|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Csiszar I., Körner J. — Information Theory: Coding Theorems for Discrete Memoryless Systems |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
 -code 101 -code 101
 -distortion rate 124 (see also “Distortion measure” “Rate -distortion rate 124 (see also “Distortion measure” “Rate
 -distortion rate computing algorithm 144 -distortion rate computing algorithm 144
 -distortion rate, alternative definitions 124 128 158 -distortion rate, alternative definitions 124 128 158
 -distortion rate, zero error 133 152 -distortion rate, zero error 133 152
 -distortion rate, zero error, computation of 159 -distortion rate, zero error, computation of 159
a-capacity and m-capacity, difference, AVC 224
a-capacity and m-capacity, equality, AVC, stochastic encoder 217
a-capacity and m-capacity, equality, DMC 111
a-capacity region see “Capacity region”
a-capacity region and m-capacity region, difference, MAC 284
a-capacity region and m-capacity region, equality, broadcast channels 291
a-capacity region and m-capacity region, equality, stochastic encoders 284 291
a-capacity, AVC 205
a-capacity, AVC, coding theorem 214
a-capacity, AVC, positivity 224
ABC coding theorem 366 (see also “Asymmetric broadcast channel”)
ABC coding theorem with input constraint 392
ABC coding theorem, alternative form 378
ABC coding theorem, converse part 364
ABC coding theorem, direct part 359
Achievable ( -achievable) rate pair, MAC 271 -achievable) rate pair, MAC 271
Achievable ( -achievable) rate region see “Source network coding theorems” -achievable) rate region see “Source network coding theorems”
Achievable ( -achievable) rate region, channel network see “Capacity region” -achievable) rate region, channel network see “Capacity region”
Achievable ( -achievable) rate region, fork network see “Fork network achievable -achievable) rate region, fork network see “Fork network achievable
Achievable ( -achievable) rate region, optimal points of 242 -achievable) rate region, optimal points of 242
Achievable ( -achievable) rate region, source network 247 -achievable) rate region, source network 247
Achievable ( -achievable) rate region, source network, particular points 402 -achievable) rate region, source network, particular points 402
Achievable ( -achievable) rate region, source network, product space characterization 255 -achievable) rate region, source network, product space characterization 255
Achievable ( -achievable) rate triple, fork network 241 -achievable) rate triple, fork network 241
Achievable ( -achievable) rate vector, channel network 281 -achievable) rate vector, channel network 281
Achievable ( -achievable) rate vector, source network 247 249 -achievable) rate vector, source network 247 249
Achievable ( -achievable) rate, channel 101 -achievable) rate, channel 101
Achievable ( -achievable) rate, source, at distortion level -achievable) rate, source, at distortion level  123 123
Achievable ( -achievable) rate-distortion pair 124 -achievable) rate-distortion pair 124
Achievable entropy triples 304 (see also “Entropy characterization problem”)
Achievable exponent triples 304 (see also “Image size problem”)
Active feedback 202 224
Aczel, J. 26 27 417
Additive noise 114
Additivity of information measures 26 49 51
Addressing 279
Ahlswede, R. VIII 95 96 120 122 182 223 224 230 231 233 269 284 289 296 302 347—352 357 358 381 383 404 416—418
Algebraic codes see “Linear codes”
Alphabet, channel input, output 4 100 270
Alphabet, code 51
Alphabet, reproduction 123
Alphabet, source 15
Alphabetic code 77
Amount of information 6 17 20—22
Amount of information, unit of 7
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC) 204 ff
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), capacity, a- and m-capacity 205
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), capacity, positivity 222 224
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), capacity, random code 212 224
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), capacity, stochastic encoder 217
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), coding theorem, a-capacity 214
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), coding theorem, m-capacity, binary output 208
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), coding theorem, stochastic encoder 217
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), feedback 224 230
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), game-theoretic approach 219 226
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), source-channel transmission 225
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), states depending on inputs 221 232 233
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), states known at input or output 220 227—229
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), stochastic decoder 226
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), zero-error capacity of DMC and 223
Arbitrarily varying source (AVS) 153 159
Arbitrarily “star” varying channel (A*VC) 221 232
Arimoto, S. 149 184 192 418
Arutunjan see “Haroutunian”
Asymmetric broadcast channel (ABC) 359 ff
Asymmetric broadcast channel (ABC) with confidential messages 413
Asymmetric broadcast channel (ABC), a- and m-capacity regions equal 362
Asymmetric broadcast channel (ABC), coding theorem see “ABC coding theorem”
Asymptotics, refined, in the noisy channel coding theorem 119
Asymptotics, refined, of average distortion 159
Asymptotics, refined, of error probability, sources 46
Asymptotics, refined, of minimax redundancy 83
Asymptotics, refined, of size of 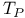 39 39
Asymptotics, refined, of size of high probability set 24
Attainable error exponent 170 173
Attainable error exponent with feedback 199—202
Attainable error exponent, universally see “Universally attainable error exponent”
Augustin, U. 185 296 418
Automata as noiseless channels 82
Average cost theorem 66
Average cost theorem, alternative proof of converse 74 76
Average fidelity criterion 123 129
Average length theorem 62 (see also “Average cost theorem”)
Average probability of error 99 173
Average probability of error at output c, channel network 281
Average probability of error, capacity for see “a-capacity”
Average probability of error, family of channels 173
Averaging distortion measure 124
Axiomatic approach 22 25—27
Bartfai, P. VIII
Beck, J. VIII
Berge, C. 119 418
Berger, T. 136 148 159 160 416 418
Berger’s lemma see “Type covering lemma”
Bergmans, P.P. 381 416 418
Berlekamp, E.R. 180 188 189 192 196 197 201 203 418 426
Better in the Shannon sense 116
Bierbaum, M. 287 418
Binary adder 398—400
Binary block code 15
Binary block code, expected common length 403
Binary channel 206
Binary channel, erasure 114
Binary channel, images for 348
Binary channel, noiseless 6
Binary channel, symmetric see “Binary symmetric channel”
Binary entropy function 11
Binary symmetric channel (BSC) 114
Binary symmetric channel (BSC), capacity 114
Binary symmetric channel (BSC), exponential error bounds 195
Binary symmetric channel (BSC), exponential error bounds, with feedback 199
Binary symmetric channel (BSC), images over 347
Binary symmetric channel (BSC), linear codes 114 198
Bit 7
Blackwell, D. 203 223 224 227 232 233 391 419
Blahut, R.E. 46 149 160 179 180 188 194 195 203 268 419
Block code 6 (see also “Linear code”)
Block code, channel networks 279
Block code, channels 100
Block code, channels, feedback 120
Block code, channels, multiple-access (MA) 271
Block code, channels, stochastic encoder, decoder 217 226
Block code, fork network 241
Block code, k-to-n 129
Block code, k-to-n, binary 15
Block code, k-to-n, source-channel networks 282
Block code, source networks 247
Block code, sources 15 123
Block code, sources, side information at the decoder 238
Blockwise coding 5
Bloh, E.L. 85 419
Blowing up lemma 92
Boee, J.M. 75 419
Boltzmann, L. 28 46 419
Branching property 26
Breiman, L. 203 223 224 227 232 233 419
Broadcast channel (BC) 359 (see also “ABC coding theorem”)
Broadcast channel (BC) with comparable components 381
Broadcast channel (BC) with confidential messages 413
Broadcast channel (BC) with degraded message sets see “Asymmetric broadcast channel (ABC)”
Broadcast channel (BC), a- and m-capacity regions are equal 291
Broadcast channel (BC), asymmetric two-output (ABC) see “Asymmetric broadcast channel (ABC)”
Broadcast channel (BC), bounds on capacity region 379 390
Broadcast channel (BC), degraded 379
| Broadcast channel (BC), deterministic 391
Broadcast channel (BC), deterministic, zero-error 392
Broadcast channel (BC), semi-deterministic 392
Broadcast channels (BC), product of degraded 384
Broadcast channels (BC), sum of degraded 387
Burnasev, M.V. 121 202 419
Capacity ( -capacity) 6 101 “Compound “Noiseless -capacity) 6 101 “Compound “Noiseless
Capacity ( -capacity) as information radius 142 147 -capacity) as information radius 142 147
Capacity ( -capacity) for a communication model 219 -capacity) for a communication model 219
Capacity ( -capacity) of a set 106 -capacity) of a set 106
Capacity ( -capacity) of a set, asymptotic independence of -capacity) of a set, asymptotic independence of  107 107
Capacity ( -capacity) region see “Capacity region ( -capacity) region see “Capacity region ( -capacity region)” -capacity region)”
Capacity ( -capacity) under input constraint 108 112 117 142 -capacity) under input constraint 108 112 117 142
Capacity ( -capacity) under input constraint, output constraint 117 -capacity) under input constraint, output constraint 117
Capacity ( -capacity) with feedback see “Feedback zero-error -capacity) with feedback see “Feedback zero-error
Capacity ( -capacity), a- and m- see “a-capacity and m-capacity” -capacity), a- and m- see “a-capacity and m-capacity”
Capacity ( -capacity), alternative definitions 111 -capacity), alternative definitions 111
Capacity ( -capacity), alternative formulas, DMC 104 142 147 -capacity), alternative formulas, DMC 104 142 147
Capacity ( -capacity), computation of see “Computation of” -capacity), computation of see “Computation of”
Capacity ( -capacity), explicit formulas 114 -capacity), explicit formulas 114
Capacity ( -capacity), generalized (for given order of magnitude of error probability) 178 183 -capacity), generalized (for given order of magnitude of error probability) 178 183
Capacity ( -capacity), independence of -capacity), independence of  see “Strong converse” see “Strong converse”
Capacity ( -capacity), input distribution achieving 147 -capacity), input distribution achieving 147
Capacity ( -capacity), per unit cost, DMC 120 -capacity), per unit cost, DMC 120
Capacity ( -capacity), secrecy 408 -capacity), secrecy 408
Capacity ( -capacity), zero-error see “Zero error capacity” -capacity), zero-error see “Zero error capacity”
Capacity computing algorithm 140
Capacity region ( -capacity region) 111 281 -capacity region) 111 281
Capacity region ( -capacity region), a- and m- see “a-capacity region and m-capacity region” -capacity region), a- and m- see “a-capacity region and m-capacity region”
Capacity region ( -capacity region), alternative definitions 283 301 -capacity region), alternative definitions 283 301
Capacity region ( -capacity region), characterization, computable see “Coding theorem for channel networks” “Broadcast “Multiple-access “Two-way -capacity region), characterization, computable see “Coding theorem for channel networks” “Broadcast “Multiple-access “Two-way
Capacity region ( -capacity region), characterization, product-space, general 301—302 -capacity region), characterization, product-space, general 301—302
Capacity region ( -capacity region), feedback may increase 298 -capacity region), feedback may increase 298
Capacity region ( -capacity region), relevance for source-channel transmission 282 284 286 292 -capacity region), relevance for source-channel transmission 282 284 286 292
Capacity region ( -capacity region), stochastic encoders 284 291 -capacity region), stochastic encoders 284 291
Capacity-constraint function 108 137
Capacity-constraint function, alternative formula 142
Capacity-constraint function, concavity 109
Capacity-constraint function, differentiability 148
Capacity-constraint function, distribution achieving 147
Caratheodory theorem see “Fenchel — Eggleston — Caratheodory theorem”
Caratheodory, C. 310
Carleial, A.B. 299 419
Cesari, Y. 74 419
Chain rules 50
Channel 2 4 “Arbitrarily “Compound “Channel
Channel as a matrix 99
Channel as a sequence of matrices 100
Channel network 279 ff
Channel network with one intermediate vertex see “Broadcast channel”
Channel network with one output vertex 293
Channel network, capacity region see “Capacity region”
Channel network, coding theorems see “Multiple-access channel” “Broadcast “Two-way
Channel network, normal see “Normal channel network”
Channel network, reduction of, problems 300—302
Channel, binary see “Binary channel”
Channel, coding theorem see “Coding theorem for channels”
Channel, equidistant 194
Channel, multiterminal see “Channel network”
Channel, noiseless see “Noiseless channel”
Channel, symmetric 114
Channels, comparison of 115 116 349
Channels, product of 115
Channels, sum of 115
Chaundy, T.W. 26 419
Chemoff, H. 128 419
Chromatic number of graphs and zero-error rate region 262
Code 3 4
Code alphabet 63
Code for channels with input set X and output set Y 99
Code for k-length messages 61
Code selector 219
Code stuffing lemma 334
Code tree 62 (see also “Tree representation”)
Code tree, entropy decomposition 77
Code with feedback 120
Code with stochastic encoder 217 284 291
Code, 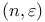 - 101 - 101
Code, alphabetic 77
Code, associated with a network 246
Code, block see “Block code”
Code, constant composition 117 161
Code, fixed-length-to-fixed-length 5
Code, fixed-to-variable length 61
Code, Gilbert — Moore 75
Code, Huffman 73
Code, infinite 80
Code, linear see “Linear code”
Code, list 196
Code, multiple-access (MA) 280
Code, prefix see “Prefix code”
Code, random 209
Code, separable see “Separable code”
Code, Shannon — Fano 85
Code, sliding block 79
Code, synchronizing 75
Code, Tunstall 78
Code, universally optimal see “Universally optimal codes”
Code, variable length see “Variable length codes”
Code-stuffed sets 330 345
Coder 246
Codeword 4 61 99
Codeword length and information of an event 75
Coding theorem 110 (see also “Exponential probability bounds”)
Coding theorem for channel networks see “Multiple-access channel” “Broadcast “Two-way
Coding theorem for channels see “Discrete memoryless channel” “Compound “Arbitrarily
Coding theorem for source networks see “Source network coding theorems”
Coding theorem for source-channel transmission see “Source-channel transmission theorem”
Coding theorem for sources see “Source coding theorems”
Coding theorem, converse part see “Converse result”
Coding theorem, direct part see “Direct result”
Coding theorem, noiseless see “Average length theorem” “Average
Coding theorem, noisy channel 104
Coding theorem, practical significance 105
Coding theorem, remainder terms in see “Asymptotics refined”
Combinatorial lemmas 29 ff 86
Combinatorial lemmas, packing 162
Combinatorial lemmas, type covering 150
Common information 402—405
Common length (of binary block codes) 403
Communication model (involving a channel with varying states) 219
Communication model (involving a channel with varying states), capacity for a 219
Communication system, Shannon’s model of 1 ff
Comparison of channels 115 116 349
Component channel (of a channel network) 279
Component source (of a DMMS) 240
Composed code 74
Composite source see “Compound source”
Composition class 29
Compound channel 172
Compound channel, discrete memoryless see “Compound DMC”
Compound channel, multiple-access 288
Compound DMC 173
Compound DMC with encoder or decoder informed 183
Compound DMC, coding theorem 173
Compound DMC, invalidity of strong converse 182
Compound DMC, maximal codes for 183 316
Compound DMC, reliability function 173
Compound source 158 159
Computable characterization 259
Computation of  -distortion rate 144 148 -distortion rate 144 148
Computation of capacity of a DMC 140
Computation of capacity of a DMC, Muroga’s method 148
Computation of capacity of a DMC, simple channels 114
Computation of capacity-constraint function 140
Computation of error exponent in channel coding 192 195
Computation of error exponent in hypothesis testing 44
Computation of error exponent in source coding 44
Computation of rate-distortion function 144 148
Conclusive result 376
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



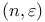 -code
-code  -distortion rate
-distortion rate  -achievable) rate pair, MAC
-achievable) rate pair, MAC