|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hartle J.B. — Gravity: An Introduction to Einstein's General Relativity |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
Gravitational waves, no monopole or dipole 502 511
Gravitational waves, plane 332
Gravitational waves, polarization 332 336—338
Gravitational waves, polarization + and x polarizations 338 465
Gravitational waves, polarization circular 345 (problem)
Gravitational waves, production of 498—500
Gravitational waves, quadrupole formula for energy loss 506—508
Gravitational waves, quadrupole formula, limitations of 510
Gravitational waves, solutions to the linearized Einstein equation 464—466
Gravitational waves, sources 331 491 see “Merging etc.
Gravitational waves, sources, strong 491 510—511
Gravitational waves, speed 332
Gravitational waves, strain produced by 336
Gravitational waves, transverse 332 336
Gravitomagnetic effects 296 303
Gravitons 91
Gravity is geometry 4 13—15 125—131
Gravity Probe B. see “GP-B experiment”
Ground state matter 524—528
Ground state matter, equation of state 526 (box) 527
Ground state matter, mass vs. radius for 528 (figure)
Ground state matter, neutron drip 526 (box)
Ground state matter, neutron matter 526 (box)
Gyro see “Gyroscopes”
Gyroscopes 35 (box) 297—308
Gyroscopes, and the dragging of inertial frames see “Lense — Thirring precession”
Gyroscopes, equation of motion for spin formulated With covariant derivative 438
Gyroscopes, equation of motion for spin in a local menial frame 298
Gyroscopes, equation of motion for spin in curved spacetime 298
Gyroscopes, geodetic precession 298—302
Gyroscopes, geodetic precession, measured by GP-B 305 (box)
Gyroscopes, in curved spacetime 297—298
Gyroscopes, in the spacetime of slowly-rotating body 303—307
Gyroscopes, Lense — Thirring precession 306—308
Gyroscopes, Lense — Thirring precession, measured by GP-B 305 (box)
Gyroscopes, spin four-vector 297
Gyroscopes, thought experiment for measuring dragging of inertial frames 303—307
GZK cutoff for cosmic rays 95 (box)
GZK effect 94 (box)
GZK effect, limits rotation of the universe 37 (box)
GZK effect, spectrum 350 (figure)
GZK effect, temperature 350 (figure) 361
Hawking radiation see “Black holes”
Hawking, S. 289
Hertzsprung — Russell diagram 357 (figure)
Hipparcos satellite 354 357
Homogeneous, isotropic cosmological models see “FRW cosmological models”
Horizon, cosmological see “FRW cosmological models”
Horizon, event horizon see “Black holes”
Horizon, of a black hole see “Black holes”
Hubble constant, defined 352
Hubble constant, relation to the scale factor 371
Hubble constant, value 352 360
Hubble Deep Field 349 (figure)
Hubble diagram 360 (figure)
Hubble distance  382 382
Hubble parameter h 372
Hubble Space Telescope 96
Hubble time  361 371 361 371
Hubble's Law 352—359 360
Hubble's law, and homogeneity 353
Hubble's law, for FRW models 371
Hubble's law, stated 352
Hulse — Taylor binary pulsar see “Binary pulsar PSRB1913+16”
Hulse, R., and discovery of the binary pulsar PSRB1913+16 250
Hydrostatic equilibrium see “Relativistic stars equations
Hyperbolic angles 58
Hyperbolic plane 184 (problem)
Hypersurface see “Three-surfaces”
Indices, balancing 139
Indices, contravariant 423
Indices, covariant 423
Indices, downstairs see “Covariant”
Indices, dummy see “Summation”
Indices, free 80 139
Indices, names for (upper and lower, upstairs and downstairs, contravariant and covariant) 423n
Indices, raising and lowering in coordinate bases 422 423
Indices, raising and lowering in orthonormal bases 423
Indices, raising and lowering on tensors 427
Indices, raising and lowering on the metric tensor 427
Indices, summation 79 139
Indices, upstairs see “Contravariant”
Inertial frames see also “Local inertial frames”
Inertial frames, and free particle motion 32
Inertial frames, and twin paradox 65
Inertial frames, connected by Lorentz transformations 65
Inertial frames, connection between 34—36 49
Inertial frames, construction of 32 52
Inertial frames, defined 32
Inertial frames, defined by free particles and gyroscopes 32
Inertial frames, defined by Newton's first law 34
Inertial frames, in Newtonian mechanics 31—36
Inertial frames, not all frames are inertial 34
Inertial frames, rotational dragging 296—297
Inertial frames, rotational dragging, measured by GP-B 305 (box)
Inertial mass 41—42 107—109
Inertial mass, defined 41
Inertial mass, equality with gravitational mass 42
Infinity, different kinds of: future and past null  , future and past timelike , future and past timelike  , spacelike , spacelike  137 (box) 274 137 (box) 274
Inflation see “Universe” “FRW
Interference pattern 340 (figure) 345
Inverse metric see “Metric”
Inverse square law 354
Inverse square law, in cosmology 402
Iron peak nuclei, ashes of thermonuclear burning 255
ISCO, innermost stable circular orbit see “Schwarzschild geometry” “Kerr
Kepler's law see “Newtonian gravity”
Kerr black holes 296 310—328 see
Kerr black holes, a, maximum realistic salue 313
Kerr black holes, accretion disk around 313
Kerr black holes, and active galactic nuclei 326—327(box)
Kerr black holes, angular velocity 314 315
Kerr black holes, Blandford — Znajek mechanism 326—327 (box)
Kerr black holes, extreme 313
Kerr black holes, Hawking temperature 330 (problem)
Kerr black holes, horizon 313—316
Kerr black holes, rotational energy 325 326—327
Kerr geometry 310—328 also “Black
Kerr geometry,  not singular 313 not singular 313
Kerr geometry, angular momentum 311
Kerr geometry, angular momentum, defined by distant gyro 312
Kerr geometry, angular momentum, maximum realistic value 313
Kerr geometry, angular momentum, maximum value 313
Kerr geometry, as a black hole 313—316
Kerr geometry, asymptotically flat 312
Kerr geometry, Boyer — Lindquist coordinates, coordinate singularity 312
Kerr geometry, Boyer — Lindquist coordinates, metric 311
Kerr geometry, ergosphere 322—328
Kerr geometry, ergosphere, no stationary observers inside 322
Kerr geometry, extracting rotational energy 323—328
Kerr geometry, extracting rotational energy, Penrose process 323—328
Kerr geometry, extreme 313
Kerr geometry, horizon 313—316
Kerr geometry, horizon, angular velocih 314—315
Kerr geometry, horizon, area 316
Kerr geometry, horizon, as a null three-surface 314—316
Kerr geometry, horizon, embedding diagram 316 (figure)
Kerr geometry, horizon, geometry 315 316
Kerr geometry, horizon, location 314
Kerr geometry, horizon, null generators 314—315
Kerr geometry, horizon, one way property 316
Kerr geometry, irreducible mass 325
Kerr geometry, irreducible mass, and area increase 325
Kerr geometry, Kerr parameter a 311
Kerr geometry, Killing vectors 312
Kerr geometry, mass 311
Kerr geometry, mass measurable by distant test particle orbit 312
Kerr geometry, not a black hole for a > M 319
Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane 316—321
Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane, conserved angular momentum 317
| Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane, conserved energy 317
Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane, effective potentials 318
Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane, ISCO (innermost stable circular particle orbit) 320—321
Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane, ISCO binding energy 321 (figure)
Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane, ISCO radius 320 (figure)
Kerr geometry, orbits in the equatorial plane, radial plunge 318
Kerr geometry, Penrose process 323—328
Kerr geometry, rotational energy 325
Kerr geometry, Schwarzschild when not rotating 312
Kerr geometry, singularity 312
Kerr geometry, stationary observers 322—323
Kerr geometry, symmetries 312
Kerr geometry, unique black hole solution of the vacuum Einstein equation 310
Kerr geometry, what's rotating? 315
Kerr metric see “Kerr geometry”
Kerr, R. 310
Killing vectors, and conserved quantities 177
Killing vectors, characterize symmetries 176
Killing vectors, defined 176
Killing vectors, Killing's equation 443 (problem)
Killing vectors, of flat space 177
Killing. W 176
Kronecker S 422
Kruskal coordinates, metric, diagram, extension etc. see “Schwarzchild geometry”
Lagrange's equations 43 44 90
Lagrangian 43
Lagrangian, for free particle motion 90
Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) 242
LBI see “Long base-line radio interferometry”
Lem, S. 74 (problem)
Length 146—148
Lens equation, see “Gravitational lensing”
Lense — Thirnng precession see “Gyroscopes”
Lensing see “Gravitational lensing”
LiF see “Local inertial frames”
Life history of a star see “Stellar evolution”
Light cones 58—60 142—145
Light cones, and simultaneity 59
Light cones, as null surfaces 162
Light cones, define "before" and "after" 59
Light cones, defined 58
Light cones, dehne causal relationships 59
Light cones, future 59
Light cones, inside 59
Light cones, null cones as an alternative name 58n
Light cones, outside 59
Light cones, past 58 59
Light rays 91—94 also
Light rays, affine parameters for 91 179
Light rays, null world lines of 59 91—92
Light rays, tangent vectors to 91
Lightlike see “Null”
LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational (Wave) Observatory) 341—342
Line element see also “Specific geometries for specific forms”
Line element, and metric 138
Line element, defined 23
Linearized Einstein equation see “Linearized gravity”
Linearized gravity 459—466 491—508
Linearized gravity, analogies with electromagnetism 462 (table)
Linearized gravity, gauge conditions 462
Linearized gravity, gauge transformations 461—163
Linearized gravity, gauge transformations, compared with gauge transformations in electromagnetism 462 (table)
Linearized gravity, general solution 496—198
Linearized gravity, general solution, satisfies Lorentz gauge 496
Linearized gravity, linearized Einstein equation 459—466 491—493
Linearized gravity, linearized Einstein equation, in Lorentz gauge 463 492
Linearized gravity, linearized Einstein equation, plane wave solutions 464—166
Linearized gravity, linearized Einstein equation, vacuum 463 492
Linearized gravity, linearized Ricci cunature 492
Linearized gravity, Lorentz gauge 463 492
Linearized gravity, metric perturbations 459 492
Linearized gravity, metric perturbations, raising and lowering indices 460
Linearized gravity, slow rotation, solution tor 497—498
Linearized gravity, transverse-traceless (TT) gauge 465
Linearized gravity, transverse-traceless (TT) gauge, transforming to 466
Linearized gravity, weak sources, low velouties assumed 492
LISA gravitational wave detector 10 (figure)
LMC see “Large Magellanic cloud”
Local inertial frames 140—142 179—183
Local inertial frames, construction of 180
Local inertial frames, Riemann normal coordinates an example 180
Local inertial frames, transforming to 165 (problem)
Long base-line radio interferometry (LBI) 225
Lorentz boosts 65—68
Lorentz boosts, and simultaneity 68
Lorentz boosts, explicit form 67
Lorentz boosts, special case of Lorentz transformations 67n
Lorentz contraction 70
Lorentz frames see “Inertial frames”
Lorentz gauge see “Linearized gravity”
Lorentz hyperboloid 160
Lorentz transformations see also “Lorentz boosts”
Lorentz transformations, connect inertial frames 65
Lorentz transformations, defined 66
Lorentz transformations, preserve the line element of flat spacetime 66
Lunar laser ranging 14 (box)
Lunenberg lens 185 (problem)
Mach's principle 37 (box)
Mach, E. 37 (box)
MACHOs (Massive compact halo objects) 242—243
Macrolensing see “Gravitational lensing”
Magnitude, absolute 356
Magnitude, apparent 356
Magnitude, distance modulus 356
Magnitude-redshift relation see “FRW redshift-magnitude relation”
Main sequence 356 357
map projections 25—26 (box)
Map projections, equal area 29 (problem)
Map projections, equirectangular 25 (box)
Map projections, Mercator 25 (box)
Mass density 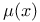 in Newtonian gravity 39 in Newtonian gravity 39
Mass function see “Binary stars”
Mass measured by gravitational lensing 239
Mass measured/defined by distant orbit 187
Mass moment tensors, moment of inertia tensor 499n
Mass moment tensors, quadrupole 507
Mass moment tensors, second 499
Massive Compact Halo Objects see “MACHOs”
Matter in its ground state see “Ground state matter”
Maximum mass of white dwarfs and neutron stars 256 283 358
Maximum mass of white dwarfs and neutron stars, bound on 535—537 539
Maximum mass of white dwarfs and neutron stars, Chandrasekhar mass 524 525
Maxwell's equations 47 419 445 483
Maxwell's equations, and inertial frames 48
Maxwell's equations, imply speed of light c 47
MCG-6-30-15 249
Mdssbauer effect 118 (box)
Mechanics, Newtonian see “Newtonian mechanics”
Messier catalog 285n
Metric perturbations see “Linearized gravity”
Metric, and line element 138
Metric, as a tensor 427
Metric, coordinate transformation of 138 164
Metric, covariant derivative vanishes 438
Metric, defined 138
Metric, in a local inertial frame 140
Metric, inverse 422
Metric, number of independent functions 138
Michelson interferometer 339—341
Michelson — Morley experiment 47—49 see
Microlensing see “Gravitational lensing”
Milky Way (our galaxy) 287 (figure)
Minkowski space see “Flat spacetime”
Minkowski, H. 56
Momentum, as a component of stress-energy 474
Momentum, conservation of in flat spacetime 478^79
Momentum, density 474—477
Momentum, density equals energy flux 475
Momentum, local conservation of in curved spacetime 480—482
Muon lifetime and time dilation 64 (box)
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå





 , future and past timelike
, future and past timelike  , spacelike
, spacelike 
 not singular
not singular 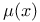 in Newtonian gravity
in Newtonian gravity