јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Sattler K.D. Ч Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenesјвтор: Sattler K.D. јннотаци€: The field of nanoscience was pioneered in the 1980s with the groundbreaking research on clusters, which later led to the discovery of fullerenes. Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes focuses on the fundamental physics of these nanoscale materials and structures. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers free clusters, including hydrogen, bimetallic, silicon, metal, and atomic clusters, as well as the cluster interactions. The expert contributors examine how carbon fullerenes are produced and how to characterize their stability. They discuss the structure, properties, and behavior of carbon fullerenes, including the smallest possible fullerene: C20. The book also looks at inorganic fullerenes, such as boron fullerenes, silicon fullerenes, nanocones, and onion-like inorganic fullerenes. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2011 оличество страниц: 912ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.07.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Ferromagnetic cluster, magnetic moments 10-11 Ferromagnetic cluster, single-sided deflections 10-10Ч10-11 First-principles molecular dynamics 32-2Ч32-3 Fluid fullerenes 38-9Ч38-10 Fluorofullerenes 36-7Ч36-8 Fourier dynamical matrix, 46-10Ч46-11 Fragmentation, cluster, Coulomb fragmentation 15-12Ч15-14 Fragmentation, cluster, mass spectrometry and cluster stabilities 15-5Ч15-8 Fragmentation, cluster, multifragmentation 15-14Ч15-16 Fragmentation, cluster, nucleation theories 15-17Ч15-19 Fragmentation, cluster, short-time fragmentation dynamics 15-3Ч15-5 Fragmentation, cluster, unimolecular dissociation theories 15-8Ч15-11 Fragmentation, fullerenes and clusters 27-20Ч27-25 Fragmentation, fullerenes, collision 27-4 Fragmentation, fullerenes, collision with neutral atoms or molecules 26-6Ч26-7 Fragmentation, fullerenes, coronene and dimers 27-4 Fragmentation, fullerenes, coulomb explosion 26-7 Fragmentation, fullerenes, electron impact 26-6Ч26-7 Fragmentation, fullerenes, endohedral complexes 26-9Ч26-10 Fragmentation, fullerenes, experiments 26-3 Fragmentation, fullerenes, heating 26-8 Fragmentation, fullerenes, ion impact 26-5Ч26-6 Fragmentation, fullerenes, kinetic energy release 26-8Ч26-9 Fragmentation, fullerenes, monomer anions stability 27-17Ч27-20 Fragmentation, fullerenes, monomer cations 27-5Ч27-17 Fragmentation, fullerenes, NMR spectra for 27-3 Fragmentation, fullerenes, photofragmentation 26-7Ч26-8 Fragmentation, fullerenes, surface impact 26-3Ч26-5 Fragmentation, fullerenes, theory 26-2Ч26-3 Fragmentation, fullerenes, window-like defects, diatomic vacancy 31-4Ч31-5 Frank Ч Kasper polyhedra 51-4 Frank Ч van der Merwe (FM) 18-8 Free cluster, aggregation kinetics, cluster-cluster 16-1Ч16-17 Free cluster, alkali and noble metals see "Alkali and noble metal clusters" "Electronic Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, applications 4-3 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, classification 4-1 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, definition 4-1 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, free metal clusters 4-4Ч4-7 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, geometric structure 4-7Ч4-8 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, properties 4-8 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, special bimetallic clusters 4-9Ч4-10 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, structure-energy principles 4-8Ч4-9 Free cluster, bimetallic clusters, types and clusters formation 4-2Ч4-3 Free cluster, electric and magnetic dipole moments 10-1Ч10-11 Free cluster, hydrogen clusters, computer simulation 11-6Ч11-9 Free cluster, hydrogen clusters, condensed matter, melting 11-1Ч11-3 Free cluster, hydrogen clusters, magic numbers 11-11 Free cluster, hydrogen clusters, phase transitions 11-3Ч11-6 Free cluster, hydrogen clusters, quantum melting 11-12Ч11-14 Free cluster, hydrogen clusters, structure and property 2-1Ч2-15 Free cluster, hydrogen clusters, superfluidity 11-9Ч11-10 Free cluster, intense laser field, atomic clusters, cluster dynamics 13-4Ч13-5 Free cluster, intense laser field, atomic clusters, composite clusters and charge migration 13-11Ч13-12 Free cluster, intense laser field, atomic clusters, Coulomb explosion 13-8Ч13-11 Free cluster, intense laser field, atomic clusters, non-perturbative light-matter interaction 13-2Ч13-4 Free cluster, intense laser field, atomic clusters, resonant light absorption 13-5Ч13-7 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, cluster generation techniques 13-10Ч13-11 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, dual-pulse excitation and angular-resolved emission 13-17Ч13-18 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, femtosecond lasers 13-9 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, ionization dynamics 13-14Ч13-15 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations 13-7Ч13-9 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, multiphoton ionization 13-2Ч13-4 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, radiation absorption 13-12Ч13-14 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, resonance-enhanced ionization, dual pulses 13-6Ч13-7 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, semiclassical Vlasov and VUU methods 13-4Ч13-6 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, surface-plasmon 13-1 Free cluster, laser-cluster interactions, time-resolved particle and photon emission 13-15Ч13-16 Free cluster, mercury 3-1Ч3-8 Free cluster, nucleation and growth, coarsening process 1-5 Free cluster, nucleation and growth, kinetics 1-4Ч1-5 Free cluster, nucleation and growth, narrow size distribution 1-9Ч1-10 Free cluster, nucleation and growth, phase separation 1-6Ч1-9 Free cluster, nucleation and growth, precipitation 1-2 Free cluster, nucleation and growth, thermodynamics 1-2Ч1-4 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), ionizing radiation and matter 7-5Ч7-6 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), metallic solids 7-20Ч7-26 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), molecular gases and liquids 7-17Ч7-20 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), organic clusters, 8-1Ч8-12 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), rare gas clusters 7-7Ч7-17 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), sources 7-6Ч7-7 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), spectral intensity 7-3 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), synchrotron 7-4 Free cluster, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), time-of-flight (TOF) 7-4 Free cluster, silicon clusters, doped silicon cages 5-6Ч5-13 Free cluster, silicon clusters, hybridization preferences 5-1 Free cluster, silicon clusters, stabilization 5-2Ч5-4 Free cluster, substrate interaction 18-1Ч18-15 Free cluster, superfluidity, helium clusters 12-1Ч12-13 Free cluster, vibrational spectroscopy, clusters in matrix isolation 9-2Ч9-3 Free cluster, vibrational spectroscopy, free electron laser (FEL)-based infrared spectroscopy 9-8Ч9-12 Free cluster, vibrational spectroscopy, gas-phase clusters 9-3Ч9-8 Free electron laser (FEL)-based infrared spectroscopy, as IR source 9-8Ч9-10 Free electron laser (FEL)-based infrared spectroscopy, IR laser sources 9-8Ч9-9 Free electron laser (FEL)-based infrared spectroscopy, multiple photon excitation, dissociation 9-10Ч9-12 Free electron laser (FEL)-based infrared spectroscopy, multiple photon excitation, ionization 9-12 Free electron laser (FEL)-based infrared spectroscopy, multiple photon excitation, mechanism 9-10 Fullerene monomer anions, stability, dianions observations 27-19 Fullerene monomer anions, stability, electron affinity (EA) 27-18 27-19 Fullerene monomer anions, stability, projectile velocity effects, collisions 27-18 Fullerene monomer cations, coincidence spectrum 27-8 Fullerene monomer cations, DFT calculated sequential ionization energies 27-12 Fullerene monomer cations, dissociation energy (DE) 27-5 27-6 Fullerene monomer cations, fission barrier (FE) 27-5 27-6 Fullerene monomer cations, fragmentation spectrum for 27-12 Fullerene monomer cations, highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) 27-11 Fullerene monomer cations, kinetic energy release distributions 27-17 Fullerene monomer cations, mass spectrometric observation of 27-9 Fullerene monomer cations, nuclear fragmentation processes 27-15 Fullerene monomer cations, Rice Ч Ramsperger Ч Kassel (RRK) theory 27-14 Fullerene monomer cations, semiempirical fission barriers 27-16 Fullerene monomer cations, slow highly charged 27-10 Fullerene suspensions in water, clusters of 40-5Ч40-6 Fullerene suspensions in water, host-guest complexes and micelles 40-3Ч40-5 Fullerene suspensions in water, hydrophilic groups attachment 40-5 Fullerene suspensions, applications of 40-7 Fullerene suspensions, endohedral fullerenes 40-6Ч40-7 Fullerene suspensions, pristine fullerenes solubility 40-2Ч40-3 Fullerene suspensions, solubility of 40-7Ч40-8 Fullerene suspensions, structures of 40-1Ч40-2 Fullerene suspensions, toxicity, health, and environmental issues 40-6 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, electron acceptor moieties 36-2Ч36-3 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, electronegative atoms 36-3Ч36-5 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, endohedral fullerenes 36-8Ч36-9 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, fluorofullerenes 36-7Ч36-8 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, fullerene derivatives 36-1 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, heterofullerenes 36-6Ч36-7 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, organic photovoltaics 36-9Ч36-12 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, periconjugative effect 36-5Ч36-6 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, pyrrolidinium salts 36-6 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, 36-8 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, anthraquinone (20) 36-4 36-5 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, azafulleroid (45) 36-11 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, azaheterofullerene dimer 37 36-7 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, fluorophore-heterofullerene conjugates 38 36-7 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, fullerotriazolines (24-25) 36-3Ч36-5 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, isoxazolo[60]fullerenes 13-18 36-4 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, ketolactam (46) 36-11 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, p-benzoquinone (19) 36-4 36-5 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) 36-10 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, polymer MDMO-PPV 36-11 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, polymer solar cells 36-12 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, pyrazolino[60]fullerenes (22-23) 36-3Ч36-5 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, pyrrolidinium salts 36-6 36-7 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, quinones 36-2 36-3 36-5 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, TCAQ (21) 36-4 36-5 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, triads 10 and 11 36-3 36-4 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, trinitroflrenone- 12 36-3 36-4 Fullerene-based electron acceptors, structures of, [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) 36-10 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, ab initio methods 50-4Ч50-5 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, delta-self-consistent-field (ASCF) scheme 50-4 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, ground-state geometries 50-2 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, HOMO-LUMO gap, exciton binding energy 50-7 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, HOMO-LUMO gap, first intense dipole-allowed electronic transition 50-8Ч50-9 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, HOMO-LUMO gap, TD-DFT result, NWChem 50-6 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, optical absorption spectra 50-2 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, optoelectronic applications 50-10 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, point groups 50-3 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, quasiparticle (QP) effects 50-2 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), excitonic effect estimation 50-3 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), frequency-space implementation 50-4 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), lowest lying excited electronic states 50-6 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), molecular polarizability 50-5 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), NWCHEM calculations 50-8 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), OCTOPUS calculations 50-6 50-8 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), optical gap 50-7 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), QP-corrected HOMO-LUMO energy gap 50-4 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), real-time propagation method 50-4Ч50-6 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), Thomas Ч Reiche Ч Kuhn dipole sum rule 50-6 Fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT), vertical ionization energy 50-7 Fullerenes clusters, decahedral sphere packing 37-14 Fullerenes clusters, geometrical structure of 37-14Ч37-15 Fullerenes clusters, honeycomb layers of spheres 37-13Ч37-14 Fullerenes clusters, icosahedral packing 37-13 Fullerenes clusters, interaction potential parameters 37-1 37-2 Fullerenes clusters, interaction potentials, 37-4Ч37-5 Fullerenes clusters, interaction potentials, 37-5 Fullerenes clusters, interaction potentials, 37-4 Fullerenes clusters, interaction potentials, 37-5 Fullerenes clusters, mass abundance spectrum, 37-2 Fullerenes clusters, mass abundance spectrum, 37-3 Fullerenes clusters, mass abundance spectrum, 37-2 37-3 Fullerenes clusters, multiply charged clusters, appearance size, theoretical calculations 37-12Ч37-13 Fullerenes clusters, multiply charged clusters, hot clusters dynamics 37-13 Fullerenes clusters, multiply charged clusters, liquid-drop model 37-11Ч37-12 Fullerenes clusters, multiply charged clusters, production of 37-11 Fullerenes clusters, packing of spheres 37-14Ч37-15 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, Leary's Tetrahedron 37-9 37-11 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, mass abundance spectra, charge dependence 37-8Ч37-10 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, mass abundance spectra, temperature dependence 37-9 37-10 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, neutral and charged clusters 37-8 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, potential energy 37-5Ч37-6 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, ranges of forces relation 37-7Ч37-8 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, structural transitions 37-9Ч37-11 Fullerenes clusters, structure of, theoretical studies 37-6Ч37-7 Fullerenes clusters, van der Waals clusters 37-7 37-8 Fulleroids, symmetry, (5,7) type 28-10Ч28-12 Fulleroids, symmetry, convex polyhedra and planar graphs 28-1Ч28-2 Fulleroids, symmetry, icosahedral fulleroids 28-6Ч28-8 Fulleroids, symmetry, local restrictions 28-4Ч28-6 Fulleroids, symmetry, multi-pentagonal faces 28-8Ч28-10 Fulleroids, symmetry, octahedral, prismatic, or pyramidal 28-10 Fulleroids, symmetry, point symmetry groups 28-2 Fulleroids, symmetry, polyhedral symmetries and graph automorphisms 28-2Ч28-3 Fulleroids, symmetry, subgroups 28-8 Fulleroids, symmetry, twofold rotational axis 28-6 Fullerol clusters, aqueous systems 44-10Ч44-11 Fullerol clusters, Derjaguin Ч Landau Ч Verwey Ч Overbeek (DLVO) theory 44-9 Fullerol clusters, dry fullerol powder, infrared spectrum 44-6 Fullerol clusters, electrophoretic mobility 44-8 44-9 Fullerol clusters, fullerenes, aqueous dispersions 44-4Ч44-5 Fullerol clusters, fullerenes, caged fullerene molecules 44-3Ч44-4 Fullerol clusters, fullerenes, carbon allotropes, molecular structures 44-2 Fullerol clusters, fullerol dispersions 44-7 Fullerol clusters, nanotechnology 44-1Ч44-2 Fullerol clusters, production techniques 44-5 Fullerol clusters, structure of 44-10 Fullerol clusters, titration curve 44-8 Fullerol clusters, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image 44-9 Fullerol clusters, ultraviolet and visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra 44-6 44-7 Fullerol dispersions 44-7 Gas-phase clusters, vibrational spectroscopy, direct absorption measurements, cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) 9-4 Gas-phase clusters, vibrational spectroscopy, direct absorption measurements, high-resolution diode laser spectroscopy 9-3Ч9-4 Gas-phase clusters, vibrational spectroscopy, electronic transitions, anion photoelectron spectroscopy 9-4Ч9-5 Gas-phase clusters, vibrational spectroscopy, electronic transitions, zero electron kinetic energy spectroscopy 9-5Ч9-6 Gas-phase clusters, vibrational spectroscopy, He droplets, spectroscopy 9-7Ч9-8 Gas-phase clusters, vibrational spectroscopy, photodissociation spectroscopy 9-6Ч9-7 Gas-phase ion mobility 32-2 Gelation transition, finite time gelation 16-9 Gelation transition, gelation kinetics regularization 16-10Ч16-12 Gelation transition, instantaneous gelation 16-10 Generalized gradient approximations (GGA) 32-3 Giant dipole plasmon resonance 26-6 Girifalco potential 37-4 Growth, free cluster, coarsening process 1-5 Growth, free cluster, kinetics 1-4Ч1-5 Growth, free cluster, narrow size distribution 1-9Ч1-10 Growth, free cluster, phase separation 1-6Ч1-9 Growth, free cluster, precipitation 1-2 Growth, free cluster, thermodynamics 1-2Ч1-4 Growth, fullerene, geometries 23-1Ч22-2 Growth, fullerene, growth models 23-3Ч23-6 Growth, fullerene, open problems 23-6 Growth, fullerene, STM images 23-7 Helium nanodroplets, bulk helium 20-3Ч20-4 Helium nanodroplets, charged helium droplets, charged droplets multiplication 20-6Ч20-7 Helium nanodroplets, charged helium droplets, negatively charged droplets 20-7Ч20-9 Helium nanodroplets, charged helium droplets, positively charged droplets 20-6 Helium nanodroplets, electric and magnetic dipole moments 10-9 Helium nanodroplets, electron attachment 20-17Ч20-19 Helium nanodroplets, electron impact ionization 20-15Ч20-17 Helium nanodroplets, fragmentation, cluster ions 20-12Ч20-13 Helium nanodroplets, ion size 20-19Ч20-21 Helium nanodroplets, ionization and fragmentation of 20-13Ч20-14 Helium nanodroplets, mass spectrometric techniques 20-9Ч20-10 Helium nanodroplets, neutral helium droplets, doped neutral droplets 20-4Ч20-5 Helium nanodroplets, neutral helium droplets, electronic excitations 20-4Ч20-5 Helium nanodroplets, neutral helium droplets, synthesis of 20-3Ч20-4 Helium nanodroplets, organic and biomolecules 20-21Ч20-22 Helium nanodroplets, rare-gas clusters 20-11Ч20-12 Helium nanodroplets, rare-gas dimers 20-10Ч20-11 Helium nanodroplets, superfluidity 2-16 Helium nanodroplets, temperature, cluster ions 20-13 Heterofullerenes 36-6Ч36-7 Highest occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) gap, 30-7Ч30-8 Highest occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) gap, 5-9 Highest occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) gap, Ag nanoclusters 17-13Ч17-14 Highest occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) gap, bimetallic clusters 4-6 Highest occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) gap, silicon fullerenes 48-7 HOMO-LUMO gap see "Highest occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital gap" Hot clusters dynamics 37-13 HPLC separation, fullerenes, alkyl-bonded silica stationary phases, 22-6Ч22-8 HPLC separation, fullerenes, alkyl-bonded silica stationary phases, comparison of 22-6 HPLC separation, fullerenes, alkyl-bonded silica stationary phases, octadecyl-bonded silica (ODS) stationary phases 22-4Ч22-5 HPLC separation, fullerenes, alkyl-bonded silica stationary phases, physical parameters, influence 22-5Ч22-6 HPLC separation, fullerenes, alkyl-bonded silica stationary phases, temperature dependence of 22-6 HPLC separation, fullerenes, aromatic system, stationary phases, 22-16 HPLC separation, fullerenes, aromatic system, stationary phases, calixarene-bonded silica phases 22-16Ч22-17 HPLC separation, fullerenes, aromatic system, stationary phases, coronenylpentylsilyl-bonded (COP) silica stationary phases 22-15 HPLC separation, fullerenes, aromatic system, stationary phases, heavy atoms 22-15 HPLC separation, fullerenes, aromatic system, stationary phases, humic-acid-bonded silica stationary phase 22-15Ч22-16 HPLC separation, fullerenes, aromatic system, stationary phases, phthalocyanine-bonded phases 22-17Ч22-18 HPLC separation, fullerenes, block diagram of 22-3 HPLC separation, fullerenes, buckminsterfullerene, endohedral metallofullerenes separation 22-21Ч22-22 HPLC separation, fullerenes, buckminsterfullerene, hydrogenated derivatives separation 22-21 HPLC separation, fullerenes, charge-transfer stationary phases, chiral stationary phases 22-14 HPLC separation, fullerenes, charge-transfer stationary phases, liquid-crystal-bonded silica phases 22-14Ч22-15 HPLC separation, fullerenes, charge-transfer stationary phases, multilegged type stationary phases 22-9 22-12Ч22-13 HPLC separation, fullerenes, charge-transfer stationary phases, nitro-derivatized phenyl-bonded phases 22-13Ч22-14 HPLC separation, fullerenes, charge-transfer stationary phases, phenylalkyl-bonded silica phases 22-9Ч22-11 HPLC separation, fullerenes, elution curve, chromatography 22-4 HPLC separation, fullerenes, polymer stationary phases 22-21 HPLC separation, fullerenes, porphyrin-bonded silica stationary phase 22-18Ч22-19 HPLC separation, fullerenes, properties and applications 22-1 HPLC separation, fullerenes, pyrenyl ligands, stationary phase, pyrenebutyric acid-modifi ed magnesia-zirconia stationary phases 22-20Ч22-21 HPLC separation, fullerenes, pyrenyl ligands, stationary phase, pyrenyl-bonded silica stationary phase 22-19Ч22-20 HPLC separation, fullerenes, seperation 22-1Ч22-2 Hueckel calculations 30-7 Hydrogen clusters, charged clusters, ab initio quantum chemical method caculation 2-8 Hydrogen clusters, charged clusters, binding energy 2-7Ч2-8 Hydrogen clusters, charged clusters, bonding and dissociation 2-7
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



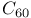
 -conjugated organic molecules
-conjugated organic molecules 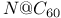
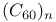 clusters
clusters 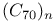 clusters
clusters 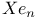 clusters
clusters 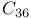
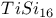
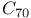 HPLC retention reversal study
HPLC retention reversal study