|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Shu F.H. Ч The Physical Universe: An Introduction to Astronomy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Microspheres 532 534 535
Milky Way 255Ч258 see
Mimas 467 470 472 474
Mini-black-holes 142
Minor planets see "Asteroids"
Mirror reflection see "Parity reversal"
Missing mass 259Ч260 304 348Ч349 393
Mitochondria 506 541 553 560
Mitosis 506 510 541
Mizar 179Ч182
MMT (Multiple Mirror Telescope) 32
Molecular biology 512Ч526
Molecular cloud complexes 242 248 282
Molecular clouds 231Ч234 269 273Ч274
Molecular hydrogen 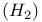 in interstellar medium 231Ч232 242 in interstellar medium 231Ч232 242
Molecular hydrogen 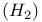 in Jovian planets 426Ч427 in Jovian planets 426Ч427
Molecular hydrogen 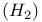 , chemical binding energy 60 , chemical binding energy 60
Molecular weight 512
Molecules 52 231Ч234 511Ч512
Moment of inertia 47 134
Momentum 14
Monomer 506 533
Moon 420
Moon, as member of double planet 418 479
Moon, eclipse of 6
Moon, geologic activity of 429
Moon, interior of 430
Moon, magnetic field of 455
Moon, origin of 429
Moon, phases of 7
Moon, tidal interaction with Earth 185 432
Moons of Jupiter 415 418 420
Moons of Mars 418 420 479
Moons of Neptune 417 418 420
Moons of Pluto 415 420
Moons of Saturn 418 420
Moons of Uranus 417 418 420
Moons, origin of 478Ч480
Morphological classification of galaxies 293Ч296
Mountain chains or ranges 486Ч487 490Ч491
Moving-cluster method 169Ч170
Multicellular organisms 495Ч496 541 545
Muon 103 407 411 see
Murchison meteorite 423
Mutation 500 526
Myelin sheath 551
N galaxies 306 309
N stars 144
n-body problem 466
Natural selection 498Ч503 525 541 560
Nebular hypothesis 475Ч482
Negative hydrogen ion 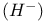 95 95
Neolithic 546 566
Neptune 415 418 455
Neptune, interior of 427
Neptune, moons of 418 420
Neptune, orbital resonance with Pluto 467 469
Nerve cell see "Neuron"
nerve impulses 550Ч552
neuron 550Ч553 556
Neurotransmitter molecules 553 559
Neutrino as lepton 105
Neutrino from Sun see "Solar neutrinos"
Neutrino, copious emission from very evolved stars 154
Neutrino, different types (flavors) 103
Neutrino, helicity 402Ч403
Neutrino, oscillations 122 392 403
Neutrino, rest mass 392
Neutrino, role in cosmology 389Ч390 392Ч393
Neutron as baryon 104Ч105
Neutron in atomic nuclei 51 110Ч112
Neutron in fission chain reactions 116
Neutron in neutron stars 129Ч130 155Ч157
Neutron star 126 129Ч134 198Ч200 208
Neutron, capture reactions 119Ч121 390Ч391
Neutron, decay 109Ч110
Newtonian cosmology 355Ч362
Nitrogen as chemical element 51
Nitrogen in amino acids 512
Nitrogen in condensation sequence 477
Nitrogen, abundance in Earth's atmosphere 492
Nitrogen, cosmic abundance 121
Nitrogen, equilibration with carbon in CN cycle 114
Nitrogen, fixation 521 539
Noncommutative transformations 408Ч409
normal 20
Normal modes 277
novae 195Ч197 350Ч351
Nuclear binding energy curve 115
Nuclear force see "Strong interaction" "Weak
Nuclear fusion in reactors see "Controlled thermonuclear fusion"
Nuclear fusion in stars see "Thermonuclear fusion reactions"
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) 507 532Ч534
Nucleoside 517 520 532Ч533
Nucleoside triphosphate (ATP, CTP, GTP, UTP) 515Ч516 532Ч533
Nucleotide (nucleoside monophosphate) 516Ч517 533
Nucleus of atom 41 110Ч117
Nucleus of cell 495
Nucleus of comet 423
Nucleus of galaxies 320Ч321 326Ч331
Nucleus of Galaxy 322Ч323
Nucleus of M31 325Ч326
Number density 67
OB stars 217 248 272 274 325
Observable Universe 11 373 376 384
Occam's razor 205
Ocean basins 484
Ocean circulation 449Ч451
Ocean rifts 486Ч490
Ocean trenches 486Ч487 490Ч491
Oceans 449Ч451 483Ч489 532
Olbers' paradox 383Ч384
Oort cloud of comets 424
Oort constants 263Ч264
Opacity 90 95 123
Open clusters 166Ч170 175
Open systems 498
Open Universe 11 368 375Ч380
Orbit decay 42 205 432
Orbital energy, electric 45
Orbital energy, gravitational 45
Orbits, elliptical (bound) 36Ч37 463Ч466
Orbits, hyperbolic (unbound) 37
Orbits, parabolic (critical) 37
Orbits, under force field of Galaxy 259 261 265Ч267
Orbits, under force field of star cluster 174Ч175 177Ч178
Order of magnitude 11
Order-disorder 63 498 565
Ordinary spiral galaxy 292Ч295
Organ system 541
Organelles 495 541
organic chemistry 512
Organic molecules in carbonaceous chondrites 423 529
Organic molecules in colored clouds of Jupiter 454
Organic molecules in interstellar space 234
Organic molecules in primordial soup 532
Orion 4
Orion Nebula 221 235Ч236
Outer Lindblad resonance 280
Oval distortions 277
Oxidation-reduction 492 537
Oxidizing atmosphere 495 538
Oxygen as chemical element 51 52
Oxygen as waste product of photosynthesis 494 537Ч539
Oxygen in condensation sequence 477
Oxygen, abundance in Earth's atmosphere 492 495
Oxygen, cosmic abundance 121
Oxygen, role in forming ozone layer 492
Oxygen, role in grain formation in cool stellar atmospheres 245
Oxygen, role in respiration 494 530 538Ч539
| Oxygen, synthesis from carbon and helium 118
Ozone 433 492Ч493 539
Palomar 200Чinch telescope 29
Pangaea 484Ч485 490 503
Panspermia hypothesis 529Ч530
Panthalassa 484 485
parabola 25 37
Parallax 5 32
Paramagnetic 99 243
Paramecia 541
Parity reversal 402Ч403
Parker instability 282
Parsec (pc) 160 567
Particle Physics 61 103Ч110 123Ч124 140Ч141 400Ч411 527
Paschen photons 46Ч47 218 234
Pasteur's experiments 530Ч531
Pauli's exclusion principle 42 50Ч51 408Ч409
Penetration probability 115
Pep reaction 122
Peppered moth 502Ч503
Peptide bond 512 517
Perfect cosmological principle 367 381
Perfect gas, Bose Ч Einstein distribution (bosons) 76
Perfect gas, classical diatomic 69 445
Perfect gas, classical monatomic 67Ч68
Perfect gas, Fermi Ч Dirac distribution (fermions) 75
Perfect gas, Maxwell Ч Boltzmann distribution (classical) 67
Period-luminosity relation 172 174
Periodic table 42 50Ч52
Permitted lines and transitions 219Ч222
Pest control 503
Ph 73
Phase transition 71Ч73 116 441 see "Evaporation" "Freezing" "Melting"
Phobos 418 420 479
Phosphate bond 516 530
Photoionize 47
Photometry 161Ч162 297Ч298
photons 18 43 103 107 406
Photosphere 86
Photosynthesis 494 537Ч539
Physical constants 567
Pi ( ) meson 109 239 399 ) meson 109 239 399
Pioneer 418 454
Planck density 398
Planck length 397 410
Planck mass 124 142 397
Planck state 397Ч400
Planck time 397 399 410
Planck's constant (h) 433 477 567
Planetary nebula 152 215 219 225
Planetesimals 478 481
Planets, ancient concept as wanderers 4Ч5 9
Planets, atmospheres 433Ч454
Planets, atmospheric circulation 444Ч447
Planets, gross properties 418 474
Planets, heliocentric view 6
Planets, interior structures 425Ч431
Planets, largest satellites 420
Planets, magnetospheres 454Ч458
Planets, orbital motions 463Ч469
Planets, origin 475Ч478
plasma 74 93Ч94
Plate tectonics 484 485
Plates 484Ч491 500
Pleiades star cluster 168Ч169
Pluto 418 455
Pluto, inclination of orbital plane 474
Pluto, moon of 415 420
Pluto, motion of 417
Pluto, orbital resonance with Neptune 4 67 469
Polar wind 458
Polaris 3
Polarization 17 50
Polarization of starlight 243Ч244
Polymer 506 531Ч533
Polynucleotides 533
Polypeptides 517 533
Polysaccharides 506 533
Population I, II, and III stars 145 173 261 296
Positrons 105 389
Potassium as chemical element 51 52
Potassium in condensation sequence 477
Potassium, radiatoactive isotope (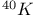 ) 461 482 ) 461 482
Potassium, role in nerve impulse 552
potential energy 36
Poynting vector 18
Praesepe star cluster 167Ч169
Pre-main-sequence stars 249Ч250
Precession of Earth's pole (spin axis) 8Ч9
Prefixes in exponent notation 567
Presolar grains 480Ч482
Pressure of blackbody radiation 79Ч80
Pressure of classical perfect gas 67Ч68
Pressure of degenerate electrons 126Ч128
Pressure of degenerate neutrons 129Ч130
Pressure of liquid 71Ч73
Presupernova star 155
Primates 543Ч544
Primeval fireball 387 459
Primordial soup 532
principal quantum number 44 46 50Ч52
Principle of equivalence 364Ч365
Principle of inertia 14
prism 21
Proinsulin 513
Project Cyclops 30
Prokaryotic cells 495 497 537Ч539
Proper motion 32 263
Protein 506Ч507 532Ч534 551Ч553
Protein synthesis 515Ч520
Protocell 528 532Ч536
Proton as baryon 104Ч105 108Ч109 123Ч124 400Ч401 405 407
Proton as nucleus of hydrogen atom 44
Proton as product of beta-decay of neutron 109Ч110
Proton as source of positive charge in nucleus 50Ч52
Proton in atomic nuclei 110Ч112
Proton in cosmic rays 240
Proton mass (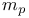 ) 39 567 ) 39 567
Proton, charge (+e) 39 406 567
Proton, decay of 124 407
Proton, equality in numbers with electrons 39 397 400Ч401
Proton-proton chain 113 147
Protoplanet 475 478
Protostar 251Ч252 480
Proxima Centauri (nearest star) 12 265
Pulsar dispersion 230
Pulsar glitches 131
Pulsars 131Ч134
Purine see "Adenine" "Guanine"
Pyrimidine see "Cytosine" "Thymine" "Uracil"
Pythagora's theorem 370 569
QSO 306 316Ч318 351 382
Quantum chromodynamics 105
Quantum electrodynamics 108 140Ч141 405 527
quantum mechanics 33 40Ч53 60Ч61
Quantum state, bound 50
Quantum state, free 76
Quark 103Ч105 123 239 406Ч407 see
R stars 144
Radiation constant (a) 79 567
Radiation pressure 79 144 146 152 245 320 424
Radiation-dominated Universe 387Ч388
Radiative envelope 148
Radio communication 547
Radio continuum emission, nonthermal (synchrotron) 133 225 227 311Ч312
Radio continuum emission, thermal (free-free) 226Ч227
Radio galaxies 306 310Ч315 327Ч329 382
Radio recombination lines 226
Radio source counts 382Ч383
Radio waves 16
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



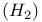 in interstellar medium
in interstellar medium 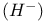
 ) meson
) meson 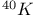 )
) 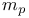 )
)