јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Sattler K.D. Ч Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenesјвтор: Sattler K.D. јннотаци€: The field of nanoscience was pioneered in the 1980s with the groundbreaking research on clusters, which later led to the discovery of fullerenes. Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes focuses on the fundamental physics of these nanoscale materials and structures. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers free clusters, including hydrogen, bimetallic, silicon, metal, and atomic clusters, as well as the cluster interactions. The expert contributors examine how carbon fullerenes are produced and how to characterize their stability. They discuss the structure, properties, and behavior of carbon fullerenes, including the smallest possible fullerene: C20. The book also looks at inorganic fullerenes, such as boron fullerenes, silicon fullerenes, nanocones, and onion-like inorganic fullerenes. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2011 оличество страниц: 912ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.07.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
33-2 33-4 33-1 33-7 33-3 33-6 33-2 33-4 33-2 33-3 33-2 33-3 33-2 33-7 33-9 33-2 33-4 33-2 33-8 33-2 33-7 33-4Ч33-5 33-3 33-5 33-3 33-6 30-3 30-2 29-2Ч29-3 30-2Ч30-3 29-4Ч29-5 29-5Ч29-6 29-3 29-4 29-3Ч29-4 29-6 29-8Ч29-9 29-7Ч29-8 30-5 30-4 30-4Ч30-5 30-6 30-3Ч30-4 30-7 30-6 30-7Ч30-8 30-9 30-8Ч30-9 30-9 30-11 30-10 32-11 32-11Ч32-12 32-12Ч32-13 32-7 32-7 32-8 32-6Ч32-9 32-8 32-9 32-6Ч32-9 35-4Ч35-6 25-7Ч25-8 38-6Ч38-8 38-4 38-5 38-5Ч38-8 25-6Ч25-7 41-2Ч41-5 41-5Ч41-9 25-7 46-13Ч46-15 25-9Ч25-10 51-9 45-6 45-4 45-5 45-3Ч45-6 35-2Ч35-3 38-3 25-15Ч25-16 45-9 45-10 45-9 45-7 45-8 45-9 45-8 45-8 49-2 46-25 46-22Ч46-23 46-24Ч46-25 46-20Ч46-22 46-26Ч46-27 46-18Ч46-23 46-15Ч46-17 46-1Ч46-3 51-1Ч51-2 46-3Ч46-4 46-3 46-9Ч46-10 46-10Ч46-11 46-9 46-7Ч46-9 46-6Ч46-7 46-4Ч46-5 38-8Ч38-9 25-8 46-1 46-2 46-13Ч46-15 46-12Ч46-13 46-11Ч46-12 25-11 25-11Ч25-12 25-10 25-15Ч25-16 33-13Ч33-14 33-16 33-16 33-14 33-17 33-14 33-15Ч33-16 42-7 45-12 45-13 45-11 45-12 45-14 45-11 45-12 45-13 42-3Ч42-5 42-10Ч42-11 42-8Ч42-9 42-5Ч42-6 42-9 42-7 42-10 42-8 42-9Ч42-10 see "Organic clusters PES" Abutting pentagon defect, 31-2 Abutting pentagon defect, destabilizing effect 31-1 Aggregation kinetics, cluster see "Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics" Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, atomic structure influence 6-6 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, deformation 6-5Ч6-6 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, density functional theory (DFT) calculation 6-6Ч6-7 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, effective single-particle potential derivation 6-3Ч6-4 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, noble metal clusters 6-14Ч6-16 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES) measurement 6-7Ч6-9 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, quantum size effect 6-1 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, size-dependence 6-1 Alkali and noble metal clusters, electronic structure, sodium clusters 6-9Ч6-17 Alkali halide clusters 10-7Ч10-8 Anion beam hole-burning technique 8-7Ч8-8 Arc discharge method, carbon onions, inert gas atmosphere 24-2Ч24-3 Arc discharge method, carbon onions, water 24-2Ч24-3 Arc discharge method, plasma synthesis 21-5 Automorphism 28-2 Benzene clusters 7-19 Bimetallic clusters, applications 4-3 Bimetallic clusters, classification 4-1 Bimetallic clusters, definition 4-1 Bimetallic clusters, free metal clusters, dispersion, surface energy 4-4 Bimetallic clusters, free metal clusters, magic clusters 4-5Ч4-7 Bimetallic clusters, free metal clusters, size evolution of properties 4-4Ч4-5 Bimetallic clusters, geometric structure 4-7Ч4-8 Bimetallic clusters, properties 4-8 Bimetallic clusters, special bimetallic clusters 4-9Ч4-10 Bimetallic clusters, structure-energy principles 4-8Ч4-9 Bimetallic clusters, types and clusters formation, free 4-2 Bimetallic clusters, types and clusters formation, passivated 4-2Ч4-3 Bimetallic clusters, types and clusters formation, supported 4-2 Body-centered-cubic (bcc) structure 30-3 Boron fullerenes, 47-4 Boron fullerenes, applications 47-7Ч47-8 Boron fullerenes, applications, cancer therapy 47-7 Boron fullerenes, applications, rotor configurations 47-7Ч47-8 Boron fullerenes, cohesive energies 47-3 Boron fullerenes, electronic structure, HOMO degeneracy 47-6 Boron fullerenes, electronic structure, molecular orbital 47-5 Boron fullerenes, isomerization 47-5 Boron fullerenes, lattice structure 47-1Ч47-2 Boron fullerenes, nanotubes, band gap dependence 47-4 Boron fullerenes, nanotubes, synthesis 47-5 Boron fullerenes, sructure and symmetry, boron clusters 47-1Ч47-2 Boron fullerenes, vibrational modes, B3LYP/STO-3G method 47-6 Boron fullerenes, vibrational modes, breathing mode frequency 47-7 Boron nitride fullerenes, definition 49-1 Boron nitride fullerenes, doping, binding sites 49-8 Boron nitride fullerenes, doping, hybrid structure 49-7 Boron nitride fullerenes, doping, magnetic moments 49-9 Boron nitride fullerenes, geometry, continuous model 49-4Ч49-5 Boron nitride fullerenes, geometry, formation energy per number 49-4 Boron nitride fullerenes, geometry, hexagonal lattices 49-2 Boron nitride fullerenes, geometry, homopolar N-N bond 49-2Ч49-3 Boron nitride fullerenes, geometry, stoichiometric octahedral fullerenes 49-3 Boron nitride fullerenes, historic review 49-1Ч49-2 Boron nitride fullerenes, non-stoichiometry, formation energy per number 49-7 Boron nitride fullerenes, non-stoichiometry, homopolar N-N bonds 49-6 Boron nitride fullerenes, non-stoichiometry, relative stability 49-5 Boron nitride nanocones, antiphase boundaries 49-10 Boron nitride nanocones, electronic states 49-10Ч49-11 Boron nitride nanocones, structure 49-9 Bose Ч Einstein condensation (BEC), hydrogen clusters 11-5Ч11-6 Brillouin zone 32-5 Buckminsterfullerene see also " Buckminsterfullerene, endohedral metallofullerenes separation 22-21Ч22-22 Buckminsterfullerene, hydrogenated derivatives separation 22-21 Calixarenes 41-5Ч41-6 Campi scatter plots 15-16 Car Ч Parrinello molecular dynamics (CPMD) 32-5Ч32-6 Carbon fullerenes, 29-2Ч29-3 Carbon fullerenes, 29-3Ч29-6 Carbon fullerenes, 29-6Ч29-9 Carbon fullerenes, 41-1Ч41-9 Carbon fullerenes, 46-13Ч46-15 Carbon fullerenes, 46-15Ч46-27 Carbon fullerenes, 46-1Ч46-3 46-26 Carbon fullerenes, 46-3Ч46-11 Carbon fullerenes, 46-1 46-2 Carbon fullerenes, 46-11Ч46-15 Carbon fullerenes, buckminsterfullerene 22-21Ч22-22 Carbon fullerenes, defects, abutting pentagon defect 31-1Ч31-2 Carbon fullerenes, defects, observation 31-5Ч31-6 Carbon fullerenes, defects, Stone Ч Wales transformation 31-2Ч31-3 Carbon fullerenes, defects, window-like defects 31-3Ч31-5 Carbon fullerenes, electronic structure, endohedral fullerenes pospects 42-11 Carbon fullerenes, electronic structure, historic perspectives 42-1 Carbon fullerenes, electronic structure, mass production method 42-2 Carbon fullerenes, electronic structure, metallofullerenes 42-1Ч42-2 Carbon fullerenes, electronic structure, mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes 42-3Ч42-9 Carbon fullerenes, electronic structure, multiple atoms-entrapped fullerenes 42-9Ч42-11 Carbon fullerenes, electronic structure, photoelectron spectroscopy 42-2Ч42-3 Carbon fullerenes, fragmentation, collision 27-4 Carbon fullerenes, fragmentation, coronene and dimers 27-4 Carbon fullerenes, fragmentation, dimers and clusters 27-20Ч27-25 Carbon fullerenes, fragmentation, monomer anions stability 27-17Ч27-20 Carbon fullerenes, fragmentation, monomer cations 27-5Ч27-17 Carbon fullerenes, fragmentation, NMR spectra for 27-3 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, decahedral sphere packing 37-14 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, geometrical structure of 37-14Ч37-15 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, honeycomb layers of spheres 37-13Ч37-14 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, icosahedral packing 37-13 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, interaction potential parameters 37-1 37-2 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, interaction potentials, 37-4Ч37-5 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, mass abundance spectrum 37-2Ч37-3 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, multiply charged clusters 37-11Ч37-13 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, packing of spheres 37-14Ч37-15 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, structure of 37-8Ч37-11 Carbon fullerenes, fullerenes clusters, van der Waals clusters 37-7 37-8 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, aqueous systems 44-10Ч44-11 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, caged fullerene molecules 44-3Ч44-4 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, carbon allotropes, molecular structures 44-2 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, Derjaguin Ч Landau Ч Verwey Ч Overbeek (DLVO)theory 44-9 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, dry fullerol powder, infrared spectrum 44-6 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, electrophoretic mobility 44-8 44-9 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, fullerol dispersions 44-7 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, nanotechnology 44-1Ч44-2 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, production techniques 44-5 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, structure of 44-10 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, titration curve 44-8 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image 44-9 Carbon fullerenes, fullerol clusters, ultraviolet and visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra 44-6 44-7 Carbon fullerenes, growth 23-1Ч23-7 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, alkyl-bonded silica stationary phases 22-4Ч22-8 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, aromatic system, stationary phases 22-15Ч22-18 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, block diagram of 22-3 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, buckminsterfullerene 22-21Ч22-22 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, charge-transfer stationary phases 22-9Ч22-15 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, elution curve, chromatography 22-4 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, polymer stationary phases 22-21 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, porphyrin-bonded silica stationary phase 22-18Ч22-19 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, properties and applications 22-1 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, pyrenyl ligands, stationary phase 22-19Ч22-21 Carbon fullerenes, HPLC separation, seperation 22-1Ч22-2 Carbon fullerenes, metal-coated, alkali earth metals case 43-3 Carbon fullerenes, metal-coated, alkali metal atoms case 43-2Ч43-3 Carbon fullerenes, metal-coated, applications 43-5Ч43-6 Carbon fullerenes, metal-coated, coating mechanisms 43-5 Carbon fullerenes, metal-coated, synthesis and characterization 43-1Ч43-2 Carbon fullerenes, metal-coated, transition metal atoms case 43-3Ч43-5 Carbon fullerenes, metal-coated, vanadium coating 43-4 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, arc discharge method 21-5 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, arc-jet plasma method 21-5Ч21-7 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, characterization of 21-8Ч21-13 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, definition 21-2Ч21-4 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, fullerene discovery history 21-2 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, laser ablation method 21-4 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, nonequilibrium plasma method 21-7Ч21-8 Carbon fullerenes, plasma synthesis, optimization of 21-13Ч21-17 Carbon fullerenes, polyhydroxylated, 45-10Ч45-14 Carbon fullerenes, polyhydroxylated, density-functional theory (DFT) methodologies 45-3 45-14Ч45-15 Carbon fullerenes, polyhydroxylated, low hydroxylated 45-3Ч45-6 Carbon fullerenes, polyhydroxylated, optical properties, 45-6Ч45-10 Carbon fullerenes, polyhydroxylated, solubility 45-1Ч45-2 Carbon fullerenes, polyhydroxylated, state of the art 45-2Ч45-3 Carbon fullerenes, Raman spectroscopy 46-15Ч46-27 Carbon fullerenes, silicon doped, 32-14Ч32-17 Carbon fullerenes, silicon doped, computational methodolgy 32-2Ч32-6 Carbon fullerenes, silicon doped, electronic and structural property, 32-6Ч32-12 Carbon fullerenes, silicon doped, main experimental results 32-2 Carbon fullerenes, silicon doped, thermal behaviour 32-12Ч32-13 Carbon fullerenes, solid-state structure, 30-2Ч30-3 Carbon fullerenes, solid-state structure, 30-3Ч30-6 Carbon fullerenes, solid-state structure, 30-6Ч30-9 Carbon fullerenes, solid-state structure, 30-9Ч30-11 Carbon fullerenes, stability, 25-15Ч25-16 Carbon fullerenes, stability, 25-12 Carbon fullerenes, stability, 25-5Ч25-12 25-15Ч25-16 Carbon fullerenes, stability, bonding features 25-4Ч25-5 Carbon fullerenes, stability, kinetic energy release 25-2 Carbon fullerenes, stability, nano-peapods 25-2 Carbon fullerenes, stability, negatively charged fullerenes 25-16Ч25-18 Carbon fullerenes, stability, rule 25-5Ч25-6 Carbon fullerenes, stability, singly and doubly charged, 25-12Ч25-15 Carbon fullerenes, stability, spherical aromaticity 25-6
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



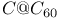 systems, 3-D electrostatic potential field maps
systems, 3-D electrostatic potential field maps ![$[5C@C_{60}]^{+2}$](/math_tex/7b6bef0cafb15f84be30f5d672d982cd82.gif)
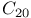 molecule, DFTB method
molecule, DFTB method 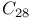 , band structure
, band structure 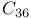 , DFTB method
, DFTB method 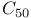 , dimerization energy
, dimerization energy 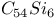 , bond length
, bond length 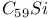 ,
, 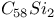 , bond length
, bond length 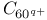 molecular ions photoionization
molecular ions photoionization 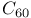 , asymmetric fission model
, asymmetric fission model 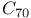 , dissociation energies
, dissociation energies 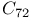 and
and 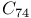
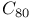 ,
, 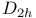 configuration, vibrational analysis
configuration, vibrational analysis 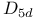 structure
structure 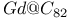
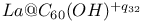 , electronic behavior and stability, eigenvalue spectra comparision
, electronic behavior and stability, eigenvalue spectra comparision 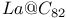
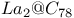
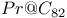
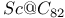
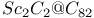 (
(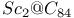 )
) 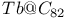
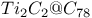
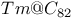
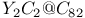 and
and 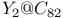
 -conjugated organic molecules
-conjugated organic molecules 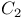 fragmentation
fragmentation  sheet structure
sheet structure 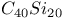 ,
, 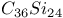 , and
, and 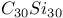 , estimated value
, estimated value 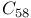 and
and 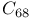 fullerenes
fullerenes