|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ward S., Halstead R. — Computation Structures (MIT Electrical Engineering and Computer Science) |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), row address 290
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), row-address strobe (RAS) 290
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), WRITE input 290
EBCDIC see "Character code EBCDIC"
ECL see "Logic families"
Edge trigger 83
Effective address 431
EMAB 592—596
EmulateL8 556—557
EmulateS8 556
Emulation, software-level 534
Encoding 269 272
Engineering 621—622
Engineering disciplines 1 621
Engineering methodology, bottom-up 303
Engineering methodology, middle-out 303
Engineering methodology, top-down 303
Entry sequence see "Procedure linkage"
Environment 401
EPROM see "Read-only memory"
Equilibrium, stable 97
Equilibrium, unstable 97
Error conditions 339
Error correction 42—44 611
Error correction, single-bit 43
Error detection 42—44 263 374
Error detection, single-bit 43
error reporting 252
Error syndrome bits 43
Error, checksum 43
Error, parity 42
Error-correcting code 43
Eventcounts see "Synchronization mechanisms"
Events 83 99 173—174 178—179 187—188 192 194
Events, asynchronous 99 195
Events, finish 181 190
Events, start 181 190
Exceptions 352
Exclusive access 561
execution 355 357
execution time 371
Execution units, multiple 355
Exit sequence see "Procedure linkage"
Expressions 362 382
Expressions, constant 316
extent see "Storage class extent"
Extracodes 550
Fairness 255 559 572—573
Fairness of semaphores 573
Fall time 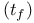 16—20 247 16—20 247
Fanin 14—15
Fanout 11
fault 349 352 411 458 539 545—546 549 593
Fault handler 352 411
Fault tolerance 44 611—612
Fault tolerance by triple modular redundancy 611
Fault vector 352
Fault, address-translation 546
Fault, divide-by-zero 546
Fault, illegal-instruction 539 546 549 556 588
Fault, segmentation 546
Feedback 76
Feedback path 80—81 86 97
Fermat's last theorem 274
FET see "Transistor" "Field-effect
Fibonacci sequence 398
FIFO see "Buffer first-in-first-out"
Finish signal see "Control signals finish"
Finite-State Machines (FSMs) 76 92 143—169 173 175 188 191 269 325 335—336 347 607
Finite-state machines (FSMs) as controllers 269
Finite-state machines (FSMs), asynchronous inputs 147
Finite-state machines (FSMs), deterministic vs. nondeterministic 151
Finite-state machines (FSMs), equivalence 148—151
Finite-state machines (FSMs), formal study of 154
Finite-state machines (FSMs), incompletely specified 151
Finite-state machines (FSMs), input timing 147
Finite-state machines (FSMs), inputs 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), Mealy machines 92 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), minimization of 149—151
Finite-state machines (FSMs), Moore machines 92 143 146
Finite-state machines (FSMs), next-state logic 146
Finite-state machines (FSMs), nondeterministic (NFSM) 151—154
Finite-state machines (FSMs), output logic 146
Finite-state machines (FSMs), output rules 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), output variable 145
Finite-state machines (FSMs), outputs 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), recognition of strings by 152
Finite-state machines (FSMs), reset input 143 218—220
Finite-state machines (FSMs), state 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), state equivalence 148—151
Finite-state machines (FSMs), state, current 143 146
Finite-state machines (FSMs), state, initial 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), state, next 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), state-transition diagram for NFSMs 152
Finite-state machines (FSMs), state-transition rules 143
Finite-state machines (FSMs), states, encoding of 145 147
Finite-state machines (FSMs), synchronous 146—147 174
Finite-state machines (FSMs), synthesis of 144—146
Five dining philosophers problem see "Synchronization problems"
Flip-flop 76 78—86 219
Flip-flop, clock input 83—84
Flip-flop, D-type 116—117 220
Flip-flop, edge-triggered 83—86 90 93
Flip-flop, edge-triggered, D-type 91 127
Flip-flop, edge-triggered, D-type, asynchronous specification of 90
Flip-flop, load-enable input 83
Flip-flop, negative edge-triggered 83
Flip-flop, positive edge-triggered 83—84
Fluid dynamics 605
Fluidies 275
Flynn, Michael 612
Forbidden zone 6 8 12 14 16 88 91 94 96
Fork 194—195 198
Formal languages 154
Formal parameter see "Procedure linkage"
Fourier transform 619
free 633
frequency 2
Frequency division 119
Frequency mismatch 260
FSM see "Finite-state machines"
Functional modularity 1
Functional partitioning 471
functional units 183 614—615
Functional units, multiple 614
Functions, computable 273 277 607
Functions, Fibonacci 629
Functions, parity 61
Functions, polymorphic 395
Functions, primality 121
Functions, uncomputable 273—275
G see "Notation g
G machine 371—372 427—469 537 723—748
G machine, CC register 439 449
G machine, microcode 441—450 728—748
G-machine addressing modes dir 430 436 439 725
G-machine addressing modes, i 430 436 725
G-machine addressing modes, iix 436 446 725
G-machine addressing modes, imm 436 725 436 725
G-machine addressing modes, imm4 438 450
G-machine addressing modes, iposti 436 438 725
G-machine addressing modes, ipred 436 438 725
G-machine addressing modes, ir 430 436 445 725
G-machine addressing modes, ix 430 432—433 436 445 450 454 459 725
G-machine addressing modes, pop 331 430 434—438 651 725
G-machine addressing modes, posti 435—438 725
G-machine addressing modes, pred 435—438 459 725
G-machine addressing modes, r 430 436 438 445 725
G-machine addressing modes, rel 436 725
G-machine instruction set, g2add 447 447
| G-machine instruction set, g2add4 451
G-machine instruction set, gaah4 438
G-machine instruction set, gadd 447 451 724 447 451 724
G-machine instruction set, gadd4 428—430 432 438 447 450—451 567—569
G-machine instruction set, gand 724 724
G-machine instruction set, gash 724 724
G-machine instruction set, gcall 452 454 458 467 724
G-machine instruction set, gccsub4 568—569
G-machine instruction set, gclear 451 451
G-machine instruction set, gcmp 440 449 463 724 440 449 463 724
G-machine instruction set, gcom 724 724
G-machine instruction set, gdiv 724 724
G-machine instruction set, gffo4 463
G-machine instruction set, ghalt 724
G-machine instruction set, ginc 451 451
G-machine instruction set, gjcond 440 724
G-machine instruction set, gjle 565 567
G-machine instruction set, gjle 463 463
G-machine instruction set, gjle1 463
G-machine instruction set, gjmp 439 449 724
G-machine instruction set, glsh 724 724
G-machine instruction set, gmove 451 461 724 451 461 724
G-machine instruction set, gmove1 435
G-machine instruction set, gmove4 435 438
G-machine instruction set, gmult 724 724
G-machine instruction set, gneg 724 724
G-machine instruction set, gor 724 724
G-machine instruction set, grem 724 724
G-machine instruction set, grtn 452 458 463 467 724
G-machine instruction set, gsext 462 462
G-machine instruction set, gsext1 462
G-machine instruction set, gsub 463 724 463 724
G-machine instruction set, gsub4 565—568
G-machine instruction set, gsubcc 463 463
G-machine instruction set, gsubcc2 463
G-machine instruction set, gsvc 458—459 571 583
G-machine instruction set, gtc1 569—570 724
G-machine instruction set, gtest 440—441 724 440—441 724
G-machine instruction set, gtest4 565-567
G-machine instruction set, gtrtn 458—459
G-machine instruction set, gxor 724 724
G-machine instruction set, macro definitions 725—728
G-machine instruction set, summary 723—725
Gain 9 12—14 16
Gallager, R. xix
Garbage collection 348
Gate 14 22 51
Gate arrays 129 134
Gate arrays, field-programmable 134
Gates see "Logic gates"
GCD 340 343 415
General address (GA) 428 430—431
General register 354 359 367 427
General-register architecture see "Architecture general-register"
Generic instruction see "Instruction" "Generic"
Glitch 63 81 92 192 247
Goddeau, D. xx
Grain size 609
Graph, complete 239 244
Graph, data-dependency 181—182 205 355 606 608 614 620
Graph, data-flow 623
Graph, directed 181
Graph, precedence 180—181 184 186 188 195
Gray code 39 58
Greatest common divisor 198 340
Greatest common divisor, Euclid's algorithm 340
Gridlock 574
Ground 19 23
H see "Notation h
HAL see "Hard array logic"
Halting problem 274
Hand calculators 325
Handler 375
Handler procedure 458
Hard array logic (HAL) 129
Hardware, specialized 363
Harris Corporation xx
Hazard-free circuits 127
Hazard-free circuits, synthesis of 65
hazards 63 65 81 192
Hazards in latch design 81—82
Hewlett — Packard Corporation, xx 367
Hillis, Danny 616
Hit ratio see "Cache hit
Hold time 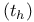 85—86 89—90 92 175 183 197 85—86 89—90 92 175 183 197
Holes 565
Hollywood 292
Horner's method 226
Hot Spot 474—475 484—485 620
Houh, H. xx
Human interface 273
I/O see "Input/output"
IBM see "International Business Machines"
IC see "Integrated circuit"
if see "R machine instruction-fetch
IFU see "Instruction-fetch unit"
Image processing 607
Impedance, characteristic 246—247
Impedance, discontinuities 246
Impedance, matching 247
Implementation transparency 354
Implementation, bit-serial 221
Implementation, byte-serial 221 225
Implementation, choices 212
Implementation, high-performance 353 459
Implementation, low-cost 353
Implementation, nibble-serial 221
Implementation, parallel 225
Implementation, parallel vs. serial 221—222
Implementation, serial 225
Implicant see "Boolean expressions implicant"
Increment enable 289
Incrementalism 606
Indeterminacy 187 195
Indeterminate behavior 187
Index register 460
indirection 433
Inference 277
Infix form 382
information 2—3 33
Information content 3
Information density 238
Information representation by continuous variables 3
Information representation, discrete 3
Information representation, electronic 2
information storage 3
Information, amount of 2—3
Information, flow of 7
Information, speed of transfer 238
Information, theoretical maximum rate of flow 7
Innovation 621
Innovation, architectural 605
Input gating 14—15
Input/Output (I/O) 253—254 264 291 348 352 356
Input/output (I/O), memory-mapped 253 548
Input/output devices 539 542 548 600
Input/output devices, device registers 253—254 548
Input/output devices, interfacing 253 591
Input/output devices, memory-mapped 619
Instruction 281 286 315 336—337 356—357 359
instruction counter see "Program counter"
Instruction formats 358—361
Instruction formats, flexible 459
Instruction formats, immediate-mode 520
Instruction formats, one-address 359
Instruction formats, short 354 451
Instruction formats, stack (zero-address) 359
Instruction formats, three-address 358 451
Instruction formats, two-address 358 451
Instruction formats, variable 451
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте