Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Sattler K.D. — Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional NanomaterialsАвтор: Sattler K.D. Аннотация: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials illustrates the importance of tailoring nanomaterials to achieve desired functions in applications. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers various composites, including carbon nanotube/polymer composites, printable metal nanoparticle inks, polymer�clay nanocomposites, biofunctionalized titanium dioxide-based nanocomposites, nanocolorants, ferroic nanocomposites, and smart composite systems. It also describes nanoporous materials, a giant nanomembrane, graphitic foams, arrayed nanoporous silicon pillars, nanoporous anodic oxides, metal oxide nanohole arrays, carbon clathrates, self-assembled monolayers, epitaxial graphene, and graphene nanoribbons, nanostructures, quantum dots, and cones. After focusing on the methods of nanoindentation and self-patterning, the book discusses nanosensors, nano-oscillators, and hydrogen storage. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2011Количество страниц: 790Добавлена в каталог: 12.07.2014Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Spin valves, linewidths 38-15 Spin valves, spectra 38-16 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), advantages 38-1 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), barrier type and stack configuration, MTJ 38-13 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), barrier type and stack configuration, spin valves 38-12 thru 38-13 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), barrier type and stack configuration, stack deposition 38-13 thru 38-14 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), barrier type and stack configuration, synthetic antiferromagnetic (SAF) layer 38-13 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), challenges 38-1 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), chip-to-chip communication 38-21 thru 38-22 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), circuit model 38-16 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), equation of motion and phase diagram with applied current 38-10 thru 38-12 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), equation of motion and phase diagram with damping 38-9 thru 38-10 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), equation of motion and phase diagram without damping 38-6 thru 38-9 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), frequency 38-14 thru 38-15 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), linewidth 38-16 thru 38-17 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), measurement 38-16 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), micromagnetics 38-17 thru 38-18 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), microwave emission 38-1 38-2 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), outputs 38-16 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), patterning geometry and magnetic configuration 38-14 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), phase locking 38-19 thru 38-20 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), schematics 38-1 38-2 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), signal processing 38-21 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spin transfer, CPP configuration 38-4 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spin transfer, density of states and conductivity 38-3 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spin transfer, device resistance 38-3 thru 38-4 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spin transfer, electrons polarization 38-2 thru 38-3 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spin transfer, MTJ 38-4 thru 38-5 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spin transfer, sd model 38-3 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spin transfer, spin torque 38-5 thru 38-6 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), spinwaves 38-18 Spin-transfer nano-oscillators (STNO), vortex oscillator 38-18 thru 38-19 Spinwaves 38-18 STNO see "Spin-transfer nano-oscillators" Strain-induced elastic buckling instability for mechanical measurements (SIEBIMM) 11-6 Stranski — Krastanow (S-K) mode 34-6 Substrate self-patterning, adsorbate-induced surface self-patterning, flatland patterning 31-8 thru 31-11 Substrate self-patterning, adsorbate-induced surface self-patterning, self-created ridges 31-11 thru 31-14 Substrate self-patterning, epitaxy 31-5 thru 31-6 Substrate self-patterning, Ge quantum dots 31-14 Substrate self-patterning, Ge quantum dots, self-organized growth technique 31-1 thru 31-2 Substrate self-patterning, Ge quantum dots, strain-induced spatial arrangement 31-1 Substrate self-patterning, low-energy electron microscopy and diffraction vs. X-ray diffraction 31-7 thru 31-8 Substrate self-patterning, low-energy electron microscopy and diffraction, instrument 31-6 thru 31-7 Substrate self-patterning, low-energy electron microscopy and diffraction, operation principle 31-7 Substrate self-patterning, surface adsorption 31-2 Substrate self-patterning, surface reconstructions and morphology, 31-4 thru 31-5 Substrate self-patterning, surface reconstructions and morphology, 31-3 thru 31-4 Substrate self-patterning, surface reconstructions and morphology, 31-5 Substrate self-patterning, surface reconstructions and morphology, scanning tunneling microscope 31-3 Substrate self-patterning, surface reconstructions and morphology, simple cubic crystal 31-2 thru 31-3 Substrate self-patterning, surface reconstructions and morphology, surface relaxation 31-2 Suction energy 36-4 Sulfur dyes 5-2 Sum frequency generation (SFG) 17-11 Supermicropores 9-3 Surface adsorption 31-2 Surface plasmon polariton (SPP) 32-11 thru 32-12 Surface reconstructions and morphology see "Substrate self-patterning" Surface relaxation 31-2 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), adenine detection, electromagnetic field enhancement 13-13 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), adenine detection, first-order optical phonon scattering 13-11 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), adenine detection, localized surface plasmons (LSPs) 13-13 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), adenine detection, metal species 13-12 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), adenine detection, Raman spectra 13-11 thru 13-12 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), adenine detection, water solutions 13-10 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), detection stability 13-13 thru 13-14 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), DNA rapid sequencing process 13-10 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), sensor 33-2 33-4 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), sensor, glucose measurement 33-10 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), sensor, metallic nanosensors 33-6 SWNH see "Single-walled carbon nanohorns" Taylor series 23-9 thru 23-10 Temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) 17-5 Thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS) 17-5 Thermal excitation processes 34-3 thru 34-4 Thermal noise current 34-10 Thermal reemission process 34-5 Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) 1-13 Thermometer, alternating current excitation, experimental configuration 32-14 thru 32-15 Thermometer, alternating current excitation, measurement 32-15 thru 32-16 Thermometer, measurement principle 32-13 Thermometer, microelectronic device heating experimental configuration 32-13 thru 32-14 Thermometer, microelectronic device heating FIR, aluminum stripe 32-14 thru 32-15 Thiazin and thiazole dyes 5-4 Tight binding 18-18 Tip roundness 27-7 thru 27-9 Titania nanohole array, electrode after measurement 15-7 Titania nanohole array, electrode with ITO 15-8 Titania nanohole array, electrode, 15-6 Titania nanohole array, electrode, charge-discharge properties 15-7 Titania nanohole array, electrode, electrical double-layer capacity 15-8 Titania nanohole array, electrode, LPD method 15-6 thru 15-7 Titania nanohole array, electrode, surface structure 15-6 thru 15-7 Titania nanohole array, electrode, XRD patterns 15-7 Titania nanohole array, network-type titania nanohole array 15-5 Transition-metal oxide 10-10 Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) 3-7 Triarylmethane dyes 5-3 Tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) device 38-1 thru 38-3 38-5 38-13 U.S. Council for Automotive Research (USCAR) 41-2 Ultramicropores 9-3 Ultrasonication process 1-4 Vat dyes 5-2 Vibrating wheel gyroscopes 35-18 Volumetric capacity 41-2 Von Mises stress distributions, coefficients of friction 27-7 27-8 Von Mises stress distributions, tip radius 27-8 27-9 Vortex oscillator 38-18 thru 38-19 Wavefunction-based (WFB) method 40-13 thru 40-14 Weighted average corporate vehicle (WACV) 41-2 Wide-angle x-ray diffraction (WAXD) 3-7 Wilhelmy balance technique 1-2 X-ray diffraction (XRD) 31-7 thru 31-8 X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) 17-5 X-ray reflexivity (XR) 17-4 Xanthene dyes 5-4 Young’s modulus 25-10 27-3 Zeeman effects 4-3 Zigzag nanoribbons, atomic structure 20-3 Zigzag nanoribbons, Brillouin zone 20-4 Zigzag nanoribbons, Dirac equation 20-5 thru 20-6 Zigzag nanoribbons, electron-electron interactions 20-7 thru 20-9
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



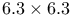 surface structure
surface structure 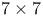 unit cell
unit cell 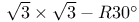 structure
structure 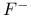 scavenger
scavenger