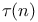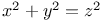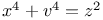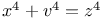|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Burton D.M. Ч Elementary Number Theory |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 -function (Mobius) 112Ч113 407Ч408 -function (Mobius) 112Ч113 407Ч408
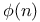 see УEulerТs phi-functionФ see УEulerТs phi-functionФ
 as irrational number 329 as irrational number 329
 , continued fractions representation 327Ч328 331Ч332 , continued fractions representation 327Ч328 331Ч332
 , decimal expansion of 353 , decimal expansion of 353
 , infinite series representation 306 , infinite series representation 306
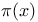 (prime counting function) for p = an + b 53 (prime counting function) for p = an + b 53
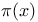 (prime counting function), approximations of 373Ч376 (prime counting function), approximations of 373Ч376
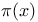 (prime counting function), defined 371 (prime counting function), defined 371
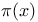 (prime counting function), Prime Number Theorem proof and 375Ч378 (prime counting function), Prime Number Theorem proof and 375Ч378
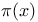 (prime counting function), properties of 371Ч373 (prime counting function), properties of 371Ч373
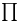 notation 106Ч107 notation 106Ч107
 factorization method 354Ч356 factorization method 354Ч356
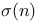 see УSum of divisorsФ see УSum of divisorsФ
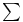 notation, defined 104 notation, defined 104
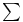 notation, multiplicative property and 109 115 notation, multiplicative property and 109 115
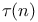 see УNumber of divisorsФ see УNumber of divisorsФ
A Course in Pure Mathematics (Hardy) 350Ч351
Absolute pseudoprime numbers 91 363
Abundant numbers 235
Adleman, Leonard 203
Agrawal, Manindra (1966Ч) 354
Alcuin (c.732Ч804) 38 219
Alembert, Jean Le Rond dТ (1717Ч1783) 63 262
Alexandrian Museum 14Ч15
Algebraic numbers 254
Amicable numbers 233
Amicable pairs 233Ч235
Amicable triples 236
An Elementary Proof of the Prime Number Theorem (Selberg) 378
Anthoniszoon, Adriaen (1527Ч1617) 332
Apery, Roger (1916Ч1994) 373
Arabic numerals 284
Archimedean property 2
Archimedean value of  331 331
Archimedes (c.287Ч212 B.C.) 331 346
Area of Pythagorean triangles 250 257
Arithmetic functions see УNumber-theoretic functionsФ
Arithmetic progressions of numbers, primes 54Ч55 375
Arithmetic progressions of numbers, pseudoprimes 90
Arithmetica (Diophantus), Bombelli and 307
Arithmetica (Diophantus), Fermat and 245Ч246 257 346
Arithmetica (Diophantus), history of 32
Arithmetica (Diophantus), recovery of script 85Ч86
Artin, Emil (1898Ч1962) 157
ArtinТs conjecture 157
Aryabhata I (476ЧC.550 a.d.) 15
Augustine, Saint (354Ч430) 219
Authentication of messages 215Ч216
Autokey cryptosystems 200Ч201
Bachet, Claude (1581Ч1638) 86 273
Barlow, Peter (1776Ч1862) 228Ч229
Bases for number systems 70
Basis for induction 4
Baudot code 202
Baudot, Jean-Maurice-Emile (1845Ч1903) 202
Bennett, G. 237
Bernoulli inequality 7
Bernoulli, Daniel (1700Ч1782) 129 130
Bernoulli, Johann (1667Ч1748) 129
Bernoulli, Nicolaus (1695Ч1726) 129 130
Bertrand, Joseph (1822Ч1900) 48
BertrandТs conjecture 48 352 371
Bhaskara II(1114Чc.1185) 83
Binary exponential algorithm 70Ч71
Binary number representation 70Ч71
Binet formula 296Ч298
Binet, Jacques-Philippe-Marie (1786Ч1856) 296
Binomial coefficients as integers 119
Binomial coefficients, defined 8
Binomial coefficients, Fibonacci numbers formula 302
Binomial coefficients, identities 8Ч10
Binomial congruences 164
Binomial theorem 8Ч10
Blum integers 369
Blum, Manuel (1938Ч) 367
BlumТs coin flipping game 367Ч370
Bombelli, Rafael (1526Ч1572) 307
BonseТs inequality 47
Bracket function 117 119Ч121
Brahmagupta (598ЧC.665) 83 346
Brent, Richard 240 241 356
Brillhart, John (1930Ч) 240 357 360
Brouncker, William (1620Ч1684) 332 335Ч336
Brun, Viggo (1882Ч1978) 375
BrunТs constant 375
Caesar, Julius (100Ч44 B.C.), cipher system 197Ч198
Caesar, Julius (100Ч44 B.C.), Julian calendar 122 123
Calendars 122Ч124
Canonical form 42
Carlyle, Thomas (1795Ч1881) 175
Carmichael numbers 91 363
Carmichael, Robert D. (1879Ч1967) 91
Catalan equation 257Ч258
Catalan numbers 12
Catalan, Eugene (1814Ч1894) 12 258
CatalanТs conjecture 258
Cataldi, Pietro (1548Ч1626) 222
Cattle problem 346
Chain of inequalities (continued fractions) 317Ч318
Chang ChТiu-chien (6th century a.d.) 36 37
Check digits 72Ч73
Chinese Remainder Theorem in BlumТs coin flipping game 368 370
Chinese Remainder Theorem, defined 79Ч81
Chinese Remainder Theorem, EulerТs generalization of FermatТs theorem and 139Ч140
Cicero, Marcus Tullius (106Ч43 B.C.) 197 198
Ciphers, autokey systems 200Ч201
Ciphers, Caesar 198
Ciphers, defined 197
Ciphers, Elgamal 213Ч216
Ciphers, Hill 201
Ciphers, Merkle Ч Hellman 209Ч212
Ciphers, Vigenere 199Ч200
Clavius, Christopher (1537Ч1612) 123
Cogitata Physica-Mathematica (Mersenne) 225
Coin flipping, remote 367Ч370
Cole Prize 351
Cole, Frank Nelson (1861Ч1926) 226
Common divisors 20Ч21
Common multiples 29
Complete set of residues modulo n 64
Composite numbers 39 305 УPrimality
Computational number theory 353
Computers in number theory, cryptography and 197 205Ч206
Computers in number theory, Mersenne primes and 229Ч230
Computers in number theory, prime number factorization and 353
Congruences 63Ч82 (see also УQuadratic congruencesФ)
Congruences in Caesar cipher 198
Congruences, basic properties 63Ч67
Congruences, binomial 164
Congruences, check digits 72Ч73
Congruences, Chinese Remainder Theorem 79Ч81
Congruences, days of the week and 123
Congruences, defined 63
Congruences, indices for solving 164Ч167
Congruences, linear in two variables 81Ч82
Congruences, partition function and 305
Congruences, place-value notation systems 69Ч71
Congruences, polynomial functions 71Ч72
Congruences, simultaneous linear 78Ч79
Congruences, single linear 76Ч78
Congruences, to perfect squares 100
Congruent modulo n, defined 63
Constant function f(n) = n 107 110
Continued fraction algorithm (irrational numbers) 326Ч328
Continued fraction factoring algorithm 357Ч360
Continued fractions, defined 306 (see also УFinite continued fractions; infinite continued fractionsФ УPellТs
Convergents of continued fractions,  327Ч328 327Ч328
Convergents of continued fractions, finite continued fractions 311Ч315 317Ч318
Convergents of continued fractions, infinite continued fractions 321Ч322 325Ч326
| Convergents of continued fractions, PellТs equation and 336 337Ч341
Critical line of the zeta function 376
Cryptography 197Ч216
Cryptography, defined 197
Cryptography, Elgamal system 213Ч216
Cryptography, knapsack problems 208Ч209
Cryptography, Merkle Ч Hellman knapsack system 209Ч212
Cryptography, monoalphabetic systems 197Ч198
Cryptography, poly alphabetic systems 198Ч201
Cryptography, RSA system 203Ч206
Cryptography, Verman one-time pad system 202Ч203
Cunningham, Allen Joseph (1848Ч1928) 229
Day of the week, determining 123Ч126
de Polignac, Alphonse (1817Ч1890) 58
Decimal number representation 71
Deciphering/decrypting, defined 197 (see also УCryptographyФ)
Decomposition into primes see УFactorization into primesФ
Deficient numbers 235
Denominator of Legendre symbol 175
Descartes, Rene (1596Ч1650), amicable pair discovery 234
Descartes, Rene (1596Ч1650), citations 235 273
Descartes, Rene (1596Ч1650), Mersenne and 217 218
Dickson, Leonard Eugene (1874Ч1954) 278 351
Difference of two squares 269Ч270
Digital alphabet for RSA cryptosystem 203Ч204
Digital signatures 215Ч216
Digits of a number, defined 71
Diophantine equations, 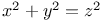 245Ч250 245Ч250
Diophantine equations, 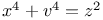 252Ч253 252Ч253
Diophantine equations, 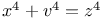 253Ч254 253Ч254
Diophantine equations, 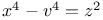 256Ч258 256Ч258
Diophantine equations, 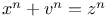 245Ч246 254Ч255 245Ч246 254Ч255
Diophantine equations, ax + by + cz = d 36Ч37
Diophantine equations, ax + by = c 32Ч35
Diophantine equations, defined 32
Diophantine equations, Fibonacci work on 283
Diophantine equations, linear congruences and 76 78
Diophantine equations, linear in two unknowns 32Ч35
Diophantine equations, word problems 35Ч37
Diophantus of Alexandria (3rd century a.d.) on sum of three squares 273
Diophantus of Alexandria (3rd century a.d.), biographical information 32
Dirichlet, Peter Gustav Lejeune (1805Ч1859), citations 54 172 186 375
Dirichlet, Peter Gustav Lejeune (1805Ч1859), FermatТs Last Theorem work 254
Dirichlet, Peter Gustav Lejeune (1805Ч1859), pigeonhole principle 264
DirichletТs Theorem 54
Discrete logarithm problems, cryptography and 213
Disquisitiones Arithmeticae (Gauss), citations 157 163 175 354
Disquisitiones Arithmeticae (Gauss), history of 61 63
Disquisitiones Arithmeticae (Gauss), Quadratic Reciprocity Law 186
Disquisitiones Arithmeticae (Gauss), regular polygons 237
Divergent series 374Ч375
Divisibility theory 13Ч38
Divisibility theory by 9 or 11 71Ч72
Divisibility theory, Diophantine equations 32Ч37
Divisibility theory, Division Algorithm 17Ч19
Divisibility theory, early number theory 13Ч16
Divisibility theory, Euclidean algorithm 26Ч31
Divisibility theory, greatest common divisor 19Ч24
Divisibility theory, Mersenne and 218
Divisibility theory, symbols for 20
Division algorithm 17Ч19
divisors see also УNumber of divisorsФ УSum
Divisors from prime factorizations 104Ч105
Divisors, common 20Ч21
Divisors, defined 20
Divisors, greatest common 21 24
Divisors, Mersenne numbers 228Ч229
Double Wieferich primes 258
e (continued fractions representation) 328Ч329
e-prime numbers 42
Early number theory 13Ч16
Eisenstein, Ferdinand Gottfried Max (1823Ч1852) 186
El Madschriti of Madrid (11th century) 234
Elements (Euclid), Diophantine equations and 32
Elements (Euclid), Euclidean algorithm 26
Elements (Euclid), EuclidТs theorem 45
Elements (Euclid), Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 39Ч40
Elements (Euclid), history of 15
Elements (Euclid), Legendre revision of 175
Elements (Euclid), perfect numbers work 220
Elements (Euclid), translations of 85
Elements de Geometrie (Legendre) 175
Elgamal cryptosystem 213Ч216
Elgamal, Taher (1955Ч) 213
Elkies, Noam 279
Elliptic curves 255
Enciphering exponent 203 204
Enciphering modulus 203
Enciphering/encrypting, defined 197 (see also УCryptographyФ)
Encke, Johann Franz (1791Ч1865) 374
Equality, congruence and 65
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (c.276Чc.194 B.C.) 45 346
Erdos, Paul (1913Ч1996) 351Ч353
Essai sur la Theorie des Nombres (Legendre) 175 186 373
Essaipour les Coniques (Pascal) 217
Euclid (c.300 B.C.), citations 246
Euclid (c.300 B.C.), early number theory 15
Euclid (c.300 B.C.), perfect numbers work 220
Euclidean algorithm, defined 26Ч28
Euclidean algorithm, least common multiple and 29Ч30
Euclidean algorithm, more than two integers 30Ч31
Euclidean algorithm, number of steps 28Ч29
Euclidean numbers 46
EuclidТs lemma 24
EuclidТs theorem, defined 45Ч48
EuclidТs theorem, EulerТs phi-function and 134Ч135
Euler polynomial 55Ч56
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783),  , symbol 327 , symbol 327
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), amicable pair work 234 235
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), biographical information 129Ч131 262
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), citations 55 57 63 87 185 221 265 279
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), e continued fractions representation 328
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), Fermat numbers work 237 240
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), FermatТs Last Theorem work 254
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), Goldbach conjecture and 51
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), Mersenne numbers work 225Ч226
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), on Catalan equation 258
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), on odd perfect numbers 231 232
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), on triangular numbers 15
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), PellТs equation and 336
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), photo of 130
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), primitive roots for primes 162
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), proof of FermatТs theorem 87 136
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), sum of four squares 273
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), WaringТs problem 351
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), word problems 38
Euler, Leonhard (1707Ч1783), zeta function formula 373
EulerТs criterion, citations 180
EulerТs criterion, defined 171Ч172
EulerТs criterion, DirichletТs proof of 172Ч173
EulerТs generalization of FermatТs theorem, applications of 139Ч140
EulerТs generalization of FermatТs theorem, defined 137Ч138
EulerТs generalization of FermatТs theorem, FermatТs Little Theorem as proof of 139
EulerТs identity 273 277
EulerТs phi-function 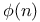 as even integer 134 as even integer 134
EulerТs phi-function 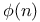 as multiplicative function 132 133 142 as multiplicative function 132 133 142
EulerТs phi-function 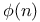 , defined 131Ч132 , defined 131Ч132
EulerТs phi-function 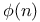 , EuclidТs theorem and 134Ч135 , EuclidТs theorem and 134Ч135
EulerТs phi-function 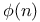 , GaussТ theorem and 141Ч143 , GaussТ theorem and 141Ч143
EulerТs phi-function 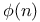 , Mobius inversion formula and 144Ч145 , Mobius inversion formula and 144Ч145
EulerТs phi-function 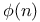 , sum of integers identity 143 , sum of integers identity 143
EulerТs phi-function 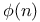 , table of 407Ч408 , table of 407Ч408
Even-numbered convergents 317Ч318 321
Even-numbered convergents in Pythagorean triples 247
Even-numbered convergents, defined 18
Even-numbered convergents, EulerТs phi-function as 134
Exponent of a prime in n! factorization 117Ч118
Exponent to which a belongs modulo n 147Ч150
Exponent, enciphering 203 204
Exponent, recovery 204
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -function (Mobius)
-function (Mobius) 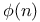
 as irrational number
as irrational number 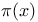 (prime counting function) for p = an + b
(prime counting function) for p = an + b 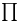 notation
notation  factorization method
factorization method 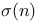
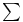 notation, defined
notation, defined