Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Sattler K.D. — Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional NanomaterialsАвтор: Sattler K.D. Аннотация: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials illustrates the importance of tailoring nanomaterials to achieve desired functions in applications. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers various composites, including carbon nanotube/polymer composites, printable metal nanoparticle inks, polymer�clay nanocomposites, biofunctionalized titanium dioxide-based nanocomposites, nanocolorants, ferroic nanocomposites, and smart composite systems. It also describes nanoporous materials, a giant nanomembrane, graphitic foams, arrayed nanoporous silicon pillars, nanoporous anodic oxides, metal oxide nanohole arrays, carbon clathrates, self-assembled monolayers, epitaxial graphene, and graphene nanoribbons, nanostructures, quantum dots, and cones. After focusing on the methods of nanoindentation and self-patterning, the book discusses nanosensors, nano-oscillators, and hydrogen storage. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2011Количество страниц: 790Добавлена в каталог: 12.07.2014Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Optochemical nanosensors, design using nanoparticle, titania nanoparticle sensor 33-6 Optochemical nanosensors, intracellular measurement 33-11 Optochemical nanosensors, laboratory assay 33-10 thru 33-11 Optochemical nanosensors, live cells 33-7 thru 33-8 Optochemical nanosensors, nanoparticle 33-3 Optochemical nanosensors, optical fibers 33-1 Optochemical nanosensors, performance 33-1 33-2 Optochemical nanosensors, schematic diagram 33-4 Optochemical nanosensors, sensing component, analyte-sensitive molecular probe 33-3 Optochemical nanosensors, sensing component, fluorescence 33-3 thru 33-4 Optochemical nanosensors, sensing component, LSPR 33-4 Optochemical nanosensors, sensing component, SERS 33-4 Optochemical nanosensors, toxicity and/or bioelimination 33-11 Ordered mesoporous materials, fundamental characteristics 10-1 thru 10-2 Ordered mesoporous materials, influence factors 10-9 Ordered mesoporous materials, inorganic-organic interaction 10-7 thru 10-8 Ordered mesoporous materials, MCM series 10-9 thru 10-10 Ordered mesoporous materials, non-silica-based mesoporous materials 10-10 Ordered mesoporous materials, ordered mesoporous films 10-10 thru 10-11 Ordered mesoporous materials, structure 10-2 thru 10-3 Ordered mesoporous materials, surfactant interaction 10-8 thru 10-9 Ordered mesoporous materials, synthesizing mechanism, auxiliary organic macromolecules 10-4 Ordered mesoporous materials, synthesizing mechanism, cooperative organization mechanism 10-5 thru 10-6 Ordered mesoporous materials, synthesizing mechanism, inorganic monomer molecule 10-3 Ordered mesoporous materials, synthesizing mechanism, liquid crystal templating (LCT) mechanism 10-3 10-5 Ordered mesoporous materials, synthesizing mechanism, MCM-41 formation 10-3 thru 10-4 Ordered mesoporous materials, synthesizing mechanism, silicate rod assembly mechanism 10-5 Ordered mesoporous materials, synthesizing mechanism, silicatropic liquid crystals’ mechanism 10-5 thru 10-6 Ordered mesoporous materials, transition-metal oxide 10-10 Oriented polymer composites 1-10 thru 1-11 Oxazin and oxazone dyes 5-4 Partially occupied molecular orbital (POMO) 24-6 Pawlow equation 2-8 PCNs see "Polymer-clay nanocomposites" Percolation threshold modeling 1-11 thru 1-12 Phonon bottleneck effect 34-2 Phonon density of states (p — DOS) 16-14 thru 16-15 Photoemission electron microscopy (PEEM) 31-7 photolithography 30-7 thru 30-8 Photoluminescence (PL) 34-6 thru 34-7 Photoluminescence (PL), band-band recombination process 13-5 Photoluminescence (PL), Gauss — Newton method 13-5 Photoluminescence (PL), PL excitation (PLE) spectra 13-5 13-7 Photoluminescence (PL), QC/luminescence center (QCLC) model 13-6 Photoluminescence (PL), quantum confinement (QC) model 13-5 thru 13-6 Photoluminescence (PL), spectra 13-5 thru 13-6 Photonic explorer for biomedical use with biologically localized embedding (PEBBLE) sensor 33-2 33-7 Physisorption 31-2 41-2 42-3 Physisorption vs. chemisorption 41-4 42-3 Physisorption, hydrogen adsorption, adsorbed density 42-4 Physisorption, hydrogen adsorption, adsorbed volume 42-3 thru 42-4 Physisorption, hydrogen adsorption, adsorption vs. desorption 42-3 Physisorption, hydrogen adsorption, differential enthalpy 42-4 Physisorption, hydrogen adsorption, supercritical and subcritical adsorption 42-3 Physisorption, hydrogen physisorption at nanoscale, GCMC simulations 41-6 Physisorption, hydrogen physisorption at nanoscale, gravimetric capacity 41-6 thru 41-7 Physisorption, hydrogen physisorption at nanoscale, Lennard — Jones interactions 41-5 thru 41-6 Physisorption, hydrogen physisorption at nanoscale, pore size distribution 41-6 Physisorption, hydrogen-surface interaction 41-4 Physisorption, specific pore volume 41-5 Physisorption, specific surface area 41-4 thru 41-5 Pi orbital vector analysis (POAV) 16-8 Piezoelectric force microscopy (PFM) 7-1 thru 7-2 Piezoelectric technique, admittance 35-14 Piezoelectric technique, applications 35-17 Piezoelectric technique, detection electrode 35-14 Piezoelectric technique, doubly clamped piezoelectric beam 35-15 thru 35-17 Piezoelectric technique, electromechanical coupling coefficient 35-14 Piezoelectric technique, equivalent electrical RLC circuit 35-15 Piezoelectric technique, free piezoelectric block 35-14 thru 35-15 Piezoelectric technique, strain 35-13 Piezoelectric technique, two-port piezoelectric bulk resonator 35-13 thru 35-14 PL see "Photoluminescence" Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), Bakelite 3-1 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), barrier properties 3-11 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), biodegradability 3-12 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), chemical resistance 3-12 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), classification 3-5 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), clay minerals, surface modification 3-4 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), clay minerals, types and structures 3-2 thru 3-4 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), composite material 3-1 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), computer-based simulation techniques 3-9 thru 3-10 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), drug delivery 3-13 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), DSC 3-8 thru 3-9 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), flame retardancy 3-12 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), mechanical properties 3-11 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), nuclear magnetic resonance 3-7 thru 3-8 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), Nylon6-clay 3-2 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), optical properties 3-12 thru 3-13 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), preparation methods in situ intercalative polymerization method 3-6 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), preparation methods, melt intercalation method 3-6 thru 3-7 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), preparation methods, polymer intercalation 3-5 thru 3-6 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), preparation methods, thermoset and thermoplastic polymers 3-7 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), rheology modifiers 3-13 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), TEM 3-7 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), thermal stability and heat distortion temperature 3-11 thru 3-12 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), wastewater treatment 3-14 Polymer-clay nanocomposites (PCNs), WAXD 3-7 Pore-filling 14-10 thru 14-11 Pre-amplifier and resonance noise 35-8 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, compact shell model 2-6 thru 2-7 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, dispersant shell volatilization 2-6 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, fee and sc structures 2-5 thru 2-6 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, hardness and Young’s modulus 2-4 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, nanocrystalline morphology 2-7 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, nominal van der Waals contact 2-4 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, rep and rip structures 2-5 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, contracted random loose packing model, SAM dispersants 2-6 thru 2-7 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, inkjet printing, droplet formation and deposition 2-21 thru 2-22 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, inkjet printing, surface tension effect 2-20 thru 2-21 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, insulator-to-metal transformation, differential scanning calorimetry 2-12 thru 2-13 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, insulator-to-metal transformation, optical spectroscopy 2-11 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, insulator-to-metal transformation, sparse shells 2-13 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, insulator-to-metal transformation, strong ligand-shell effect 2-13 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, insulator-to-metal transformation, transformation temperature ( 2-10 thru 2-11 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, insulator-to-metal transformation, vibrational spectroscopy, ligand shell 2-12 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, matrix dilution effect 2-7 thru 2-8 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, nanometal vs. ECA characteristics 2-3 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, nanoparticle core size 2-8 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, optical plasmon resonance, dilute spectra, dielectric medium 2-15 thru 2-17 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, optical plasmon resonance, dipole theory 2-14 thru 2-15 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, optical plasmon resonance, thin film spectra 2-17 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, printable electronics 2-1 thru 2-2 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, printable metal systems 2-2 thru 2-3 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, solution-phase preparation, gold nanoparticles 2-17 thru 2-20 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, solution-phase preparation, phase-transfer Brust — Schiffrin method 2-17 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, solution-phase preparation, Pt and Pd nanoparticles 2-20 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, solution-phase preparation, silver nanoparticles 2-17 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, spherical approximation 2-4 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, thermodynamic size-dependent melting temperature, conductivity vs. heat-treatment temperature 2-10 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, thermodynamic size-dependent melting temperature, Hanszen — Wronski equation 2-8 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, thermodynamic size-dependent melting temperature, nanoparticle core diameter 2-9 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, thermodynamic size-dependent melting temperature, Pawlow equation 2-8 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, thermodynamic size-dependent melting temperature, Sambles equation 2-9 Printable metal nanoparticle inks, thermodynamic size-dependent melting temperature, size-dependent melting enthalpy 2-10 Pt and Pd nanoparticles 2-20 Pyronin dyes 5-4 Qantum dot (QD) sensors 33-6 QDIPs see "Quantum dot infrared photodetectors" Quality factor 35-3 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), dark current and noise current measurement 34-9 thru 34-10 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), detection spectrum 34-8 thru 34-9 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), fabrication 34-7 thru 34-8 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), focal plane array development and characterization, 34-11 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), focal plane array development and characterization, 34-13 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), focal plane array development and characterization, cross-talk measurement 34-13 thru 34-14 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), focal plane array development and characterization, flip-chip bonding hybridization process 34-12 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), focal plane array development and characterization, ROIC chips 34-11 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), focal plane array development and characterization, sensitivity 34-13 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), focal plane array development and characterization, thermal and fully packaged FPA image 34-12 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), photoconductive gain and photoresponsivity measurement 34-10 thru 34-11 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), photodetectivity (D-) calculation 34-10 thru 34-11 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD growth and characterization 34-6 thru 34-7 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD properties, conduction band 34-1 thru 34-2 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD properties, DOS 34-2 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD properties, interaction Hamiltonian 34-3 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD properties, LO phonon-scattering process 34-2 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD properties, matrix element 34-3 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD properties, transition rates 34-2 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), QD properties, wavefunction and energy state 34-1 thru 34-2 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), structure and advantages, band diagram 34-3 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), structure and advantages, dark current density 34-4 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), structure and advantages, high photoconductive gain 34-5 thru 34-6 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), structure and advantages, low dark current 34-3 thru 34-5 Quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIPs), structure and advantages, normal incidence light detection capability 34-3 Quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) 40-10 40-17 Quinone-imine dyes 5-4 Raman spectra, Ag/Si-NPA 13-11 thru 13-12 Raman spectra, carbon foams 12-4 thru 12-9 Raman spectroscopy 12-3 thru 12-6 17-4 Ratiometric measurement 33-1 Reactive dyes 5-2 Reversible hydrogen storage 41-4 41-6 41-14 Rhodamine dyes 5-4 Saccharose-based carbon nanofoams 12-2 Sambles equation 2-9 SAMs see "Self-assembled monolayers" Scanning force microscopy (SFM) 17-4 Scanning probe microscope (SPM) lithography 28-4 Schottky barrier model 14-12 thru 14-13 Schroedinger equation 18-18 20-2 20-5 26-11 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) 30-10 thru 30-12 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), adatom geometry 7-2 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), alkanethiol molecules, Au(111), 17-7 thru 17-8 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), alkanethiol molecules, Au(111), chemical intuition 17-6 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), alkanethiol molecules, Au(111), equilibrium structures 17-7 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), alkanethiol molecules, Au(111), helium diffraction 17-6 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), alkanethiol molecules, Au(111), herringbone profile 17-7 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), alkanethiol molecules, Au(111), HREELS spectroscopy 17-6 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), chemisorb 17-1 thru 17-2 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), FTIR 7-2 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), growth and kinetics, in-plane phase 17-11 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), growth and kinetics, Langmuir kinetics 17-10 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), growth and kinetics, molecular surface density 17-9 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), growth and kinetics, phases of decanethiol 17-10 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), growth and kinetics, physical and chemical properties 17-10 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), growth and kinetics, potential curve 17-10 thru 17-11 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), growth and kinetics, SFG measurement 17-11 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), metal nanoparticles 17-8 thru 17-9 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), microcantilevers 7-3 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), molecular electronics 17-14 thru 17-15 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), nanobiomolecular applications 17-11 thru 17-12 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), nanolithography 7-3 17-13 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), nonlinear optics 17-15 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), organosilicon derivatives, hydroxylated surfaces 17-8 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), physisorption 17-1 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), preparation 7-3 thru 7-4 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), prototypical organic-inorganic interfaces 17-1 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), surface characterization 7-4 thru 17-5 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), switchable interfaces 17-12 thru 17-13 Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), two-dimensional order 7-5 SERS see "Surface-enhanced Raman scattering" Sets see "Single-electron transistors" Shot noise 35-8 Si-34 lattice, e-DOS 16-13 thru 16-14 Si-34 lattice, p-DOS 16-14 thru 16-15 Si-34 lattice, pressure 16-15 Si-NPA see "Silicon nanoporous pillar array" Silicon clathrate, 16-10 Silicon clathrate, bubble soap 16-6 thru 16-7 Silicon clathrate, clathrate I 16-4 Silicon clathrate, clathrate II 16-3 thru 16-5 Silicon clathrate, crystallography 16-10 Silicon clathrate, electronic structure, cohesive energy 16-11 Silicon clathrate, electronic structure, distortion 16-12 thru 16-13 Silicon clathrate, electronic structure, frustration 16-12 Silicon clathrate, electronic structure, Si-34 lattice 16-13 thru 16-15 Silicon clathrate, electronic structure, stacking mode 16-12 Silicon clathrate, elementary cages 16-10 thru 16-11 Silicon clathrate, fivefold symmetry and lattices 16-4 16-6 Silicon clathrate, Greek mythological etymology 16-2 Silicon clathrate, high-pressure synthesis 16-3 Silicon clathrate, laves phase vs. clathrate II 16-10 Silicon clathrate, low-pressure synthesis 16-2 thru 16-3 Silicon clathrate, tetrahedra stacking 16-10 Silicon clathrate, topology, 3D Euclidean space 16-8 Silicon clathrate, topology, Bravais lattice 16-7 Silicon clathrate, topology, nanocages 16-6 Silicon clathrate, topology, nonregular polyhedra 16-6 thru 16-7 Silicon clathrate, topology, POAV 16-8 Silicon clathrate, topology, primitive space 16-9 Silicon clathrate, topology, Riemann’s analysis 16-8 thru 16-9 Silicon clathrate, topology, Schlafli’s theorem 16-7 Silicon clathrate, topology, schwarzite structure 16-9 Silicon clathrate, topology, translational symmetry 16-8 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), biomolecule detection, Ag/Si-NPA, adenine detection 13-10 thru 13-13 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), biomolecule detection, Ag/Si-NPA, preparation and characterization 13-10 thru 13-11 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), biomolecule detection, Ag/Si-NPA, SERS detection stability 13-13 thru 13-14 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), capacitive humidity sensitivity 13-7 thru 13-8 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), CdS/Si nanoheterojunction array, electrical properties 13-19 thru 13-20 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), CdS/Si nanoheterojunction array, preparation and characterization 13-16 thru 13-18 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), CdS/Si nanoheterojunction array, semiconductor nanoheterostructures 13-16 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), CdS/Si nanoheterojunction array, three-primary-color, photoluminescence 13-18 thru 13-19 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), CNT/Si-NPA, enhanced field emission 13-15 thru 13-16 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), CNT/Si-NPA, preparation and characterization 13-14 thru 13-15 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), humidity hysteresis 13-9 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), morphology control 13-3 thru 13-4 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), nanocomposites 13-4 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), optical properties, light absorption 13-4 thru 13-5 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), optical properties, photoluminescence 13-5 thru 13-7 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), preparation 13-1 thru 13-2 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), response and recovery time 13-8 thru 13-9 Silicon nanoporous pillar array (Si-NPA), structural and morphological characterization 13-2 thru 13-3 Silver nanoparticles 2-17 Single-electron transistors (SETs) 21-14 thru 21-20 30-3 Single-input-single-output (SISO) systems 8-8 thru 8-12 Single-walled carbon nanohorns (SWNH) vs. SWNT 40-16 Single-walled carbon nanohorns (SWNH), merits 40-16 Single-walled carbon nanohorns (SWNH), QENS spectra 40-17 thru 40-19 Single-walled carbon nanohorns (SWNH), spectral line shapes 40-16 thru 40-17 Single-walled carbon nanohorns (SWNH), structure 40-15 thru 40-16 Single-walled carbon nanohorns (SWNH), synthesis 40-15 40-16 Single-walled nanotubes (SWNTs) 1-8 thru 1-10 SISO systems see "Single-input-single-output systems" Site-selective chemical etching 28-7 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, AFAMRMC 8-13 thru 8-17 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, configuration and dynamics 8-12 thru 8-13 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, dynamic model errors 8-20 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, impulse responses 8-17 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, positioning control capability 8-17 thru 8-18 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, positioning errors 8-18 thru 8-20 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, simultaneous precision positioning and vibration control capabilities 8-18 thru 8-19 Smart composite nanopositioning, MIMO, vibration suppression 8-17 thru 8-18 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, ACX PZT patch 8-8 thru 8-9 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, adaptive control schemes 8-9 thru 8-10 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, AFC 8-11 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, AIMC 8-11 thru 8-12 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, CCC PZT patches 8-8 thru 8-9 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, composite panel 8-8 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, experimental system 8-10 thru 8-11 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, HAC 8-12 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, PZT-5A piezoelectric material 8-9 Smart composite nanopositioning, SISO, relative error 8-11 thru 8-12 Smoluchowski effect 18-7 thru 18-9 Sodium alanate, hydrogen storage 42-3 Soft chemistry 15-1 Solid-state hydrogen storage 42-2 thru 42-3 Spin valves, configuration 38-12 thru 38-13 Spin valves, frequency vs. current 38-15 Spin valves, frequency vs. field variation 38-14 thru 38-15
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



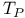 )
) 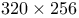 focal plane array fabrication
focal plane array fabrication 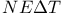
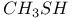
 -tungsten phase vs. clathrate I
-tungsten phase vs. clathrate I