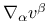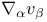|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hartle J.B. — Gravity: An Introduction to Einstein's General Relativity |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
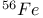 , most bound nucleus made in stars 255 , most bound nucleus made in stars 255
(Angular size)-redshift relation see “FRW cosmological models redshift-(angular
.d'Alembertian see “Wave operator”
.i Boo binary star system 346 (problem) 500
2dF redshift survey 364 (figure)
Absolute magnitude see “Magnitude”
Acceleration in curved spacetime 434
Acceleration in flat spacetime 86
Accretion disks 244—250
Accretion disks, and X-ray sources 244 282
Accretion disks, Eddington limiting luminosity 245 (box)
Accretion disks, formation 244
Accretion disks, radiation from 244
Accretion disks, spectral lines 246—250
Accretion disks, spectral lines, Fe line in MCG-6-30-15 249
Accretion disks, spectral lines, frequency shift 248
Accretion disks, temperature estimate 245 (box)
action see “Newtonian mechanics”
Active galactic nuclei 288—289
Active galactic nuclei, Blandford — Znajek mechanism 326—327 (box)
Active galactic nuclei, Cygnus A 289 (figure)
Active galactic nuclei, luminosity 288
Active galactic nuclei, powered by black holes 288—289 326—327
Active galactic nuclei, radio jets 288
Active galactic nuclei, size 288
Active galactic nuclei, spectrum 288
Addition of velocities, Newtonian 47
Addition of velocities, special relativity 71
Affine parameters see “Light rays”
AGN see “Active galactic nuclei”
Alternating tensor (three dimensions) 438 (box)
And cosmic ray energies 94 (box)
Andromeda galaxy (M31) 348 (figure) 351
Angular momentum, measured/defined by orbiting gyroscope 307
APM galaxy survey 363 (figure)
Apparent magnitude see “Magnitude”
Area 146—148
Area increase theorem see “Black holes”
Arecibo radio telescope 250 (figure) 509
ASCA X-ray satellite 249
Atom interferometry 35 (box)
Baryosynthesis see “Universe thermal
Bases 78 152—158 424—427
Bases, basis vectors 78
Bases, coordinate 155 420
Bases, dual to a given basis 424—427
Bases, orthonormal 153—158
Bases, orthonormal, construction along orthogonal coordinate directions 156
Bases, orthonormal, hats on the indices ot 96
Bases, orthonormal, of an observer 97 154
Bases, parallel propagation 440
Bases, table summarizing relations between bases and dual bases 425 (table)
Bases, transforming between coordinate and orthonormal bases 156 429
Bases, transforming between coordinate bases 429—430
Beaming see “Relativistic beaming”
Bekenstein — Hawking formula for black hole entropy 294
Berkeley, G. 37 (box)
Bianchi identity 457 482 489
big bang 3 10 12 see
Big crunch see “FRW cosmological models evolution
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, effect on orbital period detected 509 (figure)
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, gravitational waves from, effect on orbital period calculated 508
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, masses of components determined by general relativity 253
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, parameters determined by Newtonian gravity 252
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, precession of the periastron 251
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, relativistic effects measured 252
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, rotational period 252
Binary pulsar PSR B1913-16, semi-major axis 254 (problem)
Binary pulsar PSR B1913—16 250
Binary pulsars 250 see pulsar
Binary stars, gravitational radiation from see “Gravitational waves”
Binary stars, mass function 252 284
Binary stars, radial velocity curve 252 283
Birkhoffs theorem 459 468
Black holes 7—9 244 256—276 310—328 also “Kerr
Black holes, accretion disks around 282
Black holes, and active galactic nuclei 288 289 326—327
Black holes, and cosmic censors 275
Black holes, area increase theorem 276 325
Black holes, defined 261
Black holes, Hawking radiation 289—294
Black holes, horizon 8 261 313—314
Black holes, how detected 268 283
Black holes, in X-ray bmanes 281—285
Black holes, Kerr geometries as the unique family of black holes 276 310
Black holes, nonspherical collapse to 275—276
Black holes, primordial 281
Black holes, primordial, exploding 281
Black holes, quantum evaporation 289—294
Black holes, rocket thrust required to escape 261 (box)
Black holes, rotating see “Kerr black holes” “Kerr
Black holes, spherical collapse to 262—268
Black holes, supermassive see “Black hoW in galaxy centers”
Black holes, surface gravity 443 (problem)
Black holes, thermodynamics 294
Black holes, thermodynamics, first law of 294
Black holes, thermodynamics, second law ot 294
Black holes, thermodynamics, temperature 242
Blandford — Znaiek mexhanism see “Kerr black noes”
Boomerang experimen see “Cosmic backgroung radiation”
Boomerang experiment 18 (box)
Charge, charge-current four-vector 473
Charge, conservation of 473
Charge, current 473
Charge, density 473
Christoffel symbols, defined 173
Christoffel symbols, formula for 174
Christoffel symbols, Mathematica notebook for calculating see “Website”
Clocks, devices to measure timelike distances 60
Clocks, in a gravitational field 113—121 124
Clocks, in GPS 121
CMB see “Cosmic background radiation”
COBE satellite 350 (figure) 361
Conservation 478—479 see
Conservation, and spacetime symmetries 176 342 489
Conservation, of a quantity see “That quantity”
Conservation, of charge 473
Conservation, of energy-momentum in flat space 478
Conserved quantities along a geodesic see “Geodesic equation”
Coordinate bases see “Bases coordinate”
Coordinate singularity 136 258
coordinates 135—136 also e.g.” “Schwarzschild “Eddington
Coordinates, and gauge transformations in linearized giavity 461
Coordinates, arbitrary but systematic labels of points 27—28 135
Coordinates, Cartesian 21
Coordinates, different coordinates describe the same geometry 135
Coordinates, Fermi normal 182n
Coordinates, labels of points 21
Coordinates, latitude and longitude 25 (box)
Coordinates, physics independent or chohse of 27
Coordinates, plane polar 22
Coordinates, Riemann normal 180—183
Coordinates, singular 136
Coordinates, spherical polar 136
Coordinates, transformation of 28 136 420 429—430
Coordinates, utility of 135
Cosmic background radiation (CMB) 11 348 361 405—410
Cosmic background radiation (CMB), angular size 407—408
Cosmic background radiation (CMB), anisotropies 358 405—410
Cosmic background radiation (CMB), correlation function 408 409
Cosmic background radiation (CMB), signatures of deiiMtv fluctuations that grew to be galaxies 361
Cosmic censorship conjecture 275 310—311 (box)
Cosmic rays 94 (box)
Cosmological constant 376 480 483
Cosmological fluid see “FRW cosmological models”
Cosmological models see “FRW cosmological models”
Cosmological parameters see “FRW cosmological models”
Cosmological redshift 351 352 370
Cosmology see “Universe FRW
Covariant derivative 419 430—440
| Covariant derivative, and parallel propagation 438
Covariant derivative, defined 431
Covariant derivative, formula for 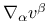 434 434
Covariant derivative, formula for 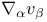 436 436
Covariant derivative, of functions 435
Covariant derivative, of tensors 436
Covariant derivative, of the metric vanishes 438
Covariant derivative, of vectors see “Vectors derivatives”
Covectors see “Dual vectors”
Crab Nebula 7 (figure)
Critical density see “FRW cosmological models”
Curl (three-dimensional), and covariant derivative 438 (box)
Curl (three-dimensional), formula for in flat three-space 438(box)
Currents, fluxes through timelike three-surfaces 473
Curvature 452—456
Curvature, Einstein 458
Curvature, Einstein, defined 483
Curvature, Mathematica program for computing see “Website”
Curvature, measurement of, by relative test particle motion 445
Curvature, measurement of, two test particles needed 445
Curvature, Ricci 471
Curvature, Ricci scalar, defined 482
Curvature, Ricci, defined 456
Curvature, Ricci, symmetry 456
Curvature, Riemann, defined 452
Curvature, Riemann, dimensions 455
Curvature, Riemann, for static, weak field metric 454
Curvature, Riemann, in a local inertial frame 454
Curvature, Riemann, number of components 454
Curvature, Riemann, of the Schwarzschild geometry 455
Curvature, Riemann, order of magnitude 455
Curvature, Riemann, properties 454—455
Curvature, Riemann, symmetries 454
Curvature, scale of 455
Cygnus A radio source 289 (figure)
Dark matter 242 347 349—351
Deflection of light see also “Schwarzschild geometry light
Deflection of light, and PPN parameters 223
Deflection of light, confusion with effect of solar corona 226 233
Deflection of light, effect on star field 224 (figure)
Deflection of light, experimental tests 223—227
Deflection of light, gravitational lensing 235
Deflection of light, measured in solar eclipses 223 225
Deflection of light, radio observations 224—227
Degenerate free fermions 516
Degenerate free fermions, density of states 518
Degenerate free fermions, equation of state 518—520
Degenerate free fermions, Fermi momentum 518
densities 471—480
Densities, fluxes through spacelike three-surfaces 473
Densities, of a specific quantity see “The quantity”
Densities, of scalars, as components of a four-vector 473
Densities, of vectors, as components of a tensor 474
Directional derivatives, correspondence with vectors 420
Directional derivatives, of functions 419
Distance ladder see “Universe distance
Distance modulus 356
Divergence (three-dimensional), and covariant derivative 437 (box)
Divergence (three-dimensional), formula for in flat three-space 437 (box)
Divergence theorem in four dimensions 487 (problem)
Doppler shift 92—93
Drag free satellites and freelv tailing frames 182 (box)
Dragging of inertial frames see “Inertial frames”
Dual vectors 419 421—423 see
Dual vectors, bases for 421
Dual vectors, components 421
Dual vectors, correspondence with vectors 422
Dual vectors, defined 421
Dual vectors, identified with vectors 423
Dummy indices see “Indices”
Dust 262 480
Dust, in FRW cosmological models 372
Dust, spherical gravitational collapse of 262
Earth, measuring the rotation rate 35 (box)
Eddington limit see “Accretion disks”
Eddington — Finkelstein coordinates see “Schwarzschild geometry”
Einstein angle see “Gravitational lensing”
Einstein equation 131 419 445 456—459 482—486
Einstein equation, as partial differential equations for metric 457
Einstein equation, compared with Newtonian field equation 452 (table)
Einstein equation, defined 483
Einstein equation, does not uniquely determine metric 457
Einstein equation, for FRW cosmologies 484
Einstein equation, for relativistic stars 537 (problem)
Einstein equation, linearized see “Linearized gravity”
Einstein equation, Newtonian limit 485—486
Einstein equation, number of independent component equations 457 484
Einstein equation, satisfies Bianchi identity 482
Einstein equation, schematic form 445 471
Einstein equation, vacuum 186 456—459 471 483
Einstein equation, vacuum, Newtonian limit 460
Einstein tensor see “Curv ature”
Einstein, A. and general relativity 4 107 131
Einstein, A. and special relativity 3 47 49
Einstein, A. on the origin of the equivalence principle 111
Electric charge see “Charge”
Elements see “Nucleo-vnthesis”
Embedding diagram 148—152
Endstates of stellar evolution see “Stellar evolution”
Energy density 348—349 400
Energy, conservation of in flat spacetime 478—479
Energy, density 474—477
Energy, density, as a component of stress-energy 474
Energy, density, geometrized units 479
Energy, density, in a Newtonian gravitational field 342 345
Energy, density, in the short wavelength approximation 343
Energy, density, measured by an observer 477
Energy, flux equals momentum density 475
Energy, local conservation of in curved spacetime 480—482
Energy, measured by an observer 98 154
Energy, no local density of in general relativity 342—343
Energy, of a particle 87
Energy, total defined in asymptotically flat spacetimes 342
Energy-momentum Four-vector 87 also four-momentum”
Energy-momentum tensor see “Stress-energy tensor”
Eoetvoes experiments 107
Eoetvoes, R. von 107
Equality of accelerations in a gravitational field see “Equality of gravitational and inertial mass”
Equality of gravitational and inertial mass 13 42 111
Equality of gravitational and inertial mass, connection with weightlessness 111
Equality of gravitational and inertial mass, tests 14(box) 107—109
Equation of geodesic deviation see “Geodesic dev mtion. equation of”
Equation of state 516 see ground radiation dust” “vacuum” etc.
Equation of state, general properties 535
Equation of state, microscopic stability 535
Equation of state, summarized by stiffness parameter 525
Equation or equations 173n
Equivalence principle 110—121 140
Equivalence principle, and clocks 113—119
Equivalence principle, and local inertial frames 140
Equivalence principle, applies to all laws of phystes 113
Equivalence principle, Einstein on 111
Equivalence principle, how small a laboratorv is needed 120
Equivalence principle, implies light attracted by gravity 113
Equivalence principle, origin 111
Equivalence principle, rate difference between signal emission and reception 115—119
Equivalence principle, rate explained by curved spacetime 126
Equivalence principle, rate explained by effect of gravity on clocks 125
Equivalence principle, rate in GPS 124
Equivalence principle, rate test 118 (box)
Equivalence principle, stated 113 119
Ergosphere see “Kerr geometry”
Ether 48
Event 53
Event horizon see “Black holes”
Exclusion principle 255 516—520
Exclusion principle, and the structure of atoms 516
Exclusion principle, stated 516
Extremum, of a function 43
Extremum, of an action functional 43
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



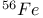 , most bound nucleus made in stars
, most bound nucleus made in stars