Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Sattler K.D. — Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional NanomaterialsАвтор: Sattler K.D. Аннотация: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials illustrates the importance of tailoring nanomaterials to achieve desired functions in applications. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers various composites, including carbon nanotube/polymer composites, printable metal nanoparticle inks, polymer�clay nanocomposites, biofunctionalized titanium dioxide-based nanocomposites, nanocolorants, ferroic nanocomposites, and smart composite systems. It also describes nanoporous materials, a giant nanomembrane, graphitic foams, arrayed nanoporous silicon pillars, nanoporous anodic oxides, metal oxide nanohole arrays, carbon clathrates, self-assembled monolayers, epitaxial graphene, and graphene nanoribbons, nanostructures, quantum dots, and cones. After focusing on the methods of nanoindentation and self-patterning, the book discusses nanosensors, nano-oscillators, and hydrogen storage. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2011Количество страниц: 790Добавлена в каталог: 12.07.2014Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Graphene quantum dots, Klein’s paradox, energy dispersion law 23-2 thru 23-3 Graphene quantum dots, Klein’s paradox, Hamiltonian matrix 23-1 thru 23-2 Graphene quantum dots, Klein’s paradox, Klein’s tunneling 23-3 Graphene quantum dots, Klein’s paradox, Pauli matrices 23-2 Graphene quantum dots, nonrelativistic systems 23-3 Graphene quantum dots, quantized energy spectrum 21-14 Graphene quantum dots, quantum confinement effects, Coulomb diamonds 21-21 thru 21-22 Graphene quantum dots, quantum confinement effects, differential conductance 21-21 Graphene quantum dots, quantum confinement effects, ground-state energy 21-22 Graphene quantum dots, quantum confinement effects, orbital quantum states 21-20 Graphene quantum dots, quantum confinement effects, plunger gate voltage 21-20 thru 21-21 Graphene quantum dots, quantum confinement effects, scanning force micrograph image 21-20 thru 21-21 Graphene quantum dots, quantum confinement effects, single-particle energy 21-22 Graphene quantum dots, regular and chaotic-confined billiard system 21-14 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, barrier gate potentials 21-15 thru 21-16 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, constriction resonance 21-18 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, Coulomb blockade 21-14 thru 21-15 21-17 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, Coulomb diamond measurements 21-17 thru 21-18 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, Coulomb resonances 21-17 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, effective tunable tunneling barrier 21-15 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, electronic transport 21-14 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, false color scanning force microscope image 21-15 thru 21-16 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, heuristic energy diagram model 21-16 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, lever arms and electrostatic coupling 21-18 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, transport characteristics 21-16 thru 21-17 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, types 23-4 thru 23-5 Graphene quantum dots, SETs, ultrathin layer, graphite 23-1 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, 24-4 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, 24-9 thru 24-10 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, activated carbon 24-2 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, CNT-FET 24-2 thru 24-3 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, diamagnetic adsorbates 24-10 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, Dirac electron 24-1 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, gas sensors 24-1 thru 24-2 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, Hall bar geometry 24-3 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, micromechanical cleavage 24-1 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, acceptor level 24-7 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, charge transfer analysis 24-4 thru 24-5 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, closed-shell molecules 24-8 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, cluster formation 24-9 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, density of states (DOS) 24-6 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, electronic and structural properties 24-5 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, electronic supercell band structures 24-8 thru 24-9 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, Hall resistance vs. gate voltage 24-7 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, LDA and GGA 24-5 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, PMMA coating 24-4 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, microscopic theory, sublattice degeneracy 24-8 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, resistance 24-3 thru 24-4 Graphene-gas molecule interaction, sensitivity 24-2 24-4 Graphitic foams see "Carbon foams" Gravimetric capacity 41-3 Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXD) 17-4 Green’s function 20-7 20-10 20-19 Halpin — Tsai equations 1-7 Hankel function 23-8 23-10 Hanszen — Wronski equation 2-8 Hardness 27-3 thru 27-5 Heaviside function 36-10 High-density polyethylene (HDPE) 1-5 thru 1-6 High-resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy (HREELS) 17-5 Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO) 24-6 24-8 Highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) 12-4 Hooke’s law 25-10 thru 25-11 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorbents, hydrogen storage, activated carbons 42-4 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorbents, hydrogen storage, carbon aerogels 42-5 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorbents, hydrogen storage, MOF 42-5 thru 42-6 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorbents, hydrogen storage, SWNT 42-4 thru 42-5 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorption isotherms, Dubinin model 42-7 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorption isotherms, Langmuir model 42-6 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorption isotherms, modified D-A isotherm fit 42-7 thru 42-8 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorption isotherms, virial series expansion 42-6 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, adsorption-based storage systems 42-8 thru 42-9 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, cryo-compressed tanks, hydrogen storage 42-2 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, hydrogen energy 42-1 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, liquid hydrogen storage 42-2 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, physisorption 42-3 thru 42-4 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, room-temperature hydrogen storage 42-2 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, solid-state hydrogen storage 42-2 thru 42-3 Hydrogen adsorption, nanoporous materials, storage system performance 42-1 Hydrogen cars 41-1 41-2 see hydrogen molecule see also "Molecular hydrogen carbon Hydrogen molecule, interaction potential 40-4 Hydrogen molecule, molecular properties 40-2 thru 40-3 Hydrogen molecule, phase diagram 40-3 Hydrogen storage, activated carbons 41-8 thru 41-10 Hydrogen storage, carbide-derived carbons 41-10 thru 41-12 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, 39-8 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, 39-11 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, 39-16 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, 39-14 thru 39-16 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, 39-4 thru 39-6 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, 39-8 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, fullerene 39-6 thru 39-7 Hydrogen storage, fullerenes, hydrogenated 39-17 Hydrogen storage, hydrogen cars 41-1 Hydrogen storage, hydrogen production 41-1 thru 41-2 Hydrogen storage, mechanism 41-3 thru 41-4 Hydrogen storage, nanoporous carbons vs. metal-organic frameworks 41-12 thru 41-13 Hydrogen storage, nanoporous carbons vs. PIMs 41-12 Hydrogen storage, nanoporous carbons vs. zeolites 41-12 Hydrogen storage, nanoporous carbons, properties 41-7 thru 41-8 Hydrogen storage, onboard hydrogen storage 41-2 thru 41-3 Hydrogen storage, physisorption 41-2 Hydrogen storage, physisorption vs. chemisorption 41-4 Hydrogen storage, physisorption, at nanoscale 41-5 thru 41-7 Hydrogen storage, physisorption, hydrogen-adsorbent surface interaction 41-4 Hydrogen storage, physisorption, specific pore volume 41-5 Hydrogen storage, physisorption, specific surface area 41-4 thru 41-5 Hydrogen storage, storage types 41-3 Immunosensor 30-13 Incoherent neutron scattering 40-9 Indamins dyes 5-4 Infrared spectroscopy 17-4 International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) 41-7 Intracellular measurement 33-1 33-2 33-7 33-11 Ion-correlation sensor 33-5 Isotropic polymer composites 1-9 thru 1-10 Johnson noise current 34-10 Kelvin equation 9-8 Kirchhoff stress 26-6 thru 26-7 Kvaerner’s Carbon-Black and Hydrogen (KCB) process 25-8 25-9 25-15 25-16 Laboratory assay 33-10 thru 33-11 Landau level spectrum 19-8 Landau Lifshitz Gilbert (LLG) equation 38-9 38-10 Landau — Lifshitz — Gilbert — Slonczewski (LLGS) equation 38-10 thru 38-11 38-17 Langmuir — Blodgett approach 11-2 Laser excitation energy, 12-8 thru 12-9 Laser excitation energy, best-fit frequencies 12-9 thru 12-10 Laser excitation energy, linear equation 12-10 thru 12-11 Laser excitation energy, skewness 12-10 Laser excitation energy, TO + LA feature 12-9 Laser-induced desorption 30-7 LEEM see "Low-energy electron microscopy" Lennard — Jones potential constant, graphitic systems 36-3 Lennard — Jones potential description 36-2 thru 36-3 Lennard — Jones potential graph 36-3 Lennard — Jones potential integral 36-14 thru 36-15 Lennard — Jones potential integral 36-15 Li-ion battery 15-6 Li-ion charge-discharge properties 15-6 thru 15-8 Lieb’s theorem 20-12 Liquid hydrogen storage 41-3 42-2 Liquid phase deposition (LPD) method 15-2 15-6 Local density of states (LDOS) 25-12 thru 25-13 Local-density-approximation (LDA) 40-13 thru 40-14 Localized field, fluorescence enhancement 32-10 thru 32-11 Localized field, metallic nanoparticle 32-9 thru 32-10 Localized field, nanostructure properties 32-8 thru 32-9 Localized field, near-field optical distribution 32-10 Localized field, propagation 32-9 Localized field, structure 32-8 thru 32-9 Localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) sensor 33-2 33-4 Localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) sensor, cancer imaging in vivo 33-9 Localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) sensor, metallic nanosensor 33-6 Localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) sensor, reflectance imaging 33-9 Localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) sensor, scattering imaging 33-10 Low-Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED) 17-4 Low-energy electron microscopy (LEEM) vs. X-ray diffraction 31-7 thru 31-8 Low-energy electron microscopy (LEEM), adsorbate-induced self-patterning see "Adsorbate-induced surface self-patterning" Low-energy electron microscopy (LEEM), instrument 31-6 thru 31-7 Low-energy electron microscopy (LEEM), operation principle 31-7 Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LUMO) 24-6 24-8 LSPR sensor see "Localized surface plasmon resonances sensor" Luminescent sensors see "Nanoscale luminescent sensors" Macropores 9-2 thru 9-3 Madelung energy 18-17 Magnetic devices, anisotropy 38-8 Magnetic devices, characterization 38-2 Magnetic devices, damping 38-10 Magnetic devices, free precession orbits 38-7 thru 38-8 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, benzenoid graph theory and Lieb’s theorem 22-3 thru 22-4 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, ferromagnetism 22-1 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, finite graphene fragments 22-4 thru 22-5 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, magnetic materials 22-1 thru 22-2 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, point defects 22-7 thru 22-8 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, spintronics 22-2 22-6 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, tight binding and mean-field Hubbard model 22-2 thru 22-3 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, zigzag edges and nanoribbons, atomic structures 22-5 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, zigzag edges and nanoribbons, localized magnetic moments 22-6 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, zigzag edges and nanoribbons, scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) 22-7 Magnetic graphene nanostructures, zigzag edges and nanoribbons, transverse and longitudinal spin fluctuations 22-6 Magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) 38-4 thru 38-5 38-13 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, composites, demagnetizing field 6-2 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, composites, device applications 6-3 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, composites, magnetostrictive and piezoelectric phases 6-1 thru 6-2 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, composites, product and sum properties 6-1 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, composites, static magnetic field dependence 6-2 thru 6-3 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, definition 6-1 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, axial forces 6-4 thru 6-5 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, cobalt ferrite-barium titanate 6-3 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, Landau — Ginsburg — Devonshire phenomenological thermodynamic theory 6-5 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, longitudinal axial strains 6-4 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, moment equilibrium 6-5 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, NFO PZT bilayer 6-4 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, piezoelectric and magnetostrictive phases 6-3 thru 6-4 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, PZT volume fraction dependence 6-6 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, transverse field orientation 6-4 Magnetoelectric (ME) effects, nanobilayer, voltage coefficients 6-3 6-6 Magnetomotive technique, advantages 35-17 Magnetomotive technique, doubly clamped beam 35-3 35-10 Magnetomotive technique, equivalent electrical RLC circuit 35-10 thru 35-11 Magnetomotive technique, induced emf, resonating beam 35-10 Magnetomotive technique, Lorentz force 35-9 Magnetomotive technique, measurement setup 35-10 Magnetomotive technique, sensor 37-10 Magnetoresistance (MR) ratio 38-4 38-5 Manganese oxide mesoporous structures (MOMS) 10-10 Maxwell equation 7-7 Maxwell — Garnet EMA 2-15 ME effects see "Magnetoelectric effects" Mean field Hubbard model 20-7 Mechanical Johnson noise 35-7 Mechanical resistance 35-13 Mechanosynthesis 32-5 thru 32-6 Mesophase pitch-based carbon foams 12-2 Mesopores 9-2 thru 9-3 Mesoporous titania 10-10 Mesoporous zirconia 10-10 Metal oxide nanohole array, bottom-up and top-down approach 15-1 Metal oxide nanohole array, formation mechanism, anodic alumina, surface structure 15-3 Metal oxide nanohole array, formation mechanism, boric acid and aluminum ions 15-4 thru 15-5 Metal oxide nanohole array, formation mechanism, cross-sectional structure 15-3 thru 15-4 Metal oxide nanohole array, formation mechanism, deposition and removal process 15-4 Metal oxide nanohole array, formation mechanism, network-type titania nanohole array 15-5 Metal oxide nanohole array, formation mechanism, titania nanohole array 15-3 Metal oxide nanohole array, formation mechanism, titania nanorod array 15-4 15-6 Metal oxide nanohole array, Li-ion battery 15-6 Metal oxide nanohole array, Li-ion charge-discharge properties 15-6 thru 15-8 Metal oxide nanohole array, soft solution process 15-1 Metal-assisted chemical etching, porous silicon formation 28-7 Metal-assisted chemical etching, silicon column arrays, colloidal crystal mask 28-7 Metal-assisted chemical etching, silicon column arrays, mechanism 28-9 Metal-assisted chemical etching, silicon column arrays, schematics 28-7 Metal-assisted chemical etching, silicon column arrays, SEM images, Ag particles on Si 28-8 thru 28-9 Metal-assisted chemical etching, silicon hole arrays 28-9 thru 28-10 Metal-assisted chemical etching, silicon microwell arrays 28-10 thru 28-11 Metal-organic framework (MOF) 42-5 thru 42-6 see Metal-organic framework (MOF), advantages 41-13 Metal-organic framework (MOF), gravimetric and volumetric capacities 41-12 thru 41-13 Metal-organic framework (MOF), isosteric heat 41-13 Metal-organic framework (MOF), porosity 41-12 Metal-organic framework (MOF), specific surface area 41-12 thru 41-13 Metallic nanosensors 33-6 Microcontact printing 30-10 Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) 26-1 26-13 Microemulsion method 32-6 thru 32-7 Micromagnetics, discretized device structure 38-17 thru 38-18 Micromagnetics, spinwaves 38-18 Micromagnetics, vortex oscillator 38-18 thru 38-19 Micropores 9-2 thru 9-3 Microwave oscillation 38-1 38-2 Miller indices 31-2 31-5 MIMO systems see "Multi-input-multi-output systems" Mobil composition of matter (MCM) 10-3 thru 10-5 10-9 Modified slopes method (MSM) 29-12 mof see "Metal-organic framework" Moire and dislocation networks, force field theory approach 18-6 thru 18-7 Moire and dislocation networks, h-BN nanomesh, relief view 18-6 Moire and dislocation networks, Moire-type superstructures 18-7 Moire and dislocation networks, overlayer system 18-5 thru 18-6 Moire and dislocation networks, superstructure lattice constant 18-5 Moire and dislocation networks, valley and mounds 18-7 Molecular hydrogen, bulk vs. microscopic probes, coherent neutron scattering 40-8 thru 40-9 Molecular hydrogen, bulk vs. microscopic probes, incoherent neutron scattering 40-9 Molecular hydrogen, bulk vs. microscopic probes, Langmuir model 40-7 Molecular hydrogen, bulk vs. microscopic probes, neutron spectroscopy 40-9 Molecular hydrogen, bulk vs. microscopic probes, pressure-temperature dependence 40-7 thru 40-8 Molecular hydrogen, bulk vs. microscopic probes, QENS 40-10 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, 40-20 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, 40-24 thru 40-25 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, adsorption sites 40-23 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, electron densities 40-22 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, experimental vs. PW-DFT calculations 40-22 40-23 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, INS spectra 40-20 thru 40-21 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, minimum-energy configuration 40-22 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, neutron Bragg reflection 40-20 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, orientational potential 40-22 thru 40-23 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, potential energy curves 40-21 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, PW-DFT calculations 40-21 thru 40-22 Molecular hydrogen, carbon nanostructures, alkali-doped graphite intercalates, quantum delocalization 40-24 thru 40-25 Molecular hydrogen, chemisorption 40-6 thru 40-7 Molecular hydrogen, computer simulation, computational experiment 40-10 thru 40-11 Molecular hydrogen, computer simulation, first-principles (ab initio) modeling 40-12 thru 40-14 Molecular hydrogen, computer simulation, quantum effects 40-12 Molecular hydrogen, computer simulation, semiempirical simulation 40-11 thru 40-12 Molecular hydrogen, GCMC 40-25 40-26 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, 40-19 thru 40-20 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, elastic form factor 40-19 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, neutron spectra 40-16 40-17 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, phonon spectrum 40-19 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, QENS spectra 40-17 thru 40-19 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, spectral line shapes 40-16 thru 40-17 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, structure 40-15 thru 40-16 Molecular hydrogen, geometric confinement, carbon nanohorns, TEM 40-15 40-16 Molecular hydrogen, hydrogen molecule, bulk properties and phase diagram 40-3 thru 40-4 Molecular hydrogen, hydrogen molecule, molecular properties 40-2 thru 40-3 Molecular hydrogen, hydrogen storage 40-1 thru 40-2 Molecular hydrogen, no-man’s land region, binding energy 40-6 Molecular hydrogen, physisorption challenge 40-6 Molecular hydrogen, physisorption charge-induced-dipole interactions 40-5
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



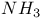 and
and 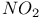 adsorption
adsorption 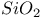 substrate
substrate  system
system  system
system 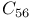 system
system 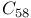 and its derivatives
and its derivatives 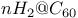 system
system 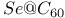 system
system 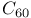
 ratio
ratio  evaluation
evaluation  evaluation
evaluation  adsorption
adsorption