|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hartle J.B. Ч Gravity: An Introduction to Einstein's General Relativity |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Spacetime, separated into space and time by families of spacelike surtaces 160
Spacetime, slice of 53
Spacetime, spelled as one word 52n
Spatial vector see УThree-vectorsФ
Special relativistic mechanics 82Ч99
Special relativistic mechanics, dynamics 85Ч91
Special relativistic mechanics, four-acceleration 86
Special relativistic mechanics, four-force, defined 86
Special relativistic mechanics, four-force, in terms of three-force 88
Special relativistic mechanics, four-momentum 87
Special relativistic mechanics, four-momentum, of a zero rest mass particle 92
Special relativistic mechanics, four-velocity, as a unit timelike four-vector 85
Special relativistic mechanics, four-velocity, defined 84
Special relativistic mechanics, four-velocity, in terms of three-velocity 84
Special relativistic mechanics, four-velocity, normalization 85
Special relativistic mechanics, four-velocity, unit tangent vector to world line 84
Special relativistic mechanics, kinematics 82Ч85
Special relativistic mechanics, Newton's first law 52 85
Special relativistic mechanics, Newton's second law 85Ч86
Special relativistic mechanics, Newton's third law 88
Special relativistic mechanics, Newtonian approximation 87 88
Special relativistic mechanics, principle of extremal proper time 89
Special relativistic mechanics, variational principle for free particle motion 89Ч91
Special relativistic mechanics, world lines 82
Special relativity see also УSimultaneityФ УLorentz УSpecial УTime УFlat etc.
Special relativity, Einstein's motivating assumptions 49
Special relativity, not restricted to constant velocity 62n
Sphere (two-dimensional) 18Ч20 23Ч25
Sphere (two-dimensional), approximate geometry of Earth 25 (box)
Sphere (two-dimensional), line element 23
Spherically symmetric geometries, line element 458
Spherically symmetric geometries, Schwarzschild the unique vacuum solution 468 (problem)
Spin four-vector see УGyroscopesФ
Stability in Newtonian mechanics see УNewtonian mechanicsФ
Standard candles 354 402
Standard rulers 414 (problem)
Stars, relativistic see УRelativistic starsФ
Static, weak field metric 126 453 485
Static, weak field metric, derived 469 (problem)
Static, weak field metric, satisfies Einstein equation 460
Stellar evolution 255Ч256
Stellar evolution, and the main sequence 357 (figure)
Stellar evolution, endstates 244 255Ч256 282 515 533
Stellar evolution, hydrogen burning 255
Stellar evolution, life history of a star 255
Stellar evolution, thermonuclear burning 515
Stellar evolution, thermonuclear burning, and gravitational collapse 255
strain 336
Stress 476
Stress, gives force on enclosed volume 478
Stress, pressure as an example 476
Stress, stress-tensor defined 476
Stress, stress-tensor for a fluid 476
Stress-energy 474Ч482
Stress-energy tensor see УStress-energyФ
Stress-energy, and conservation of energy 478
Stress-energy, and equations of motion 478
Stress-energy, components 474Ч477
Stress-energy, components summarized 477
Stress-energy, conservation of in flat spacetime 478Ч479
Stress-energy, defined 474
Stress-energy, local conservation of in curved spacetime 480Ч482
Stress-energy, local conservation of in FRW cosmological models 481
Stress-energy, of a gas of particles 475
Stress-energy, of a perfect fluid 480
Stress-energy, of electromagnetism 488 (problem)
Stress-energy, of vacuum see УVacuumФ
Stress-energy, perfect fluid see УPerfect fluidФ
Stress-energy, relation to stress-tensor 476
Stress-energy, symmetric tensor 475 477 487
Stress-tensor see УStressФ
String, vibrating see УNewtonian mechanics stabilityФ
Summation convention 79 138Ч140
Summation convention, rules with upper and lower indices 424
Summation indices see УIndicesФ
Sun, as a gravitational lens 253 (problem)
Sun, oblateness of 233 (problem)
Sun, rotational period 296
Superluminal motion 61 (box)
Superluminal motion, in 3C345 61 (box) 74
Supernova 1994D 359 (figure)
Supernovae 282
Supernovae Type la 358
Surface brightness 240 also
Symmetries, and conservation 176
Symmetries, characterized by Killing vectors 176
Symmetries, of spacetime 176
Table comparing flat, Newtonian, and general spacetimes 170 (table)
Tachyons 59 102
Taylor, J., and discovery of the binary pulsar PSRB1913+16 250
Tensors 427Ч430
Tensors, components of 427
Tensors, contraction operation 428
Tensors, defined 427
Tensors, derivative 436
Tensors, metric 427
Tensors, rank 427
Tensors, transforming between coordinate and orthonormal bases 429
Tensors, transforming between coordinate bases 429^430
Test masses, test bodies see УTest particlesФ
Test particles, defined 169
Test particles, explore curved spacetimes 169
Tests of general relativity 6 see УDeflection УPrecession УTime УBinary УGyroscopesФ
Thermonuclear burning 255
Thermonuclear fusion see also УThermonuclear burningФ
Thermonuclear fusion, energy released in 290 (box)
Thermonuclear fusion, vs. gravitational binding 290 (box)
Thermonuclear reactions in stars 515
Thome, K., 151 (box)
Three-momentum 87
Three-surfaces 158Ч163
Three-surfaces, constant time 159
Three-surfaces, families of 160
Three-surfaces, intrinsic geometry 159
Three-surfaces, Lorentz hyperboloid 160
Three-surfaces, normal direction to 159
Three-surfaces, normal vector 159
Three-surfaces, normal vector, and gradient 426
Three-surfaces, null 162
Three-surfaces, null, "one-way" property 163
Three-surfaces, null, defined 162
Three-surfaces, null, generated by light rays 162
Three-surfaces, spacelike 160
Three-surfaces, spacelike and general notion of "space" 160
Three-surfaces, tangent directions to 159
Three-vectors 79
Three-velocity 84
Tides, and tidal gravitational forces 448 (box)
Tides, lag of 448 (box)
Tides, shape of 466 (problem)
Tides, why two a day 448 (box)
Time delay of light 229Ч230 also УLight
Time delay of light, and PPN parameters 223
Time delay of light, effect of solar corona 230
Time delay of light, experimental tests 229Ч230
Time delay of light, measured on Viking mission to Mars 229
Time dilation 60Ч65
Time dilation, experimental test 64 (box)
Time dilation, in GPS 124
Time machines 151 (box) 192
Timelike, and velocity less than c 59
Timelike, distances 142
| Timelike, distances, measured by clocks 60
Timelike, four-vectors 78
Timelike, separation 58
Timelike, world lines 59 96 142
Timelike, world lines, inside light cone 59
topology 152
Torsion pendulum 107 108
Torsion pendulum, used to test equality of gravitational and inertial mass 108
Transverse traceless (TT) gauge see УLinearized gravityФ
Trapped surfaces, and singularity theorems 266 (box)
Trapped surfaces, defined 266 (box)
Twin paradox 63Ч65
Twin paradox, and inertial frames 65
Twin paradox, test with atomic clocks 130 (box)
Unipolar generator 326 (box)
Units, c converts between length and time 72
Units, c= 1 (ML) 71Ч73
Units, conversion between see УAppendix BФ
Units, definition of the meter and second 72n
Units, geometrized, c = G = 1 (L) 188
Units, putting back the c's 73
Universe 10
Universe, age 381 (figure)
Universe, baryons 400 401
Universe, big bang 361
Universe, big bang, as a singularity 381 (box)
Universe, big bang, what came before? 381 (box)
Universe, big crunch 390
Universe, composition 347Ч351
Universe, cosmological parameters 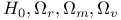 best buy values 402 best buy values 402
Universe, cosmological parameters 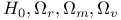 from CMB anisotropics 405 410 from CMB anisotropics 405 410
Universe, cosmological parameters 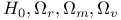 from SNIa redshift-magnitude relation 405 406 from SNIa redshift-magnitude relation 405 406
Universe, dark matter 349Ч351
Universe, distance scale 353 (box) 354Ч359
Universe, distance scale, Cepheid variable stars 356
Universe, distance scale, main sequence fitting 356
Universe, distance scale, triangulation 354 355
Universe, distance scale, Type la Supernovae 358
Universe, energy density in galaxies 348
Universe, energy density of CMB 348
Universe, expansion 347 351Ч364
Universe, expansion of see УFRW cosmological modelsФ УHubble's
Universe, expansion, Hubble's law 352Ч359
Universe, expansion, no center to 353 (figure)
Universe, expansion, what's expanding? into what? from where? 367
Universe, explaining the 410Ч413
Universe, homogeneity 347 363Ч364
Universe, inflation, and homogeneity and isotropy 413
Universe, inflation, and horizon size 412
Universe, inflation, and spatial flatness 413
Universe, inflation, defined 412
Universe, inflation, mechanism for 412 (box)
Universe, isotropy 347 361Ч363 see
Universe, isotropy, galaxies 363 (figure)
Universe, isotropy, radiation 361
Universe, mapping its contents 360Ч364
Universe, missing mass 351 Set also Dark matter
Universe, quantum initial condition 12
Universe, thermal history 375 (box)
Universe, thermal history, baryosynthesis 375 (box)
Universe, thermal history, first few minutes 380
Universe, thermal history, freeze out 375 (box)
Universe, thermal history, initial thermal equilibrium 375 (box)
Universe, thermal history, nucleosynthesis 375 (box) 380 400 400Ч401
Universe, thermal history, recombination 375 (box) 405
Universe, wave function of 410
Universe, which one is ours? 400Ч410
Vacuum Einstein equation see УEinstein equationФ
Vacuum, energy density 347 351
Vacuum, stress-energy 480 483
Vacuum, stress-energy, and cosmological constant 480
Variational principle for free particle motion 89
Variational Principle for Newtonian mechanics 43
Vector field see УVectorsФ
Vectors 152Ч158 419Ч441 see УFour-vectorsФ
Vectors, as directional Jematrves 419Ч421
Vectors, as rank 1 tensors 427
Vectors, constant 439
Vectors, contravariant components 423
Vectors, coordinate basis for 155
Vectors, correspondence with dual vectors 422
Vectors, covariant components 423
vectors, defined 152
Vectors, defined as directional dematives 420
Vectors, derivative of 430Ч440 see
Vectors, derivative of as a rank 2 tensor 434 436
Vectors, derivative of defined 431
Vectors, derivative of formula for 434
Vectors, downstairs somponents 423
Vectors, Killing see УKilling vectorsФ
Vectors, orthonomial basis for 153Ч158
Vectors, para. e. propagation along a curse 438
Vectors, parallel transport of 430Ч440
Vectors, proiecting out components 424
Vectors, relations between different kinds of bases and components 425 (table)
Vectors, transforming between coordinate and orthonormal bases 156 424
Vectors, transforming between coordinate bases 420
Vectors, upstairs components 423
Vectors, vector Fields 152
Velocities, addition of see УAddition of velocitiesФ
Velocity of light, as a denned quantity 72
Very-long-baseline radio interferometry (VLBI) 226
Vibrating string 530
Viking radar ranging time delay experiment 213 (figure)
VLBI see УVery-long-bavehne radio interferometryФ
Volume 146Ч148
Warpdrive geometry 144Ч145
Warpdrive geometry, light cones 145 (figure)
Warpdrive geometry, negative energy required 145 489
Wave equation 463Ч464 493Ч496
Wave equation, long wavelength approximation 495
Wave equation, outgoing wave boundary conditions 494
Wave equation, retarded solution 494
Wave equation, solution of 463Ч464 493Ч496
Wave operator see УWave equationФ
Wave operator in flat space  460 492 460 492
Weak energy condition 488 (problem)
Weak gravitational waves see УGravitational wavesФ
White dwarf stars see УWhite dwarfsФ
White dwarfs 7 255 515
White dwarfs, endstates of stellar evolution 515 533
White dwarfs, equation of state 524
White dwarfs, internal structure 524 (figure)
White dwarfs, mass vs. radius 525 (figure)
White dwarfs, maximum mass 256 358 524 525
White dwarfs, stability 533
World lines 53
World lines, of light rays (null curves) 142
World lines, of light rays parametrized by affine parameters 92
World lines, of particles (timelike curves) 142
World lines, of particles (timelike curves), parametrized by proper time 82
World lines, parametrized description 82
World lines, proper time along 82
Wormhole geometry 148Ч152
Wormhole geometry, Christoffel symbols 174
Wormhole geometry, embedding diagram 151 (figure)
Wormhole geometry, negative energy required 151 (box) 490
Wormholes 151 (box)
Wormholes, Schwarzschild geometry as a 273 (box)
X-ray sources 244Ч250
X-ray sources, binaries 244 282Ч284
X-ray sources, luminosity 245 (box)
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



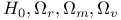 best buy values
best buy values 