|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Levine I.N. Ч Molecular Spectroscopy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Matrix elements 5 94Ч96
Matrix isolation method 269
Matrix mechanics 93Ч102
Matrix representatives of functions 96Ч97
Matrix representatives of operators 94Ч96
Maxwell, J.C 114
McConnell equation 379Ч380
McConnell, H.M. 379
Mclver, J.W. 360 458
Measurement 9Ч10 113Ч114
Metastable states 128Ч129
Methane in planetary atmospheres 269
Methane, dipole moment of 225
Methane, meta, ortho, and para 289
Methane, symmetry number of 289
Methyl radical 367 379
Meyer, W. 317
Micrometer 132
Micron 132
Microwave spectrometer 219Ч221
Microwave spectroscopy 130 219Ч231
Microwave spectroscopy and molecular structure 221Ч225
Microwave spectroscopy and rotational barriers 226Ч228
Microwave spectroscopy and vibrational frequencies 225Ч226
Microwave spectroscopy, compilations of results of 231
Microwave spectroscopy, dipole-moment measurements in 225
Microwave spectroscopy, experimental procedures in 219Ч221
Microwave spectroscopy, frequency measurements in 220
Mid infrared 261
MINDO method 71 76
MINDO method and force constants 245
MINDO method and ionization potentials 318Ч319
Minimal basis set 65
Minor 14
Modal matrix 106
Molecular orbitals and group theory 418Ч427
Molecular orbitals for diatomics 58
Molecular orbitals for polyatomics 66 (see also УHartree Ч Fock method OrbitalsФ)
Molecule-fixed axes 175 178 196
Moment of inertia 40 148 149 197 200
Momental ellipsoid 198Ч202 439Ч444
Morse function 161 162
Mossbauer spectroscopy 130Ч131
Mulliken, R.S. 405
Multiconfiguration SCF method 70
Multiplication table of a group 389Ч392
Multiplicity 50 58
Mutual exclusion rule 270 457
n orbital 310
Nanometer 132
Naphthalene negative ion 367 379 380
Natural line width 134
Near infrared 261
Near-degenerate vibrational levels 278Ч279
Negative levels 177 280
Negative spin density 378
Neutron 178 324
Nitrogen molecule, calculation of ionization potentials of 318
Nitrogen molecule, photoelectron spectrum of 316Ч317
Nongenuine vibrations 432
Nonradiative transitions 129 183Ч185
Nonsingular matrix 84
Normal coordinates 239Ч240 246Ч247 272
Normal modes 240Ч244
Normal modes and group frequencies 266Ч268
Normal modes and symmetry 246Ч249 430439
Normal modes of benzene 438Ч439
Normal modes of boron trifluoride 281 290
Normal modes of carbon dioxide 242 248 262 265
Normal modes of ethylene 291
Normal modes of water 431Ч437
Normal modes, IR active 457
Normal modes, Raman active 457
Normal operator 108
Normalization 6
Nuclear g factor 3 24
Nuclear magnetic moments 323Ч325
Nuclear magnetic resonance 129Ч130 323Ч366
Nuclear magnetic resonance and rate processes 364Ч365
Nuclear magnetic resonance and rotational barriers 364Ч365
Nuclear magnetic resonance for 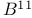 compounds 357 compounds 357
Nuclear magnetic resonance for 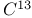 compounds 356Ч357 compounds 356Ч357
Nuclear magnetic resonance for 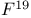 compounds 357 compounds 357
Nuclear magnetic resonance of solids 357Ч359
Nuclear magnetic resonance of water in tissues 363Ч364
Nuclear magnetic resonance, 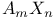 case in 349Ч352 case in 349Ч352
Nuclear magnetic resonance, 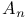 case in 348Ч349 352Ч354 case in 348Ч349 352Ч354
Nuclear magnetic resonance, AB case in 339Ч346
Nuclear magnetic resonance, AX case in 346Ч347
Nuclear magnetic resonance, biochemical applications of 357 363Ч364
Nuclear magnetic resonance, broad-line 359
Nuclear magnetic resonance, chemical shifts in 331Ч337
Nuclear magnetic resonance, classification of spectra in 346Ч348
Nuclear magnetic resonance, coupling constants for 339 345Ч346 352Ч354 360
Nuclear magnetic resonance, delta scale for 356
Nuclear magnetic resonance, deuterium substitution in 354Ч355
Nuclear magnetic resonance, double resonance in 354 356
Nuclear magnetic resonance, energy levels for 325 327 333 342Ч343
Nuclear magnetic resonance, experimental procedures in 328Ч331 354
Nuclear magnetic resonance, first-order approximation in 349Ч352
Nuclear magnetic resonance, four-spin cases 348
Nuclear magnetic resonance, Fourier-transform 330Ч331 356
Nuclear magnetic resonance, frequencies for nuclei 327Ч328
Nuclear magnetic resonance, high-resolution 331
Nuclear magnetic resonance, intensities in 337 343Ч344 351 352
Nuclear magnetic resonance, secular equation for 355
Nuclear magnetic resonance, selection rules for 326Ч327 333 343
Nuclear magnetic resonance, spin relaxation in 361Ч364
Nuclear magnetic resonance, spin-spin coupling in 337Ч356 357Ч360
Nuclear magnetic resonance, three-spin cases 347Ч348
Nuclear magneton 324
Nuclear Overhauser effect 354
Nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR), spectroscopy 366
Nuclear quadrupote moment 229Ч231 365Ч366
Nuclear Schrodinger equation 57 142Ч149 195Ч197
Nuclear spin 178Ч185 229 283Ч289 323Ч327
Nuclear statistical weights 182 284Ч289
Null matrix 83
Null operator 12
O branch 188
Oblate symmetric top 199 211
Odd function 32 33
Olefins, electronic spectra of 310
Olefins, NMR coupling constants of 346
One-electron methods 71
Operator(s) 1Ч11 12Ч13
Operator(s) and matrices 94Ч96
Operator(s) for electric dipole moment 62
Operator(s), adjoint of 107Ч108
Operator(s), Coulomb 64
Operator(s), difference 170
Operator(s), eigen functions of 2 98Ч102
Operator(s), eigenvalues of 2 5 98Ч102
Operator(s), exchange 64
Operator(s), Hamiltonian 3 4Ч5 47 56Ч57
Operator(s), Hartree Ч Fock 63Ч64
Operator(s), Hermitian 4 5Ч8
Operator(s), inverse of 108
Operator(s), linear 3
Operator(s), matrix elements of 94Ч96
Operator(s), matrix representatives of 94Ч96
Operator(s), normal 108
Operator(s), null 12
Operator(s), parity 32Ч33 56
Operator(s), projection 425 426
Operator(s), self-adjoint 108
Operator(s), symmetry 55Ч56 59Ч62 398
Operator(s), unit 12
Operator(s), unitary 108
Optical pumping 136
| Optimized valence configuration method 70 245
Orbital angular momentum 27Ч29 49
Orbital degeneracy 61 62
Orbital energy 64
Orbital exponent 65
Orbitals 48
Orbitals and group theory 418Ч427
Orbitals, canonical 69 310
Orbitals, energy-localized 69 103Ч104
Orbitals, Hartree Ч Fock see УHartree Ч Fock methodФ
Orbitals, localized 69 103Ч104 309Ч310
Orbitals, n 310
Orbitals, pi 68 310 317
Orbitals, pi-star 309 310
Orbitals, Rydberg 308Ч309
Orbitals, SCF 65
Orbitals, sigma 68
Orbitals, Slater-type 65
Orbitals, symmetry 67 419Ч427
Orbitals, valence 309
Orbitals, virtual 68 69
Order of a group 388
Order of a square matrix 82
Ortho deuterium 185
Ortho forms of homonuclear diatomics 183Ч185
Ortho hydrogen 185
Ortho methane 289
Ortho water 288
Orthogonal matrix 85Ч86 87
Orthogonal transformation 93
Orthogonal vectors 86
Orthogonality 5Ч6
Orthonormal vectors 86
Orthonormality 6
Oscillator strength 307Ч308 313
OVC CI method 70 245
Overtone band 169
Overtone level 252
Oxygen molecule, localized MOs for 104
Oxygen molecule, microwave spectrum of 221
Oxygen molecule, rotational levels of 191
P branch 171Ч173 218 303
Para forms of homonuclear diatomics 183Ч185
Para hydrogen 185
Para water 288
Parallel band 259 265
Paramagnetic contribution to shielding constant 332
Pariser Ч Parr Ч Pople (PPP) method 71 74Ч75 313
Parity 32Ч33 126Ч127 128
Parity and selection rules 126Ч127 128 178 299
Parity in atoms 52
Parity in diatomics 59 175Ч178
Parity in polyatomics 276 279Ч282
Parity operator 32Ч33 56
Particle in a box 23Ч25 71 124
Partitioned matrix 88
PascalТs triangle 351
Pauli principle 45Ч47 178Ч182 284Ч287
Pauli spin matrices 96
Perpendicular band 259 265
Perturbation theory 35Ч38 102
Perturbation theory for nuclear motion 149Ч159
Perturbation theory, degenerate 36Ч38
Perturbation theory, time-dependent 110Ч114
Perturbation, spectroscopic 283
Phase 13
Phenol 225
Phosphorescence 128
Phosphorous trichloride, structure of 222 223
Photoelectron spectroscopy 314Ч320
Photoelectron spectroscopy, UV 315Ч318
Photoelectron spectroscopy, x-ray 319Ч320
Photosynthesis 381
Physical constants, table of 467
Pi orbitals 68 310 317
Pi-electron approximation 71
Pi-star orbital 309 310
Pigpen 320
Planarity 224Ч225
Planck, M. 122
Plane of symmetry 53
Plane polar normal coordinates 272
Plane-polarized wave 114
Point groups 53Ч56 388Ч389
Point groups, character tables of 458Ч462 (see also УGroup theoryФ)
Polar vector 434
Polarizability 187 188 202 269 270 457
Polarizability ellipsoid 202 270
Poly water 320
Polyenes, conjugated 71Ч72
Polymethine ions 72
Pople, J.A. 75 337 360 380
Population inversion 135
Positive levels 177 280
potential energy 3
Potential-energy functions for diatomics 144Ч145 160Ч162
Potential-energy functions for polyatomics 244Ч245
Poynting vector 115
Precession 52
Predissociation 306
Pressure broadening 134
Principal axes 198Ч202
Principal diagonal 15
Principal moments of inertia 198Ч202
probability 9
probability density 9
Probability of a transition 119Ч122
Products of inertia 200
Progression 304
Project Ozma 374n
Projection operators 425 426
Prolate symmetric top 199 211
Propane, dipole moment of 225
Proper axis of symmetry 53
Proper rotation 395Ч396
Proton 178
Pseudovector 434
Pulse laser 137 139
Purcell, E.M. 328 360
Pure-rotation spectra 165
Pure-rotation spectra of diatomics 165Ч167
Pure-rotation spectra of polyatomics 216Ч231
Purely electronic energy 57
Q branch 173 218 265 303
Quadratic form 92Ч93 200Ч201 238
Quadratic integrability 1
Quadrupole coupling constants 231 366
Quadrupole moments 229Ч231 365Ч366
Quantum Chemistry Program Exchange 76 244 355
Quantum electrodynamics 116
Quantum field theory 116
quantum mechanics 1Ч11
Quantum mechanics, matrix formulation of 93Ч102
Quenching of radiation 129
R branch 171Ч172 218 303
R-centroid 301
Rabi, I.I. 328
Radiation, electromagnetic 114Ч117
Radiation, electromagnetic, absorption of 118
Radiation, electromagnetic, coherent 139
Radiation, electromagnetic, density of 119
Radiation, electromagnetic, electric and magnetic fields of 114Ч116
Radiation, electromagnetic, intensity of 115 119
Radiation, electromagnetic, polarized 114
Radiation, electromagnetic, scattering of 186 188
Radiation, electromagnetic, spontaneous emission of 121Ч122
Radiation, electromagnetic, stimulated emission of 118 120 122 135Ч139
Radiationless transitions 129 183Ч185
Raising, operator 30
Raman spectroscopy of diatomics 186Ч188
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



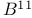 compounds
compounds 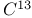 compounds
compounds 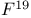 compounds
compounds 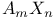 case in
case in 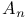 case in
case in