|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ward S., Halstead R. Ч Computation Structures (MIT Electrical Engineering and Computer Science) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 see "MAYBE microarchitecture" "Microcode see "MAYBE microarchitecture" "Microcode
 see "Microstack pointer" see "Microstack pointer"
% 316 626
& 316 626
* 316 351 626
+ 316 626
- 316 626
. 317 351 410 626
. notation, for structure selection see "C programming language ."
/ 316 626
7400 TTL series 106
7400 TTL series, 7400 quad 2-input NOR gate chip 106
7400 TTL series, 74151 8-input multiplexer chip 107Ч111
7400 TTL series, 74161 4-bit counter chip 119
7400 TTL series, 74163 4-bit counter chip 119
7400 TTL series, 74181 ALU chip, function select inputs 114
7400 TTL series, 74181 ALU chip, mode control input 114
7400 TTL series, 74181 arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) chip 114 132 284
7400 TTL series, 74190 4-bit counter chip 119
7400 TTL series, 74191 4-bit counter chip 119
7400 TTL series, 74194 4-bit shift register chip 118
7400 TTL series, 74198 8-bit shift register chip 118
7400 TTL series, 74LS181 arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) chip 386
: 317 629Ч631
= 317 404 626 630
@ 368
Abstract machine 269 275Ч277 313Ч314 325
Abstraction 1Ч2 275Ч277 313 315 325 357
Abstraction barriers, nondiscretionary 348
Abstraction, design of 335
Abstraction, digital 2 4 89 100 173 246 276 335
Abstraction, layers of 276
Abstraction, levels of 275Ч276 363 533
Abstraction, mechanisms 348
Abstraction, memory 473
Abstraction, virtual memory see "Virtual memory"
Access time 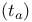 94 475 479Ч480 94 475 479Ч480
Access time 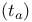 , average 471 479Ч480 , average 471 479Ч480
Accumulator 359 460
ACR see "Addressing-context register"
Activation record see "Stack frame"
Active high see "Logic conventions"
Active low see "logic conventions"
Actor 623
actual parameter see "Procedure linkage"
Adder 111 201Ч210 214
Adder, binary n-bit 111
Adder, carry 111Ч116 322Ч323
Adder, carry chain 214
Adder, carry input 284
Adder, carry look-ahead 111Ч112 132 203
Adder, carry out 284 298 307
Adder, carry propagation 284
Adder, end-around carry 38
Adder, full 111 114 130 132 201
Adder, serial 114Ч116 218
Adder, tree-structured 203 210
Addition see "Arithmetic"
Address 226 249Ч252 337 357 471Ч472
Address Assignment 249
Address in memory 127
Address register 288
Address size, maximum 472
address space 249 337 358 471 473 487 489 544Ч547 550
Address space, 32-bit 368
Address space, common 544
Address space, global 472
Address space, linear 545
Address space, segmented 545Ч547
Address space, separate 523
Address space, shared 544
Address space, single 547
Address space, virtual 489 539
address translation 494Ч495 545Ч547
Address, 32-bit 337
Address, physical 486Ч490 492Ч495 544Ч547 555
Address, virtual 486Ч495 544Ч547 555
Addressing 263Ч264
Addressing context 490 493Ч495 546Ч547 549
Addressing modes 428Ч434 460 514 520
Addressing modes, direct 429 431 520
Addressing modes, imm 430
Addressing modes, immediate 431 435
Addressing modes, implementation on MAYBE 442Ч447
Addressing modes, indexed 431Ч433 435 520 525
Addressing modes, indexed indirect 433
Addressing modes, indexed, implementation of 445
Addressing modes, indirect 431
Addressing modes, indirect indexed 431 433 446
Addressing modes, indirect register 431Ч432
Addressing modes, ix2 433
Addressing modes, offset 520
Addressing modes, PC-relative 389Ч391 435 451 525
Addressing modes, postincrement 434Ч435 442 446
Addressing modes, predecrement 434Ч435 442 446
Addressing modes, register 428 431
Addressing modes, register indirect 525
Addressing modes, short forms 450
Addressing modes, SP-relative 434Ч435 454
Addressing modes, stack pop 435
Addressing modes, stack push 435
Addressing-context register (ACR) 489Ч490 493Ч494
AdrTab 443
Agarwal, A. xx
AGT see "Timing disciplines"
Algorithm 225 325
Algorithmic transformations 609
Aliasing 495 507
Allen, Jon xix
Alt see "Timing disciplines"
ALT control modules 194
ALT operator modules 194
ALU see "Arithmetic and logic unit" "7400 "74181
Amplifier 9
Analysis 621
Analysis of machines 269
And, bitwise 316
Anderson, T. xx
Arbiter 93Ч100 195 560
Arbiter, control module 195
Arbiter, improved 96
Arbiter, naively designed 95
Arbiter, reliable asynchronous 196
Arbiter, specification of 93
Arbitration 99Ч100 241 263 560 616
Arbitration, anticipatory 176
Arbitration, asynchronous arbiter problem 94
Arbitration, problem 99Ч100 175Ч176 195Ч196 260 262
Arbitration, time 94
Architecture, complex-instruction-set (CISC) 363 530
Architecture, data-flow see "Computers data-flow"
Architecture, general-register 354Ч355 427Ч469 514 537
Architecture, graph-reduction 607
Architecture, Harvard 523
Architecture, logical-inference 607
Architecture, mesh of processing elements 622
Architecture, microcoded 282 357 529
Architecture, microinterpreter 303
Architecture, multiple instruction stream, multiple data stream (MIMD) 613 616Ч619 623
Architecture, multiprocessor 264
Architecture, no instruction stream, multiple data stream (NIMD) 613
Architecture, one-address see "Instruction formats" "One-address"
Architecture, parallel 363
Architecture, pipelined 225 531
Architecture, pre-von Neumann 364
Architecture, processor 363Ч366
Architecture, reduced-instruction-set (RISC) 134 299 363 365 513Ч532
Architecture, single instruction stream, multiple data stream (SIMD) 612Ч613 615Ч616
Architecture, single instruction stream, single data stream (SISD) 612Ч613
Architecture, stack (zero-address) 351 367Ч412
| Architecture, tagged 339Ч340
Architecture, three-address 371 427 430
Architecture, two-address 427 514
Architecture, von Neumann see "von Neumann machine"
Area on a chip 8 107
Area on a circuit board 289
Arguments see "Procedure linkage"
Arithmetic 34Ч39 284
arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) 114 197 284 288 292Ч293 297Ч298 307 515
Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), control inputs 284
Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), function 284 297
Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), function select 284
Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), mode input 284
Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), outputs 284
Arithmetic functions 127
Arithmetic modules 111
Arithmetic, 16-bit addition 322
Arithmetic, 16-bit, on MAYBE 308
Arithmetic, addition on Turing machine 270
Arithmetic, binary addition 35 111Ч116
Arithmetic, binary division 36
Arithmetic, binary multiplication 35
Arithmetic, binary subtraction 36
Arithmetic, fixed-point 35Ч36
Arithmetic, multiple-precision 322
Arithmetic, multiple-precision, in MAYBE microcode 322Ч323
Arithmetic, signed comparison 387
Arithmetic, signed test 387
Arithmetic, unsigned test 387
Arithmetic, vector addition 612
Array 338 631Ч633
array of characters 338 405 633
Array processors, associative 616
Array, dynamically allocated 433
Array, element 338
Array, element access 432Ч433
Array, zero-indexed 631
ART 621Ч622
ASCH see "Character code ASCII"
Assembler 314 361
assembly 314
Assembly language 315Ч318 361Ч362 365
Assembly language, .include directive 318Ч319 370
Assembly language, .macro directive 317Ч318
Assembly language, arithmetic expressions 362
Assembly language, colon (:) 317
Assembly language, current location 317
Assembly language, pseudo-operations 389
Assembly language, symbolic names 314 317
Assembly language, vertical bar 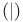 319 319
Assertion edge see "Bus protocol assertion
ASSIGNMENT 277 630
assignment statement 365 609
Astable behavior 77
Asynchrony 176Ч177
Atomic action 372
Atomic instruction see "Instruction atomic"
Atomic update 576
atomicity 566Ч569
Atomicity by disabling interrupts 567Ч568
Automata 154
Automata, cellular 607 613 621Ч622
Automata, trainable 607
automobile 597
Ayers, A. xx
Back-out 491 543 576
backplane 245 248
Backtracking 607
Bandwidth 7Ч8
banking system see "Systems on-line
Base 545 555
Base address 432
Base-of-frame pointer 368 393 395 454
Base-of-frame register 434
Batcher, Kenneth 222
Baud 7
BCD see "Number representations binary-coded
Bell Telephone Laboratories 625
Berkeley, University of California at 530
BINARY 316
Binary tree 242Ч243
Binding 319
Bit 2 33Ч34 147Ч148 337
Bit frequency 261Ч262
Bit time 260Ч261
bits per second 7
Blair, M. xx
Block 345 487 628
Block structure 348
Boolean algebra 16 49Ч54
Boolean algebra, absorption identity 52
Boolean algebra, associative law 49 52
Boolean algebra, commutative law 49 52
Boolean algebra, complement identity 52
Boolean algebra, DeMorgan's law 52 55
Boolean algebra, distributive law 52
Boolean algebra, duality 53Ч54
Boolean algebra, idempotence 52
Boolean expressions 49Ч51 58
Boolean expressions, implicant 59 126
Boolean expressions, implicant, prime 59 65
Boolean expressions, literal 59
Boolean expressions, manipulation of 52Ч54
Boolean expressions, product 49
Boolean expressions, product-of-sums see "Product-of-sums expressions"
Boolean expressions, sum 49
Boolean expressions, sum-of-products see "Sum-of-products expressions"
Boolean expressions, term 49 58
Boolean functions 4 14 47Ч51 58
Boolean functions, AND 47Ч54 58
Boolean functions, complete set 49
Boolean functions, NAND 48Ч49 51 55Ч56
Boolean functions, NOR 48Ч49 51
boolean functions, not 48Ч54 56 58
Boolean functions, OR 47Ч54 58 238
Boolean functions, XOR (exclusive OR) 47Ч49 51
Bound 555
Brain 605
Branch conditions 386Ч387 697
Branch delay 524Ч525
Branch, conditional 523
Branch, multiway 629
Branch, target address 307
Buffer memory, lookaside 480
Buffer memory, TLB miss 489
Buffer memory, translation lookaside buffer (TLB) 487 489Ч490 492 494Ч497 507 549
Buffer, circular 563
Buffer, first-in/first-out (FIFO) 563
Buffer, overflow 564Ч565 588
Buffer, underflow 563 589
buffered output 588
Bug 187
Bus 183 239Ч241 244Ч259 264 617Ч619
Bus arbitration 254Ч257 573
Bus arbitration, arbitration contest 254Ч257
Bus arbitration, arbitration priority 256
Bus arbitration, binary-OR 256Ч257 265
Bus arbitration, centralized 267
Bus arbitration, centralized arbitration logic 256
Bus arbitration, daisy-chained 256
Bus arbitration, fair 265 573
Bus arbitration, grant signal 254Ч255
Bus arbitration, request signal 254Ч255
Bus protocol 254
Bus protocol, assertion edge 248 255
Bus protocol, continue code 257
Bus protocol, hold code 258
Bus protocol, locally timed 248
Bus protocol, OK code 257
Bus protocol, overhead 257
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте