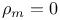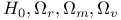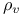|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hartle J.B. Ч Gravity: An Introduction to Einstein's General Relativity |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Fermat's principle of least time 185 (problem)
Fermi normal coordinates see УFreeh-tailing framesФ
Fermi pressure 255 151 516Ч520
fermions 516 see
Flat Earth theory 125Ч126
Flat space, in Newtonian mechanics 31
Flat spacetime 52Ч60
Flat spacetime, geometry 53
Flat spacetime, light cones 58Ч60
Flat spacetime, line element 53 56 81
Flat spacetime, line element, conventions 56n
Flat spacetime, line element, invariance under Lorentz transformations 66
Flat spacetime, metric 81
Flat spacetime, straight timelike lines are longest distances 65
Fluid see УPerfect fluidФ
Force density 478
Foucault pendulum 35 (box) 37
Four-acceleration see УSpecial relativistic mechanicsФ
Four-momentum see УSpecial relativisitic mechanicsФ
Four-vectors 77Ч85 see
Four-vectors, addition 77
Four-vectors, basis vectors for 78
Four-vectors, defined 77
Four-vectors, displacement 79
Four-vectors, handwritten notation for 79n
Four-vectors, invariance 77
Four-vectors, length 78
Four-vectors, lightlike see УNullФ
Four-vectors, Lorentz transformation 80
Four-vectors, multiplication by numbers 77
Four-vectors, null 78
Four-vectors, scalar product 80Ч82
Four-vectors, scalar product, defined 81
Four-vectors, scalar product, explicit forms 81
Four-vectors, spacelike 78
Four-vectors, timelike 78
Four-vectors, transformation between inertial frames 80
Four-velocity see УSpecial relativistic mechanicsФ
Four-volume 146Ч148
frames see also УInertial framesФ УLocal УFreely
Frames, defined 31
frames, rotating 35 (box) 183
Frames, usage discussed 31n
Free indices see УIndicesФ
Free particle, in general relativity 169
Free particle, in Newtonian mechanics 31
Free particle, notions in general relatyvity and Newtonian mechanics compared 169n
Freely falling frames 181Ч183 440Ч441
Freely falling frames, and drag free satellites 182 (box)
Freely falling frames, construction 182 308
Freely falling frames, in the Schwarzschild geometry 441
Freely falling frames, other terms for 182n
Freely falling frames, propagation of basis vectors 440
Friedman equation see УFRW cosmological modelsФ
Friedman Ч Robertson Ч Walker cosmological models see УFRW cosmological modelsФ
FRW cosmological models 366Ч413 see
FRW cosmological models,  defined 389 defined 389
FRW cosmological models, 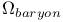 400 401 400 401
FRW cosmological models, 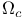 391 391
FRW cosmological models, 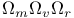 377 377
FRW cosmological models, age 381 392
FRW cosmological models, big bang 379 380
FRW cosmological models, big bang, as a singularity 380
FRW cosmological models, closed models 385
FRW cosmological models, closed models, finite volume but no boundary 385
FRW cosmological models, closed models, line element 387
FRW cosmological models, closed models, qualitative evolution 393
FRW cosmological models, comoving coordinates 367
FRW cosmological models, cosmological fluid 367 372
FRW cosmological models, critical density 377 389
FRW cosmological models, defining approximations 366 372
FRW cosmological models, dimensionless variables for 391
FRW cosmological models, effective potential 378 (figure) 391 394
FRW cosmological models, Einstein equation for 484
FRW cosmological models, Einstein static universe 398 (problem)
FRW cosmological models, evolution of curved models 387Ч395
FRW cosmological models, evolution of curved models, big crunch 390
FRW cosmological models, evolution of curved models, explicit solution for matter dominated models 389
FRW cosmological models, evolution of curved models, Mathematica program for computing see УWebsiteФ
FRW cosmological models, evolution of curved models, qualitative behavior 393Ч395
FRW cosmological models, evolution of flat models 376Ч380
FRW cosmological models, evolution of flat models, explicit solutions for matter, radiation, and vacuum dominated cases 378
FRW cosmological models, evolution of flat models, normalization of scale factor 377
FRW cosmological models, evolution of flat models, three stages 378 (figure) 379
FRW cosmological models, expansion 367
FRW cosmological models, expansion, what's expanding? into what? from where? 367
FRW cosmological models, first few minutes 380
FRW cosmological models, flat models 366Ч368
FRW cosmological models, flat models, evolution 378
FRW cosmological models, flat models, line element 366
FRW cosmological models, Friedman equation 387 388 484
FRW cosmological models, Friedman equation, Mathematica program for solving see УWebsiteФ
FRW cosmological models, Friedman equation, motivated by Newtonian physics for pressureless matter 388
FRW cosmological models, Friedman equation, rescaled form 391
FRW cosmological models, geometries of space 384Ч386
FRW cosmological models, geometries of space, closed 385
FRW cosmological models, geometries of space, curvature of 386
FRW cosmological models, geometries of space, embedding diagrams 386 (figure)
FRW cosmological models, geometries of space, flat models 367
FRW cosmological models, geometries of space, open 385
FRW cosmological models, homogeneous, isotropic spacetimes 366Ч368 384Ч387
FRW cosmological models, homogeneous, Robertson Ч Walker metrics 367 368 384 387
FRW cosmological models, horizon 382 383 407
FRW cosmological models, horizon, growth during inflation 412
FRW cosmological models, horizon, matter and radiation dominated flat models 383
FRW cosmological models, horizon, present size 383
FRW cosmological models, horizon, size of region in causal contact 407
FRW cosmological models, Hubble constant 371
FRW cosmological models, Hubble'slaw 371
FRW cosmological models, inflation 412
FRW cosmological models, k parameter 387
FRW cosmological models, last-scattering surface 407 (figure)
FRW cosmological models, light cones 383 (figure)
FRW cosmological models, line elements summarized 387
FRW cosmological models, local conservation of stress-energy 481
FRW cosmological models, luminosity distance 403n
FRW cosmological models, Mathematica program for evolution see УWebsiteФ
FRW cosmological models, matter 373
FRW cosmological models, matter dominated models 389
FRW cosmological models, matter dominated models, explicit solutions 390
FRW cosmological models, matter, energy density 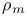 373 373
FRW cosmological models, matter, pressure 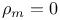 373 373
FRW cosmological models, matter, variation with scale factor 373
FRW cosmological models, metrics summarized 387
FRW cosmological models, open models 386
FRW cosmological models, open models, line element 387
FRW cosmological models, open models, qualitative evolution 393
FRW cosmological models, parameters 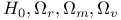 392 400 see cosmological 392 400 see cosmological
FRW cosmological models, parameters  395 (figure) 395 (figure)
FRW cosmological models, particle horizons see УHorizonФ
FRW cosmological models, radiation 373Ч374
FRW cosmological models, radiation, energy density  374 374
FRW cosmological models, radiation, energy density today 400
FRW cosmological models, radiation, pressure  373 373
FRW cosmological models, radiation, temperature T 373
FRW cosmological models, radiation, variation with scale factor 374
FRW cosmological models, redshift 368Ч372
FRW cosmological models, redshift-(angular size) relation 407Ч408 414
FRW cosmological models, redshift-magnitude relation 402Ч405 414
FRW cosmological models, redshift-number relation 414 (problem)
FRW cosmological models, scale factor 366 372
FRW cosmological models, singularity theorem 399 (problem)
FRW cosmological models, thermodynamics, first law of 372Ч373
FRW cosmological models, vacuum, cosmological constant 376
FRW cosmological models, vacuum, energy density 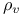 374 374
FRW cosmological models, vacuum, pressure  376 376
Functional 43
Future light cones see УLight conesФ
Galaxies, as components of the universe 349 (figure)
Galaxies, smoothed out energy density 348
| Galaxies, typical properties 347
Galilean transformation 36 47 49
Gamma-ray bursts 510
Gauge transformations in electromagnetism 462 (table)
Gauge transformations in linearized gravity see УLinearized gravityФ
Gauss, C.F., test of plane geometry 15
General relativity 3Ч537
General relativity, compared to Newtonian gravity 452 (table) 486
General relativity, compared to Newtonian gravity formulated geometrically 129 (table)
General relativity, gravitomagnetic effects 303
General relativity, tests of see УGravitational redshiftФ УDeflection УPrecession УTime УBinary УGyroscopesФ
Geodesic deviation, equation of 450Ч454
Geodesic deviation, equation of, compared with Newtonian deviation equation 452 (table)
Geodesic deviation, equation of, in freely falling frame 452
Geodesic deviation, equation of, Newtonian limit 453Ч154
Geodesic equation 169Ч174
Geodesic equation, compared with Newton's second law 452 (table)
Geodesic equation, conservation laws 176Ч178
Geodesic equation, conserved normalization of u 176
Geodesic equation, equations vs. equation 173n
Geodesic equation, expressed with covanant demames 434
Geodesic equation, first integrals 176 178 see
Geodesic equation, for plane in polar coordinates 171
Geodesic equation, for wormhole geometry 172
Geodesic equation, general form 173
Geodesic equation, in terms of four-velocity 173
Geodesic equation, Lagrangian for 172
Geodesic equation, procedure for finding 171 Mathematica see
Geodesic equation, table comparing in flat, Newtonian, and general spacetimes 170 (table)
Geodesic equation, tor null geodesic 179
Geodesies see also УGeodesic equationФ
Geodesies, as paths of extremal proper time 170
Geodesies, defined 170
Geodesies, null 178Ч179
Geodesies, null, geodesic equation 179
Geodetic precession see УGyroscopesФ
Geometized units see УUnitsФ
Geometry, defined by distance between nearby points 21
Geometry, differential 21
Geometry, intrinsic description 20
Geometry, line element specifies 23
Geometry, measurement of 15Ч17
Geometry, same geometry described in different coordinates 135
Geometry, ways of describing 20Ч21
Global Positioning System (GPS) 3 121Ч125
Global Positioning System (GPS), rate difference between signal emission and reception 124
Global Positioning System (GPS), simultaneity in 69 125
Global Positioning System (GPS), time dilation in 124
Global Positioning System (GPS), toy model 69
GP-B experiment 182 (box) 305
GPS see УGlobal Positioning SystemУФ
Gradient (three-dimensional), and covariant Jemative 437 (box)
Gradient (three-dimensional), formula tor in flat three-space 437 (box)
Gradient, and normal vectors 426
Gradient, as a covariant derivative 435
Gradient, as a dual vector 421
Gradient, defined 421
Graviational collapse, general 8 275Ч276 310Ч311 see
Graviational collapse, general cosmic censorship ton eaure 275
Graviational collapse, general formation of a Mat k hole 275 281
Graviational collapse, general formation of a singularity 275
Graviational collapse, general singularity theorems 275
Graviational collapse, general, big crunch 390
Gravitational binding, energy released in 290 (box)
Gravitational binding, vs. thermonuclear fusion 290 (box)
Gravitational collapse, spherical 262Ч268
Gravitational collapse, spherical, area of horizon increases 268 278
Gravitational collapse, spherical, formation of a black hole 264 (figure) 265Ч268
Gravitational collapse, spherical, inside the horizon 262Ч265
Gravitational collapse, spherical, inside the horizon, no escape after horizon crowed 265
Gravitational collapse, spherical, inside the horizon, singularity hidden inside horizon 265
Gravitational collapse, spherical, inside the horizon, singularity inevitable after horizon crosed 265
Gravitational collapse, spherical, of dust 262
Gravitational collapse, spherical, outside the horizon 265Ч268
Gravitational collapse, spherical, outside the horizon, indistinguishable from Schwarz^hild geometry 267
Gravitational collapse, spherical, outside the horizon, lumminocity approaches zero 267
Gravitational collapse, spherical, outside the horizon, never crosses  265 265
Gravitational collapse, spherical, outside the horizon, redshift approaches intinity 265 266
Gravitational collapse, spherical, outside the horizon, time seaeditor approaching a black hove 267
Gravitational collapse, spherical, story observers 264Ч268 272 274
Gravitational constant G. 38
Gravitational held see УNewtonian gravityФ
Gravitational ineraction see also УRelitivitic gravityФ
Gravitational ineraction, governuniverse on largescales 4
Gravitational ineraction, long range 4 516
Gravitational ineraction, Newton's law 3
Gravitational ineraction, strength ot compared to ether forces 4
Gravitational ineraction, universal 4
Gravitational ineraction, unscreened 4
Gravitational ineraction, where important 4
Gravitational lensing 234Ч243
Gravitational lensing, achromatic 238
Gravitational lensing, by MACHOs 242Ч243
Gravitational lensing, by MACHOs, characteristic variation time 243
Gravitational lensing, Einstein angle 237
Gravitational lensing, Einstein ring 237
Gravitational lensing, idea 235 (figure)
Gravitational lensing, images, brightness 240Ч243
Gravitational lensing, images, number 238 253
Gravitational lensing, images, positions 238
Gravitational lensing, images, shapes 238 (figuie 1
Gravitational lensing, lens equation 236 (figure) 237
Gravitational lensing, macrolensing 237
Gravitational lensing, microlensing 237 243
Gravitational lensing, surface brightness 240
Gravitational lensing, thin lens approximation 236
Gravitational lensing, time difference between fluctuations in images 242
Gravitational lensing, used to measure mass 239
Gravitational lensing, uses 234
Gravitational mass 41Ч42 108Ч109
Gravitational mass, and weight 42
Gravitational mass, defined 41
Gravitational mass, equality with inertial mass 42
Gravitational physics 3Ч12
Gravitational physics, two frontiers 3
Gravitational potential see УNewtonian gravityФ
Gravitational radiation see УGravitational wavesФ
Gravitational redshift 119
Gravitational redshift, measured in spectra 219
Gravitational redshift, Schwarzschild geometry 189Ч191
Gravitational redshift, tests 118 (box) 219Ч221
Gravitational waves 9 331Ч344 459Ч466 491Ч511 also
Gravitational waves, analogies with electromagnetism 501 (table) 501Ч502 507
Gravitational waves, angular momentum loss 512 (problem)
Gravitational waves, astrophysical interest 331
Gravitational waves, detection 9 331 333Ч342 491
Gravitational waves, detection, interferometers 339Ч342
Gravitational waves, detection, LIGO 341
Gravitational waves, detection, Michelson interferometer 339 (figure)
Gravitational waves, detection, single test mass not enough 333
Gravitational waves, effect of detected in binary pulsar 508Ч509
Gravitational waves, energy density 342Ч344
Gravitational waves, energy flux 332 343
Gravitational waves, ertect on test masses 332Ч336 337
Gravitational waves, from binary stars 502Ч509 see also УBinary pulsarФ
Gravitational waves, from binary stars, amplitude far away 504
Gravitational waves, from binary stars, angular power distribution 505Ч506
Gravitational waves, from binary stars, decrease in period 508
Gravitational waves, from binary stars, estimates for i Boo 500
Gravitational waves, from binary stars, frequency twice orbital frequency 504
Gravitational waves, from binary stars, long wavelength approximation satisfied 503
Gravitational waves, from binary stars, polarization 505Ч5116
Gravitational waves, from merging black holes 510
Gravitational waves, large r approximation 498Ч502
Gravitational waves, linearized 331 333
Gravitational waves, linearized, amplitude 332
Gravitational waves, linearized, metric and metric perturbations 332 492
Gravitational waves, linearized, superposition of 333
Gravitational waves, long wavelength (slow motion) approximation 498Ч502
Gravitational waves, metric perturbations at large r 499
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 defined
defined