 see
Catalysts in nuclear reactions 113Ч114
Catalysts, role of dust grains 231Ч232
Catalysts, role of inorganic micas and clays 533
cD galaxy 342Ч345 352 378 see
Cell differentiation 495 523Ч524 541
Cell division 506 521 see
Cell wall 506 536
Cell, as chemical factory 515Ч521
Cell, as unit of life 504Ч507
Cell, role in growth and reproduction 521Ч523
Cell, role in higher organisms 523Ч524 541
Center of mass 37 180 182Ч183 464
Centimeter (cm) see "cgs units"
Central bulge of Galaxy 258Ч259
Central dogma 515
Centrifugal force 180 480
centripetal acceleration 15
Cepheid variables 170Ч173 291 350Ч351
Cerebral cortex 554Ч555
cgs units 11
Chain of galaxies 350
Chain reaction 116
Chandrasekhar limit 128
Charge reversal 403
Charge, color 103 105
Charge, electric 16 103 406
Charge, gravitational (mass) 103
Charge, strong (baryon number) 104
Charge, weak 103
Charmed quark 103 407 see
Charon 415 420
Chemical elements, age of 462Ч463
Chemical elements, cosmic abundance 121
Chemical elements, list of 571Ч572
Chemical elements, periodic table 51
Chlorophyll 494 537
Chloroplasts 506 507 541 560
chromatic aberration 22 26
Chromosomes 509 523 524
Chromosphere 96 101 248
Circumference of a circle 569
Civilization 543
Classical mechanics 14 33
Cloning 524
Close binaries, effective gravity 186
Close binaries, equipotential surfaces 186
Close binaries, Lagrangian points 186
Close binaries, reflection effect in 189
Close binaries, Roche lobes 186
Close binaries, theoretical classification 186Ч188
Closed Universe 11 368Ч375 378Ч380
Clouds 80 416 437Ч438 445 452Ч454
Clusters see "Open clusters" "Globular "Clusters
Clusters of galaxies 339Ч341 345Ч350
CNO cycle 113Ч114 147
Coacervates 532 534 535
Coalsack nebula 212
Collisionless shocks 242
Color excess 162
Color index 162
Color of light 21
Color of quarks 105 406
Color of stars 32 159 161Ч162
Coma cluster 339 341 342
comets 415 423Ч425 480 545
Commensurability 467
Compact H II region 248
Complementary variables 106
Compton scattering 325
Compton time 399
Compton volume 399
Compton wavelength 108 399
Computers 32 298 557 560
Concentration classes 296
Condensation (precipitation) 72 245 437Ч438 448 452 454 475Ч478 484
Consciousness 554
Conservation principles, angular momentum 47Ч50
Conservation principles, baryon number 109 123Ч124 401
Conservation principles, electric charge 109
Conservation principles, energy 35Ч38 60
Conservation principles, lepton number 109 123Ч124 401
Conservation principles, mass-energy 60
Conservation principles, relation to global symmetries 404Ч405
Constancy of speed of light 53Ч54
Constellations, appearance in mythology 4
Constellations, use in navigation 3
Constellations, use in timekeeping 4
Constructionist 526
Contact binaries 188Ч191
Continental drift 484Ч485 491 497
Continents 484Ч492
Continuum 21Ч22 46Ч47
Controlled thermonuclear fusion 92Ч94 101
Convection 95Ч96 100 146 148Ч149 151 436Ч437 453 485
Copernican revolution 9
Coriolis force 188 446 453
Corona 96Ч98 101
Coronal gas in interstellar medium 239 247
Cosmic abundances 121 475
Cosmic microwave background radiation (relict of primeval fireball) 384Ч386
CosmicЧray particles 239Ч242 462
Cosmological constant 367 381 411
Cosmological principle 355
Cosmological redshift 316 350 374
Coulomb energy 74 426
Coulomb's law 38
covalent bond 71 512
CPT theorem 403
Crab Nebula 133Ч134 223Ч225
Crab pulsar 133Ч134 225
Craters 421Ч423 425
Creation of particles 61 132 140Ч142 323 389 396Ч401
Critical density to close universe 359
Critical mass 116
Critical point 73
Cross product (vector cross product) 18
Crossing over 511 526
Crystal lattice 72
CTP see "Nucleoside triphosphate"
Cultural evolution 544Ч546
Curie point 99
Cyanobacteria 539
Cyclic AMP 554
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



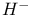 negative ion
negative ion 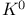 meson
meson 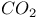 )
) 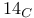 )
)