|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ward S., Halstead R. — Computation Structures (MIT Electrical Engineering and Computer Science) |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Computation, bit-serial 616
Computation, mathematics of 271
Computation, models of 277 606—608
Computation, neural models of 622
Computation, numerical 287 364
Computation, parallel 363 606 622
Computation, serialization of 184
Computation, symbolic 364
Computation, von Neumann model of 606
Computational complexity 225
Computational power 270—275
Computer architecture 225 277 472 621
Computer architecture, research in 264
Computer Consoles, Inc. 529
Computer science 269 277 325
Computer science, modern 277
Computers 286
Computers, 32-bit 359
Computers, AMD Am2900 chip family 325
Computers, Atlas 497 550
Computers, Berkeley RISC 530
Computers, Burroughs B5000 412 496
Computers, Burroughs B6500 365 412 496
Computers, Burroughs B6700 340 365 412 548 550
Computers, Burroughs B7500 365 412 496
Computers, Burroughs B7700 365 412
Computers, C.mmp 623
Computers, Caltech Cosmic Cube 623
Computers, Cm* 623
Computers, commercial 364
Computers, commercial parallel computers 623
Computers, Connection Machine 616 622
Computers, Control Data CDC 6600 365
Computers, Control Data CDC 7600 355 365 614
Computers, Control Data CDC STAR 615
Computers, Control Data CYBER series 355 365
Computers, Cray-1 365 477 615
Computers, Cray-2 365
Computers, Cray-X/MP 365
Computers, Cray-Y/MP 365
Computers, CRISP 496
Computers, data-flow 606 614 620
Computers, DEC PDP-1 600
Computers, DEC PDP-10 439 460
Computers, DEC PDP-11 245 264 286 299 325 358 427 434 460 550
Computers, DEC VAX-11 286 299 325 427 434 451 460
Computers, DEC VAX-11/780 497
Computers, families of 353
Computers, fixed-word-length 287
Computers, Fujitsu VP series 365
Computers, general-purpose 210 224 272—273 281 295 605
Computers, Goodyear MPP (Massively Parallel Processor) 622
Computers, Goodyear STARAN 616 622
Computers, Harris HCX series 529
Computers, high-performance 264 287 299 365 471 513 613
Computers, Honeywell 6180 550
Computers, Honeywell 645 497 550
Computers, IBM 360/91 365 614
Computers, IBM 801 530
Computers, IBM personal computer 460
Computers, IBM Series/1 433
Computers, IBM System/360 286 299 325 353 427 433 460
Computers, IBM System/370 325 427 433 460
Computers, ILLIAC IV 615—616 622
Computers, Inmos Transputer 529
Computers, Intel 8008 460
Computers, Intel 80286 550
Computers, Intel 8080 460
Computers, Intel 8086 286 460 550
Computers, Intel 80X86 496
Computers, Intel iPSC 623
Computers, LISP machine 325 340
Computers, LMI Lambda 529
Computers, mainframe 460 496 600
Computers, MAYBE see "MAYBE computer"
Computers, microcoded 275
Computers, Motorola 68000 286 427 433 460
Computers, Motorola 680X0 496
Computers, MuNet 623
Computers, National 32032 460
Computers, NEC SX series 365
Computers, NEC SX-2 477
Computers, PEPE 622
Computers, personal 496
Computers, Sanders OMEN 616
Computers, single-chip 22
Computers, SOLOMON 622
Computers, Stanford MIPS 530
Computers, stored-program 356
Computers, Symbolics 3600 365 412 496
Computers, TI ASC 615
Computing environments, shared 348
Concurrency 181 190 471 477
concurrency control 576
Condition code 440 449 458 612
Condition register bit 298
Condition-code bits 385
Condition-code byte 372 385—386 388 439
Condition-code register 306—307 323 439
Connector 254
Connector, design 246
Constants 307
Constants, immediate 520
Constants, quick 521
Constants, short immediate 521
Constraints 1-2
Constraints, control structure 183
Constraints, cost 133
Constraints, hard real-time 594
Constraints, mutual-exclusion 183—184 187 195 199 559—561
constraints, precedence see "Precedence constraints"
Constraints, real-time 594
Constraints, timing 172
Constraints, topological 183
Contamination delay 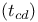 4 18—19 85 89—90 92 4 18—19 85 89—90 92
Contention 243 263—264
Contention networks 263—264
context 535
Context information 349—352 408—411
context switching 349—351 458 494 535—536 543 592
Context switching, overhead 543
Control 127
Control circuitry 171 175 217
Control disciplines see "Timing disciplines"
Control logic 282
Control of digital systems 83
Control signals 178 188 190 198 246—247 269 294 303 313 612
Control signals, asynchronous 177
Control signals, finish 176—177 190 194 248—252
Control signals, start 176—177 183 194 248—252 260
Control signals, timing of 179 184
Control structure 171—200
Control structure, modular 194—196 198—199
Control structure, self-timed 182
Control systems, adaptive 607
Control, inputs 190 282 304
Control, links 194
Control, machines 269
Control, mechanisms 365
Control, modules 195 199
Control, outputs 182 190—191 283 292
Control, registers 282
Controller 188 190 198
Conversion between different operand lengths 369
Conway, John Horton 607
Coordinates, Cartesian 228
Coordinates, polar 228
Copy rule 364
Core see "Memory magnetic
Cost 201 207 221 224—225 310 353 473 479 482 513 517 530 608—612 616 622
| Cost of integrated circuits 105—106
Cost of software development 273
Cost of software maintenance 273
Cost of wiring 245
Cost per bit 289
Cost, asymptotic 238
Cost, hardware 243 298
Cost, wiring 192
Cost-performance trade-offs 133 201 212—221 428 473
Cost/performance ratio 530
Cost/performance ratio of RISC architectures 363
Cost/throughput ratio 221
Counter 118 173 188 288
Counter, binary 118—119
Counter, clear input 119
Counter, count input 119
Counter, divide-by-2 159
Counter, divide-by-3 164
Counter, divide-by-5 146
Counter, init input 119
Counter, load input 119
Counter, modulo N 138
Counter, up/down 160 531
CPU see "Central processing unit"
CPU load 597
Creativity 621—622
Critical path 18
Critical region 562 590—591
Critical region, conditional 576
Crosstalk 247
CurProc 538 542
Current, output 11
Cycle time 475
Cycles in logic circuit 76
Cyclic path 91
Cyclic redundancy check 43
Daisy chain 254—255
Dally, W. xx
DATA 356
Data base 576—577
Data base, on-line 576
Data channel 600
Data dependencies 180—185 206 210 224 559 608 614
Data dependencies, deduction of 181
Data dependencies, essential 620
Data formats 360—361
Data packets 226
Data paths 171 178—179 188 190 269 282—283 287 612—613 616
Data paths, application-specific 178
Data paths, bit-serial 616
Data paths, replicated 612
Data paths, topology 180 183—186
Data paths, universal 178
Data paths, width 286 514
Data registers 282
Data representation, parallel 116—118
Data representation, serial 116—118
Data structures 337—338 365
Data structures, aggregate 338
Data transmission 162
Data transmission, serial 162
Data transmission, serial vs. parallel 7
Data types 337—340 625—626 633
Data types, abstract 404
Data types, compound 337—338
Data types, first-class 404
Data types, run-time type discrimination 339—340
data types, simple 337
Data types, type-checking hardware 530
data types, user-defined 365
Data, bit-serial 259
Data, multibyte 286—287 359 368
Data, multibyte, representation of 299
Data, scalar 612
Data, self-clocking 260—264
Data, sizes 221 286—287 360—361
Data, stale 618
Data, tagged 365
Data, textual 633
Data, vector 612
Data, widths 368
Data-channel controller 600
Deadlock 559 573—576
Deadlock, avoidance 574—575 577
Deadlock, avoidance via banker's algorithm 577
Deadlock, recovery 574 577
Debugger 546
Debugging 356
declaration 339 345 347 537 625—626 628 630
Declaration of pointers 351
Declaration of procedures 628
Declaration of structures 633
Declaration of variables 625
Decoder 121—122 127 293
Delay 61
Delay element 86 91
Delay line 173—174
Dennis, Jack B. xix 194
density 21 289
Density of circuits 21—24
Density, limits to 22
Dereferencing 351
Design automation 134
Design discipline 2
Design of complex systems 1
Design of machine languages 337—353
Design, custom-chip design tools 106
Design, speed-independent 65
Design, system 276
Design, TTL 107
Design, VLSI 134
Determinacy 186—187
Device timings, data-dependent 190
Device, electronic 2
Device, external 291
Device, linear 13—14
Device, nonlinear 13
Device, passive 14—15
Diagonal proof 275
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) 245 264 530 600
Dijkstra, E.W. 566 576
Dimensionality of space 238
Diode 15 19
Diode, Schottky 21
Diode, silicon 19
Direct Memory Access (DMA) 600
Discipline, dynamic 8 85 89—93 147 171 173—174
Discipline, static 5—7 12—13 91
Discrete time 89 171 191
Disk see "Memory magnetic
Dispatch 307 357
Dispatch table 308
Display, seven-segment 72 136—137
Distance, physical 238
distributed system 264
Division see "Arithmetic"
DMA see "Direct memory access"
Domain 348—349
DRAM see "Dynamic RAM"
Drum see "Memory magnetic
Dry run 492 496
DTL see "Logic families"
Dummy argument see "Procedure linkage" "Formal
Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 289—291 311 321 323 374 376 475
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), chips 290 475
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), column address 290
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), column-address strobe (CAS) 290
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), frequency of refresh 323
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), refresh 290 311 323 332 375
Dynamic RAM (DRAM), row 311
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте