Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Sattler K.D. — Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional NanomaterialsАвтор: Sattler K.D. Аннотация: Handbook of Nanophysics: Functional Nanomaterials illustrates the importance of tailoring nanomaterials to achieve desired functions in applications. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers various composites, including carbon nanotube/polymer composites, printable metal nanoparticle inks, polymer�clay nanocomposites, biofunctionalized titanium dioxide-based nanocomposites, nanocolorants, ferroic nanocomposites, and smart composite systems. It also describes nanoporous materials, a giant nanomembrane, graphitic foams, arrayed nanoporous silicon pillars, nanoporous anodic oxides, metal oxide nanohole arrays, carbon clathrates, self-assembled monolayers, epitaxial graphene, and graphene nanoribbons, nanostructures, quantum dots, and cones. After focusing on the methods of nanoindentation and self-patterning, the book discusses nanosensors, nano-oscillators, and hydrogen storage. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2011Количество страниц: 790Добавлена в каталог: 12.07.2014Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Electron trapping, interference, heights of confinement potential 23-9 Electron trapping, interference, radius fluctuation ( 23-10 Electron trapping, interference, resonance 23-8 Electron trapping, interference, sharp boundaries 23-7 thru 23-8 Electron trapping, interference, Taylor series 23-9 thru 23-10 Electron trapping, interference, time-independent solution 23-8 Electron trapping, tunneling barrier formation, classical turning points 23-5 thru 23-6 Electron trapping, tunneling barrier formation, electron angular momentum 23-5 Electron trapping, tunneling barrier formation, escape rate 23-6 Electron trapping, tunneling barrier formation, interlevel separation 23-6 thru 23-7 Electron trapping, tunneling barrier formation, semiclassical quantization 23-6 Electron trapping, tunneling barrier formation, transverse momentum 23-7 Electrostatic funneling 30-8 thru 30-9 Electrostatic sensor 37-10 Electrostatic technique, applications 35-17 Electrostatic technique, displacement vs. resonance frequency 35-12 Electrostatic technique, equation of motion 35-11 Electrostatic technique, equivalent electrical RLC circuit 35-13 Electrostatic technique, measurement setup 35-11 Electrostatic technique, output voltage 35-12 Ellipsometry 17-5 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-10 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-13 thru 39-14 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-8 thru 39-9 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-10 thru 39-11 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-7 thru 39-8 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-11 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-11 thru 39-12 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, 39-8 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, hydrogen and fullerenes 39-1 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, hydrogen storage capacity, 39-16 thru 39-17 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, hydrogen storage capacity, 39-14 thru 39-16 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, hydrogen storage capacity, 39-6 thru 39-7 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, hydrogen storage capacity, 39-4 thru 39-6 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, hydrogen storage capacity, hydrogenated 39-17 thru 39-18 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, solid-state NMR studies 39-4 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, synthesis, 39-3 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, synthesis, 39-2 thru 39-3 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, synthesis, dihydrogen-encapsulated fullerenes 39-3 thru 39-4 Endohedrally hydrogen-doped fullerenes, synthesis, fullerene derivative 39-3 Epitaxial graphene, ballistic transport 19-9 Epitaxial graphene, Bernal stacking 19-1 19-5 Epitaxial graphene, carbon nanotube 19-2 Epitaxial graphene, crystal structure 19-1 thru 19-2 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, Dirac cones 19-5 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, electron waves 19-3 thru 19-4 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, Fermi level 19-4 thru 19-5 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, Fermions 19-4 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, pi-bonds 19-3 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, quantum mechanical 19-3 thru 19-4 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, traveling waves 19-4 Epitaxial graphene, electronic structure, valence electrons 19-3 Epitaxial graphene, energy gap 19-8 Epitaxial graphene, exfoliated graphene 19-2 Epitaxial graphene, gate doping 19-9 Epitaxial graphene, inter-sheet van der Waals bonding 19-1 Epitaxial graphene, optical microscopic method 19-2 Epitaxial graphene, patterned graphene 19-9 Epitaxial graphene, properties 19-5 thru 19-6 Epitaxial graphene, silicon carbide, 4H and 6H structures 19-6 Epitaxial graphene, silicon carbide, C-face 19-6 thru 19-8 Epitaxial graphene, silicon carbide, chemically modified epitaxial graphene 19-8 Epitaxial graphene, silicon carbide, Si-face 19-6 Epitaxial graphene, two-dimensional electron gases 19-3 Epitaxial QDs 34-1 Equation of motion with applied current, angular momentum 38-10 Equation of motion with applied current, critical current 38-10 Equation of motion with applied current, effective damping 38-10 thru 38-11 Equation of motion with applied current, phase diagram 38-11 thru 38-12 Equation of motion with applied current, polar angle 38-11 Equation of motion with applied current, spin-transfer stabilized orbits 38-11 thru 38-12 Equation of motion with damping 38-9 thru 38-10 Equation of motion without damping, anisotropy energy 38-7 thru 38-8 Equation of motion without damping, effective field 38-6 thru 38-7 Equation of motion without damping, free layer moment 38-7 Equation of motion without damping, magnetostatic energy 38-7 Equation of motion without damping, resonant frequency 38-8 thru 38-9 Equation of motion without damping, torque 38-6 Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymer 1-6 Euler’s law 16-8 Evanescent field 32-8 thru 32-9 see Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, ambient potential 7-7 Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, dielectric anisotropy media 7-8 Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, dielectric particle 7-6 Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, dimensionless ratio 7-8 Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, dipole moment 7-8 thru 7-9 Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, equations of state 7-7 Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, partial screening 7-6 Ferroic nanocomposites, depolarization field calculations, polarization screening 7-8 thru 7-9 Ferroic nanocomposites, ferroelectric/ferromagnetic domain switching 7-1 Ferroic nanocomposites, Gibbs energy, spherical ferroelectric nanoparticle, equations of state 7-5 Ferroic nanocomposites, Gibbs energy, spherical ferroelectric nanoparticle, perovskite symmetry 7-4 Ferroic nanocomposites, Gibbs energy, spherical ferroelectric nanoparticle, spherical coordinate system 7-5 Ferroic nanocomposites, Gibbs energy, spherical ferroelectric nanoparticle, uniformly strained particles 7-6 Ferroic nanocomposites, Gibbs energy, spherical ferroelectric nanoparticle, uniformly stressed particles 7-5 Ferroic nanocomposites, inhomogeneous elastic strains 7-2 Ferroic nanocomposites, Landau — Ginzburg phenomenological approach 7-3 Ferroic nanocomposites, PFM 7-1 thru 7-2 Ferroic nanocomposites, phenomenological approach 7-3 thru 7-4 Ferroic nanocomposites, Raman spectra 7-2 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain and depolarization field, dielectric susceptibility 7-11 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain and depolarization field, dynamic response 7-10 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain and depolarization field, phase transition 7-10 thru 7-11 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain and depolarization field, quasi-static ferroelectric hysteresis loops 7-10 thru 7-11 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain and depolarization field, remnant polarization 7-10 7-12 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain and depolarization field, square-to-slim transition 7-10 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain and depolarization field, uniform electric field 7-10 Ferroic nanocomposites, strain- and size-induced effects 7-9 Ferroic nanocomposites, superparaelectric phase 7-3 Fick equations 14-7 Field-effect transistors, band-gap engineering, electronic transport 20-19 thru 20-20 Field-effect transistors, band-gap engineering, on-off state 20-18 Field-effect transistors, band-gap engineering, threshold voltage 20-18 Field-effect transistors, electronic versatility 20-13 Field-effect transistors, electrostatics and gating, density vs. 20-15 thru 20-16 Field-effect transistors, electrostatics and gating, Hartree approximation 20-14 thru 20-15 Field-effect transistors, electrostatics and gating, ideal conductance vs. 20-17 Field-effect transistors, electrostatics and gating, long-range interactions 20-14 Field-effect transistors, electrostatics and gating, self-consistent electronic structure 20-15 Field-induced oxidation (FIO) 30-11 Finite element analysis, Boussinesq — Love indentation problem 26-10 Finite element analysis, contact problems, friction, bipotential method 26-9 Finite element analysis, contact problems, friction, contact kinematics 26-7 thru 26-8 Finite element analysis, contact problems, friction, equilibrium equations 26-9 Finite element analysis, contact problems, friction, governing equations 26-7 Finite element analysis, contact problems, friction, nonlinear Gauss — Seidel-like algorithm 26-9 thru 26-10 Finite element analysis, contact problems, friction, Signorini conditions and Coulomb friction laws 26-8 thru 26-9 Finite element analysis, contact problems, friction, Uzawa algorithm 26-10 Finite element analysis, elastoplastic materials, finite strains, cumulated plastic strain 26-5 thru 26-6 Finite element analysis, elastoplastic materials, finite strains, Kuhn — Tucker condition 26-5 Finite element analysis, elastoplastic materials, finite strains, linear Prager kinematic hardening 26-6 Finite element analysis, elastoplastic materials, finite strains, radial return mapping 26-6 thru 26-7 Finite element analysis, elastoplastic materials, finite strains, total deformation gradient 26-6 Finite element analysis, nanoindentation 26-10 thru 26-11 Finite element analysis, nonlinear phenomena 26-5 Finite element method (FEM) 35-8 Fluorene dyes 5-4 Fluorescence lifetime 33-8 thru 33-9 Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) sensors 33-6 Fluorescent nanoparticles, fluoride materials, coprecipitation method 32-6 thru 32-8 Fluorescent nanoparticles, fluoride materials, glass-ceramics 32-5 Fluorescent nanoparticles, fluoride materials, glasses 32-4 thru 32-5 Fluorescent nanoparticles, fluoride materials, mechanosynthesis 32-5 thru 32-6 Fluorescent nanoparticles, fluoride materials, microemulsion method 32-6 thru 32-7 Fluorescent nanoparticles, fluoride materials, soft chemistry method 32-6 Fluorescent nanoparticles, inorganic luminescent material 32-1 Fluorescent nanoparticles, nanoscale luminescent sensors, local (evanescent) field detection 32-8 thru 32-12 Fluorescent nanoparticles, nanoscale luminescent sensors, nanoscale thermometer 32-13 thru 32-16 Fluorescent nanoparticles, nanoscale luminescent sensors, tip fabrication 32-8 32-9 Fluorescent nanoparticles, rare earth ions, energy transfers 32-3 thru 32-4 Fluorescent nanoparticles, rare earth ions, energy-level scheme 32-2 Focused ion beam (FIB) lithography 30-1 30-6 30-7 Food dyes 5-2 Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer 34-8 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) 7-2 FTIR spectrometer 34-8 thru 34-9 Full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) 1-10 Gamow’s vectors 23-8 Gas molecule collision noise 35-8 Gaseous hydrogen storage 41-3 Gauss — Bonnet theorem 16-8 Gaussian membership function 8-5 thru 8-6 Generalized-gradient approximations (GGA) 40-13 thru 40-14 Georgia Institute of Technology (GIT) 19-2 Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) device 38-1 thru 38-4 Giant nanomembrane, definition 11-1 Giant nanomembrane, fabrication, electrostatic layer-by-layer assembly 11-2 Giant nanomembrane, fabrication, gold foil 11-1 Giant nanomembrane, fabrication, Langmuir — Blodgett approach 11-2 Giant nanomembrane, fabrication, metal oxides 11-3 Giant nanomembrane, fabrication, organic and inorganic hybrids 11-3 11-5 Giant nanomembrane, fabrication, organic nanomembranes 11-3 thru 11-4 Giant nanomembrane, functional potentials 11-8 Giant nanomembrane, physical properties, electrical property 11-7 Giant nanomembrane, physical properties, macroscopic behavior and microscopic morphology 11-5 thru 11-6 Giant nanomembrane, physical properties, mechanical properties measurement 11-6 thru 11-7 Giant nanomembrane, physical properties, membrane robustness and crosslinking density 11-7 Giant nanomembrane, physical properties, thermal and chemical stabilities 11-7 thru 11-8 Gibbs free energy 16-19 Gigahertz oscillator see "Nanoscaled oscillators" Glass, energy transfers 32-3 Glass, fluorescence spectra 32-13 Glass, glass transition temperature 32-4 Glass, glass-ceramics synthesis 32-5 Glass, optical properties 32-4 thru 32-5 Glass, stability and synthesis 32-4 Glass, thermal analysis curve 32-6 Gold nanoparticles 2-17 thru 2-20 Grand canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulation 40-11 40-14 40-25 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, 18-16 thru 18-17 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, atomic structure, BN bond strength 18-3 thru 18-4 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, atomic structure, corrugated layers 18-5 thru 18-7 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, atomic structure, flat layers, domain boundaries 18-4 thru 18-5 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, atomic structure, lattice mismatch 18-3 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, chemical vapor deposition 18-2 thru 18-3 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, dielectric/metallic layer 18-1 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic band structure, 18-18 thru 18-19 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic band structure, 18-19 thru 18-20 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic band structure, Madelung energy 18-17 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic band structure, two-dimensional honeycomb structure 18-17 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic structure I, corrugated layers 18-8 thru 18-9 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic structure I, flat layers, vertical polarization 18-7 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic structure II, corrugated layers, 18-10 thru 18-12 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, electronic structure II, flat layers 18-9 thru 18-10 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, inverted topography 18-2 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, segregation 18-3 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, sticking and intercalation 18-12 thru 18-13 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, templates, dN molecules 18-16 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, templates, h-BN/Rh(111) nanomesh 18-14 thru 18-15 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, templates, initial coverages and desorption energies 18-16 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, templates, super cell 18-14 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, templates, template unit cell geometry 18-14 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, templates, Xe/h-BN/Rh(111) vs. Xe/g/Ru(0001) TDS 18-14 thru 18-15 Graphene and boron nitride single layers, tunneling junctions 18-13 thru 18-14 Graphene cones, atomic and electronic structure models, Bloch waves and Dirac electrons 25-7 thru 25-8 Graphene cones, atomic and electronic structure models, DFT 25-6 thru 25-7 Graphene cones, atomic and electronic structure models, fundamentals 25-5 thru 25-6 Graphene cones, atomic and electronic structure models, molecular mechanics 25-6 Graphene cones, atomic and electronic structure models, tight-binding and the Hueckel model 25-7 Graphene cones, Bucky ball 25-2 Graphene cones, carbon chemistry 25-2 Graphene cones, conic radicals 25-16 Graphene cones, electronic properties, continuum models and TB results 25-13 thru 25-14 Graphene cones, electronic properties, DFT results 25-14 Graphene cones, electronic properties, LDOS and petal superstructures 25-12 thru 25-13 Graphene cones, electrorheological fluid 25-15 thru 25-16 Graphene cones, fullerenes 25-2 Graphene cones, geometry and topology constraints 25-2 thru 25-3 Graphene cones, geometry, topology and stability 25-9 thru 25-10 Graphene cones, hexagonal carbon network 25-1 Graphene cones, history 25-3 thru 25-5 Graphene cones, hydrogen storage 25-14 thru 25-15 Graphene cones, mechanical properties, Brenner — Tersoff potential 25-10 thru 25-11 Graphene cones, mechanical properties, elastic energy vs. indenter displacement 25-11 thru 25-12 Graphene cones, mechanical properties, Hooke’s law 25-10 thru 25-11 Graphene cones, mechanical properties, mechanical stress 25-11 Graphene cones, mechanical properties, Young’s modulus 25-10 Graphene cones, nucleation 25-16 Graphene cones, nucleation and growth mechanism 25-1 Graphene cones, pentagon road 25-16 thru 25-17 Graphene cones, substitutional atoms and tip functionalization 25-16 Graphene cones, synthesis and characterization 25-8 thru 25-9 Graphene nanoribbons, bipartite lattices 20-9 Graphene nanoribbons, Brillouin zone 20-4 Graphene nanoribbons, bulk graphene 20-2 thru 20-3 Graphene nanoribbons, charge neutrality point 21-11 Graphene nanoribbons, chemisorption 20-10 Graphene nanoribbons, condensed-matter quantum electrodynamics 20-1 Graphene nanoribbons, Coulomb blockade, nano constrictions 21-13 thru 21-14 Graphene nanoribbons, electron-electron interactions, armchair nanoribbons 20-7 Graphene nanoribbons, electron-electron interactions, defects and magnetism 20-11 thru 20-13 Graphene nanoribbons, electron-electron interactions, mean field Hubbard model 20-7 Graphene nanoribbons, electron-electron interactions, zigzag nanoribbons 20-7 thru 20-9 Graphene nanoribbons, energy gaps, bias direction 21-12 Graphene nanoribbons, energy gaps, edge roughness 21-11 Graphene nanoribbons, energy gaps, energy scales 21-12 thru 21-13 Graphene nanoribbons, energy gaps, source-drain current measurement 21-11 thru 21-12 Graphene nanoribbons, energy gaps, transport gap in back gate 21-12 Graphene nanoribbons, field-effect transistors see "Field-effect transistors" Graphene nanoribbons, hydrogen adsorption 20-9 Graphene nanoribbons, low source-drain bias vs. back-gate characteristics 21-10 Graphene nanoribbons, non-interacting theory, defects and magnetism 20-9 thru 20-11 Graphene nanoribbons, non-interacting theory, Dirac equation 20-5 thru 20-7 Graphene nanoribbons, non-interacting theory, tight-binding approximation 20-4 thru 20-5 Graphene nanoribbons, quasi-1D wire 20-3 Graphene nanoribbons, scanning force microscope images 21-10 Graphene nanoribbons, Schroedinger equation 20-2 Graphene nanoribbons, semiconducting behavior 21-9 Graphene nanoribbons, thermal fluctuation 20-1 Graphene nanoribbons, voids 20-9 thru 20-10 Graphene nanoribbons, zero-energy states 20-9 thru 20-10 Graphene nanostructures, 21-1 Graphene nanostructures, direct backscattering 21-3 Graphene nanostructures, etching 21-8 thru 21-9 Graphene nanostructures, Fermi energy 21-1 Graphene nanostructures, mechanical exfoliation, graphite 21-6 Graphene nanostructures, nanodevice contacting 21-9 Graphene nanostructures, nanoribbons see "Graphene nanoribbons" Graphene nanostructures, pseudo-relativistic Klein tunneling 21-3 Graphene nanostructures, pseudospin 21-2 Graphene nanostructures, quantum dots see "Graphene quantum dots" Graphene nanostructures, quasi-particle spectrum 21-2 thru 21-3 Graphene nanostructures, single-layer graphene identification, Raman imaging 21-7 thru 21-8 Graphene nanostructures, single-layer graphene identification, visibility 21-6 thru 21-7 Graphene nanostructures, transport properties, electron density 21-4 Graphene nanostructures, transport properties, graphene gates 21-5 thru 21-6 Graphene nanostructures, transport properties, half-integer quantum Hall effect 21-5 Graphene nanostructures, transport properties, Hall bar geometries 21-3 thru 21-4 Graphene nanostructures, transport properties, minimum conductivity 21-5 Graphene nanostructures, transport properties, mobility 21-5 Graphene nanostructures, transport properties, zero-temperature conductivity 21-3 Graphene nanostructures, wave function 21-2 thru 21-3 Graphene quantum dots, charge detection, conductance 21-20 Graphene quantum dots, charge detection, Coulomb blockade resonances 21-19 thru 21-20 Graphene quantum dots, charge detection, integrated graphene device 21-18 thru 21-19 Graphene quantum dots, charge detection, large-scale current fluctuation 21-19 Graphene quantum dots, charge detection, spin-qubit and molecular states 21-18 Graphene quantum dots, electron trapping, interference 23-7 thru 23-11 Graphene quantum dots, electron trapping, tunneling barrier formation 23-5 thru 23-7 Graphene quantum dots, Klein’s paradox, continuum limit 23-1
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



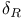 )
) 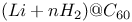
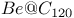 structure
structure 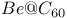
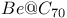
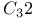 cluster
cluster 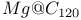 nanotube
nanotube 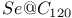 nanotube
nanotube 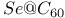
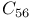 system
system 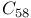 and its derivatives
and its derivatives 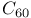
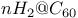 geometries and energies
geometries and energies 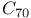
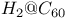
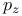 orbital
orbital 
 hybridization
hybridization  bands
bands  bands
bands