|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Burton D.M. Ч Elementary Number Theory |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Meditationes Algebraicae (Waring) 277
Merkle Ч Hellman knapsack cryptosystem 209Ч212
Merkle, Ralph 209
Mersenne numbers, defined 225
Mersenne numbers, divisor properties 228Ч229
Mersenne numbers, primality tests 226 227Ч228 230Ч231
Mersenne numbers, search for larger numbers 226 229Ч230 231
Mersenne primes, defined 225
Mersenne primes, table of 230
Mersenne, Marin (1588Ч1648), biographical information 217Ч218
Mersenne, Marin (1588Ч1648), citations 97 102 237
Mersenne, Marin (1588Ч1648), correspondence on amicable pairs 234
Mersenne, Marin (1588Ч1648), Fermat correspondence 265
Mersenne, Marin (1588Ч1648), Mersenne numbers work 225 226
Mersenne, Marin (1588Ч1648), photo of 219
Mertens conjecture 115Ч116
Mertens, Franz (1840Ч1927) 115
Mihailescu, Preda 258
Miller Ч Rabin primality test 365Ч366
Mills, WH. (1921Ч) 57
Mobius  -function 112Ч113 407Ч408 -function 112Ч113 407Ч408
Mobius inversion formula, defined 113Ч115
Mobius inversion formula, EulerТs phi-function and 144Ч145 155
Modulo n (congruence), check digits and 73
Modulo n (congruence), defined 63Ч64
Monoalphabetic cryptosystems 197Ч198
Monte Carlo factorization method 354Ч356
Morain, Francois 241
Morehead, J. C 239 240
Morrison, Michael A. 240 357 360
Muller, Johannes see УRegiomontanus (1436Ч1476)Ф
Multiples, defined 20
Multiplicative functions, 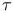 and and  as 108 109Ч110 as 108 109Ч110
Multiplicative functions, defined 107Ч108
Multiplicative functions, EulerТs phi-function as 132 133 142
Multiplicative functions, Mobius  -function as 112 144 145 -function as 112 144 145
Multiplicative inverse of a modulo n 11
Multiplicatively perfect numbers 224
Multiply perfect numbers 224
Natural numbers, defined 1
NewtonТs identity 10
Nickel, Laura 229
Nicomachus of Gerasa (c.100 a.d.) 15 79 219
Noll, Curt 229
Nonalphabetic cryptosystems 202Ч203
Nonnegative residues modulo n 64
Nonresidues, quadratic 171 172Ч173 178Ч179
Notation systems, 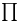 notation 106Ч107 notation 106Ч107
Notation systems, 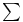 notation 104 109 115 notation 104 109 115
Notation systems, binary numbers 69Ч71
Notation systems, decimal numbers 71
Notation systems, finite continued fractions 310
Notation systems, infinite continued fractions 321
Number of divisors 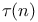 as multiplicative function 108 109Ч110 as multiplicative function 108 109Ч110
Number of divisors 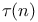 , basic properties 103Ч107 , basic properties 103Ч107
Number of divisors 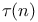 , greatest integer function and 120 , greatest integer function and 120
Number of divisors 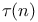 , table of 407Ч408 , table of 407Ч408
Number-theoretic functions 103Ч126 (see also УEulerТs phi-functionФ)
Number-theoretic functions, calendar applications 122Ч126
Number-theoretic functions, defined 103
Number-theoretic functions, greatest integer function and 119Ч121
Number-theoretic functions, Mobius inversion formula 112Ч116
Number-theoretic functions, multiplicative functions 107Ч110
Number-theoretic functions, number of divisors 103Ч107
Number-theoretic functions, sum of divisors 103Ч107
Numbers see also УComposite numbersФ УFermat УFibonacci УMersenne УPerfect УPrime УRelatively
Numbers, absolute pseudoprime 91 363
Numbers, abundant 235
Numbers, algebraic 254
Numbers, amicable 233
Numbers, Catalan 12
Numbers, deficient 235
Numbers, e-prime 42
Numbers, Euclidean 46
Numbers, even 18 134 247
Numbers, Germain 182
Numbers, highly composite 305
Numbers, ideal 254
Numbers, k-perfect 224
Numbers, Lucas 301
Numbers, multiplicatively perfect 224
Numbers, multiply perfect 224
Numbers, natural, defined 1
Numbers, odd 18 160Ч162 231Ч233 247 394Ч403
Numbers, palindromes 75
Numbers, Pell 348
Numbers, pentagonal 16
Numbers, pseudoprime 90Ч92 242
Numbers, regular prime 254
Numbers, repunit 48Ч49
Numbers, Skewes 377
Numbers, square-free 43 91
Numbers, square-full 43
Numbers, strong pseudoprime 367
Numbers, superperfect 225
Numbers, triangular 15Ч16 257 295
Numerator of Legendre symbol 175
Odd-numbered convergents 317Ч318 321
Odd-numbered convergents in Pythagorean triples 247
Odd-numbered convergents, defined 18
Odd-numbered convergents, perfect 231Ч233
Odd-numbered convergents, prime factors, table of 394Ч403
Odd-numbered convergents, primitive roots for 160Ч162
Odlyzko, Andrew M. 116
One-time pad cryptosystems, Verman 202Ч203
One-time pad cryptosystems, Vigenere 200
Opera Mathematica (Wallis) 336
Order of a modulo n 147Ч150
Pairs of quadratic residues 171
Palindromes 75
Parkin, Thomas 279
Partial denominators 307 310
Partial quotients 310
Partition theory 304Ч305
Pascal, Blaise (1623Ч1662), mathematical induction work 10
Pascal, Blaise (1623Ч1662), scholarly gatherings 217 218
PascalТs rule 8
PascalТs triangle 9
Pell numbers 348
Pell, John (1611Ч1685) 336
PellТs equation, continued fraction expansions 337Ч341
PellТs equation, fundamental solution 343Ч344
PellТs equation, history of 334Ч336 346
PellТs equation, integral solutions 345Ч346
PellТs equation, positive solutions 337 342Ч343 344Ч345
Pentagonal numbers 16
Pepin, Theophile (1826Ч1904) 238
PepinТs test 238Ч240
Perfect numbers, defined 219Ч220
Perfect numbers, discovery of larger numbers 226 229Ч230 231
Perfect numbers, final digits of 223
Perfect numbers, general form 220Ч222
Perfect numbers, odd 231Ч233
Period (continued fraction expansions) 322 338 339
Periodic continued fractions 322 338Ч340
Personal identification numbers, check digits for 72Ч73
Peter the Great (1672Ч1725) 130
Phi-function 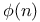 see УEulerТs phi-functionФ see УEulerТs phi-functionФ
Piazzi, Giuseppi (1746Ч1826) 63
Pigeonhole Principle 264
Place-value notation systems 69Ч71
Plaintext 197
Plutarch (c.46Чafter 119 a.d.) 15
Pocklington, Henry (1870Ч1952) 364
PocklingtonТs theorem 364Ч365
Poe, Edgar Allan (1809Ч1849) 198Ч199
Polignac, Alphonse de (1817Ч1890) 58
Pollard, John M., citations 240 241
Pollard, John M., p - 1 factorization method 356Ч357
Pollard, John M., rho factorization method 354Ч356
| Polya conjecture 353
Polya, George (1888Ч1985) 353
Polyalphabetic cryptosystems 198Ч201
POLYGONS 62 237Ч238
Polynomial congruences, divisibility tests 71Ч72
Polynomial congruences, LagrangeТs theorem and 152Ч154
Positive solutions (PellТs equation) 337 342Ч343 344Ч345
Powerful numbers 43
Powers, R. E. 229
Primality tests, computers and 229Ч230
Primality tests, efficient algorithms for 354
Primality tests, FermatТs Little Theorem methods 89 362Ч365
Primality tests, Mersenne numbers 226 227Ч228 230Ч231
Primality tests, Miller Ч Rabin test 365Ч366
Primality tests, PepinТs test 238Ч240
Primality tests, WilsonТs theorem 95
prime factors see УFactorization into primesФ
Prime Number Theorem, arithmetic proofs of 352 378
Prime Number Theorem, complex proofs of 375Ч377
Prime Number Theorem, defined 371
Prime numbers 39Ч57 (see also УInfinitude of primesФ УPseudoprime
Prime numbers as sum of four squares 275Ч277
Prime numbers of the form  240 242 240 242
Prime numbers of the form  46 46
Prime numbers of the form 4n + 1 53 54 177Ч178 188 265Ч267
Prime numbers of the form 4n + 3 53Ч54 188 264 267Ч268
Prime numbers of the form 8k + 1/3/5/7 181
Prime numbers of the form 8k - 1 181
Prime numbers of the form an + b 53
Prime numbers of the form n! + 1 96
Prime numbers, arithmetic progressions of 54Ч55 90 375
Prime numbers, defined 39
Prime numbers, double Wieferich 258
Prime numbers, EuclidТs theorem 45Ч48
Prime numbers, Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 39Ч42
Prime numbers, gaps between 50Ч51
Prime numbers, Germain 182
Prime numbers, Goldbach conjecture 51Ч52
Prime numbers, length of intervals 377Ч378
Prime numbers, of the form  53 53
Prime numbers, prime-producing functions 55Ч57
Prime numbers, primitive roots 154Ч157
Prime numbers, repunit 48Ч49
Prime numbers, sieve of Eratosthenes 44Ч45
Prime numbers, tables of 404Ч406
Prime numbers, twin 50 375 406
Prime-producing functions 55Ч57
Prime-triplets 58
Primers (autokey cryptosystems) 200
Primitive Pythagorean triples defined 246
Primitive Pythagorean triples defined, properties of 247Ч249
Primitive Pythagorean triples defined, table of 249
Primitive roots, composite numbers 158Ч162
Primitive roots, cryptography application 213
Primitive roots, defined 150Ч151
Primitive roots, Legendre symbol and 181Ч182
Primitive roots, number of 151
Primitive roots, prime numbers 154Ч157
Primitive roots, tables of 156 393
Probabilistic primality tests 366
Progressions of numbers see УArithmetic progressions of numbersФ
Proth, E. 367
Pseudoprime numbers 90Ч92 242 363
Public-key crypto systems, defined 203
Public-key crypto systems, Elgamal system 213Ч216
Public-key crypto systems, Merkle Ч Hellman knapsack system 209Ч212
Public-key crypto systems, RSA system 203Ч206
Puzzle problems, cattle 346
Puzzle problems, congruences 79Ч80
Puzzle problems, Diophantine equations 35Ч37
Puzzle problems, hundred fowls 36Ч37
Puzzle problems, square/rectangle geometric deception 293Ч294
Pythagoras (c.580Чc.500 B.C.) on irrational numbers 42
Pythagoras (c.580Чc.500 B.C.) on triangular numbers 15
Pythagoras (c.580Чc.500 B.C.), citations 235 246
Pythagoras (c.580Чc.500 B.C.), early number theory 13Ч14
Pythagorean triangles 250 257
Pythagorean triples 246 247Ч249
Pythagoreans on perfect numbers 219 221
Pythagoreans, amicable pairs and 234
Pythagoreans, history of 14
Pythagoreans, number classification 42
Quadratic congruences in BlumТs coin flipping game 367Ч369
Quadratic congruences with composite moduli 189Ч190 192Ч195
Quadratic congruences, indices for solving 164Ч165
Quadratic congruences, primitive roots 155Ч156
Quadratic nonresidues, defined 171
Quadratic nonresidues, EulerТs criterion 172Ч173
Quadratic nonresidues, Legendre symbol and 178Ч179
Quadratic Reciprocity Law and 189Ч190
Quadratic Reciprocity Law and simplification of 169Ч170
Quadratic Reciprocity Law and solvability criteria 192 194 195
Quadratic Reciprocity Law and WilsonТs theorem and 95Ч96
Quadratic Reciprocity Law, defined 186
Quadratic Reciprocity Law, generalized 192
Quadratic Reciprocity Law, history of 169 185Ч186
Quadratic Reciprocity Law, properties of 188Ч190
Quadratic residues, defined 171
Quadratic residues, EulerТs criterion 171Ч173
Quadratic residues, Legendre symbol and 178Ч179
Quadratic residues, sum of four squares problem and 275
Quadratic sieve factoring algorithm 360Ч362
Quadrivium 13
Quotients 17
Radius of inscribed circle of Pythagorean triangles 250
Ramanujan, Srinivasa Aaiyangar (1887Ч1920), biographical information 303Ч306
Ramanujan, Srinivasa Aaiyangar (1887Ч1920), fraction expansions 320
Ramanujan, Srinivasa Aaiyangar (1887Ч1920), photo of 304
Ramanujan, Srinivasa Aaiyangar (1887Ч1920), sum of two cubes 272
RamanujanТs conjecture 305
Rational numbers as finite continued fractions 307Ч310
Rational numbers as irrational numbers approximation 329Ч331
Recovery exponent 204
Rectangle/square Fibonacci number problem 293Ч294
Recursive sequences 286
Reduced set of residues modulo n 141
Regiomontanus (1436Ч1476) 83 85 279
Regius, Hudalrichus (fl. 1535) 222
Regular polygons 62 237Ч238
Regular prime numbers 254 (see also УPrime numbersФ)
Relatively prime numbers in Pythagorean triples 247
Relatively prime numbers, convergent numerators and denominators as 314Ч315
Relatively prime numbers, defined 22Ч23
Relatively prime numbers, Fermat numbers as 238
Relatively prime numbers, Fibonacci numbers as 286Ч288
Relatively prime numbers, multiplicative property and 107
Remainder 17 28
Remote coin flipping 367Ч370
Representation of integers, difference of two squares 269Ч270
Representation of integers, sum of four squares 263 273Ч277
Representation of integers, sum of three squares 272Ч273
Representation of integers, sum of two squares 264Ч269
Representation of integers, WaringТs problem 277Ч279 350Ч351
Representation of integers, Zeckendorf 295Ч296
Repunit numbers 48Ч49
Residues, complete set 64
Residues, least nonnegative 64
Residues, quadratic 171Ч173 178Ч179 275
Residues, reduced set 141
Rho factorization method 354Ч356
Riemann hypothesis 376
Riemann, Georg Friedrich Bernhard (1826Ч1866) 375Ч376
Rivest, Ronald L. 203
RSA public-key cryptosystem 203Ч206
RSA-129 cryptosystem 206
RSA-576 cryptosystem 206
Rudolff, Christoff (fl. 1526) 38
Running keys 200
Saxena, Nitin 354
Second Principle of Finite Induction 5Ч6
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -function
-function 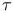 and
and  as
as 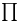 notation
notation 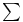 notation
notation 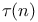 as multiplicative function
as multiplicative function