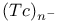јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Sattler K.D. Ч Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenesјвтор: Sattler K.D. јннотаци€: The field of nanoscience was pioneered in the 1980s with the groundbreaking research on clusters, which later led to the discovery of fullerenes. Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes focuses on the fundamental physics of these nanoscale materials and structures. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers free clusters, including hydrogen, bimetallic, silicon, metal, and atomic clusters, as well as the cluster interactions. The expert contributors examine how carbon fullerenes are produced and how to characterize their stability. They discuss the structure, properties, and behavior of carbon fullerenes, including the smallest possible fullerene: C20. The book also looks at inorganic fullerenes, such as boron fullerenes, silicon fullerenes, nanocones, and onion-like inorganic fullerenes. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2011 оличество страниц: 912ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.07.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Hydrogen clusters, charged clusters, potential energy surface 2-8Ч2-9 Hydrogen clusters, computer simulation, Feynman's path integral 11-7Ч11-8 Hydrogen clusters, computer simulation, mathematical model 11-6Ч11-7 Hydrogen clusters, computer simulation, Monte Carlo simulation 11-8Ч11-9 Hydrogen clusters, condensed matter, melting, entropy 11-1Ч11-2 Hydrogen clusters, condensed matter, melting, helium characteristics 11-2Ч11-3 Hydrogen clusters, condensed matter, melting, zero-point motion 11-2 Hydrogen clusters, laser irradiation and Coulomb explosion, deuterium, electric dipole moment 2-12 Hydrogen clusters, laser irradiation and Coulomb explosion, deuterium, frequency 2-10Ч2-11 Hydrogen clusters, laser irradiation and Coulomb explosion, deuterium, kinetic energy and ionization potential 2-11Ч2-12 Hydrogen clusters, laser irradiation and Coulomb explosion, deuterium, multiple ionization 2-10 Hydrogen clusters, laser irradiation and Coulomb explosion, deuterium, significances 2-9Ч2-10 Hydrogen clusters, laser irradiation and Coulomb explosion, deuterium, time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) 2-10 Hydrogen clusters, liquid-to-gas phase transition 2-9 Hydrogen clusters, magic numbers 11-11 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, ab initio quantum chemical calculations 2-3 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, binding energy 2-3 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, intrinsic derealization 2-5 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, multilayer icosahedral (MIC) growth 2-4 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, quantum Monte Carlo (MC) calculations 2-5 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, sizes 2-3Ч2-4 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, stability function 2-4 Hydrogen clusters, neutral clusters, thermal effects 2-6Ч2-7 Hydrogen clusters, nuclear fusion reactions 2-1 Hydrogen clusters, phase transitions, Bose Ч Einstein condensation (BEC) and superfluidity 11-5Ч11-6 Hydrogen clusters, phase transitions, cluster melting and freezing 11-4 Hydrogen clusters, phase transitions, finite and infinite system 11-3Ч11-4 Hydrogen clusters, phase transitions, mixed hydrogen clusters 11-6 Hydrogen clusters, phase transitions, quantum clusters 11-4Ч11-5 Hydrogen clusters, pressure effects, encapsulation, 2-13Ч2-15 Hydrogen clusters, pressure effects, gradual dissociation 2-13 Hydrogen clusters, pressure effects, molecular 2-12 Hydrogen clusters, pressure effects, preferred packing structures 2-12Ч2-13 Hydrogen clusters, production, cryogenic jets 2-2Ч2-3 Hydrogen clusters, quantum effects 2-16Ч2-17 Hydrogen clusters, quantum melting, chemical potential 11-12 Hydrogen clusters, quantum melting, doped clusters and exchange cycles 11-14 Hydrogen clusters, quantum melting, exchange cycle frequency 11-13Ч11-14 Hydrogen clusters, quantum melting, radial density profile, temperature 11-13 Hydrogen clusters, quantum melting, superfluid fraction 11-12Ч11-13 Hydrogen clusters, structure, radial density profiles 11-10Ч11-11 Hydrogen clusters, structure, three-dimensional representation 11-11 Hydrogen clusters, superfluidity 11-9Ч11-10 Hydrogen clusters, supported clusters 2-15 Hydrogenated 33-11 33-13 Hydrogenated 33-12 Hydrogenated 33-10 Hydrogenated 33-11 Hydrogenated 33-10 Hydrogenated 33-11 33-12 Hydrogenated 33-9 Hydrogenated 33-12 Hydrogenated 33-12 33-13 Hydrogenated 33-11 33-12 Hydrogenated 33-10 Hydrogenated 33-10 Icosahedral packing, clusters 37-14 Implantation, cluster, clearing-the-way effect 19-8 Implantation, cluster, gas cluster ions 19-10 Implantation, cluster, p-MOSFET, SEM image 19-9 Implantation, cluster, shallow 19-10 Impulsive and electronic excitations, electron impact excitations 15-4 Impulsive and electronic excitations, potential energy surfaces 15-3 Inorganic fullerenes, boron nitride, definition 49-1 Inorganic fullerenes, boron nitride, doping 49-7Ч49-9 Inorganic fullerenes, boron nitride, geometry 49-2Ч49-5 Inorganic fullerenes, boron nitride, historic review 49-1Ч49-2 Inorganic fullerenes, boron nitride, non-stoichiometry 49-5Ч49-7 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, 47-4 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, cohesive energies 47-3 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, electronic structure 47-5Ч47-6 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, isomerization 47-5 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, lattice structure 47-1Ч47-2 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, nanotubes 47-4Ч47-5 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, sructure and symmetry, boron clusters 47-1Ч47-2 Inorganic fullerenes, boron, vibrational modes 47-6Ч47-7 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, ab initio methods 50-4Ч50-5 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, delta-self-consistent-field (ASCF) scheme 50-4 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, ground-state geometries 50-2 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, HOMO-LUMO gap 50-6Ч50-9 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, optical absorption spectra 50-2 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, optoelectronic applications 50-10 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, point groups 50-3 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, quasiparticle (QP) effects 50-2 Inorganic fullerenes, fullerene-like III-V binary compounds, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) 50-3Ч50-8 Inorganic fullerenes, onion-like compounds, computational techniques and stability 51-10Ч51-11 Inorganic fullerenes, onion-like compounds, definition 51-1 Inorganic fullerenes, onion-like compounds, experimental realizations 51-9Ч51-10 Inorganic fullerenes, onion-like compounds, geometric properties 51-2Ч51-5 Inorganic fullerenes, onion-like compounds, symmetries and building principles 51-5Ч51-9 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, bond formation 48-2 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, combined benfits 48-4 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, direct method 48-4Ч48-6 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, hybridization 48-2 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, indirect method 48-6Ч48-12 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, intermediate approach 48-6Ч48-7 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, orbital, combination 48-1Ч48-2 Inorganic fullerenes, silicon, vs. carbon fullerenes 48-1 48-3Ч48-4 Intense laser field, atomic clusters see also "Laser-cluster interactions" Intense laser field, atomic clusters, cluster dynamics, cluster preparation 13-4 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, cluster dynamics, evolution 13-5 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, cluster dynamics, pump-probe technique 13-5 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, composite clusters and charge migration 13-11Ч13-12 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, Coulomb explosion, pulse-profile and size-distribution effects 13-9Ч13-11 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, Coulomb explosion, single-cluster explosion 13-8Ч13-9 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, non-perturbative light-matter interaction, atoms, energy absorption principle 13-2Ч13-3 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, non-perturbative light-matter interaction, optical slingshots 13-3Ч13-4 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, resonant light absorption, damped oscillator 13-5Ч13-7 Intense laser field, atomic clusters, resonant light absorption, nanoplasma model 13-7 Ion impact, fullerene fragmentation 26-5Ч26-6 Isolated pentagon rule (IPR) 42-3 Jahn Ч Teller effect 30-7 Keplerate fullerene-like cages, building principle 51-7 Keplerate fullerene-like cages, icosahedral symmetry 51-9 Keplerate fullerene-like cages, molecular structure 51-8 Keplerate fullerene-like cages, point group symmetry 51-7 Keplerate fullerene-like cages, potential energy surface (PES) 51-10 KERD see "Kinetic energy release distribution (KERD)" Kinetic energy release distribution (KERD), fullerene fragmentation 26-8 Lanthanide elements, 42-7 Lanthanide elements, 42-8Ч42-9 Lanthanide elements, 42-7 Lanthanide elements, 42-8 Lanthanide elements, overview 42-7 Laser ablation method, matrix deposition of 9-3 Laser ablation method, plasma synthesis 21-4 Laser ablation method, surface erosion 19-4 Laser irradiation, carbon onion production 24-5 Laser irradiation, hydrogen clusters 2-9Ч2-12 Laser-cluster interactions see also "Intense laser field" "Atomic Laser-cluster interactions, cluster generation techniques 13-10Ч13-11 Laser-cluster interactions, dual-pulse excitation and angular-resolved emission, acceleration of ions 13-17 Laser-cluster interactions, dual-pulse excitation and angular-resolved emission, asymmetric Coulomb explosion 13-17Ч13-18 Laser-cluster interactions, dual-pulse excitation and angular-resolved emission, plasmon-enhanced ionization 13-18 Laser-cluster interactions, dual-pulse excitation and angular-resolved emission, surface-plasmon-assisted rescattering in clusters (SPARC) 13-18 Laser-cluster interactions, femtosecond lasers 13-9 Laser-cluster interactions, ionization dynamics 13-14Ч13-15 Laser-cluster interactions, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, high energy cluster charge 13-7Ч13-9 Laser-cluster interactions, multiphoton ionization (MPI) 13-2Ч13-4 Laser-cluster interactions, radiation absorption, critical radius 13-13Ч13-14 Laser-cluster interactions, radiation absorption, energy absorption fraction 13-12 Laser-cluster interactions, radiation absorption, energy and laser power absorption, Xe 13-12 Laser-cluster interactions, resonance-enhanced ionization, dual pulses 13-6Ч13-7 Laser-cluster interactions, semiclassical Vlasov and Vlasov Ч Uehling Ч Uhlenbeck (VUU) methods, Hartree term 13-5 Laser-cluster interactions, semiclassical Vlasov and Vlasov Ч Uehling Ч Uhlenbeck (VUU) methods, normalized Gaussians 13-5Ч13-6 Laser-cluster interactions, semiclassical Vlasov and Vlasov Ч Uehling Ч Uhlenbeck (VUU) methods, Vlasov Ч Uehling Ч Uhlenbeck equation 13-5 Laser-cluster interactions, semiclassical Vlasov and Vlasov Ч Uehling Ч Uhlenbeck (VUU) methods, von Neumann equation 13-4 Laser-cluster interactions, semiclassical Vlasov and Vlasov Ч Uehling Ч Uhlenbeck (VUU) methods, Wigner transform 13-4 Laser-cluster interactions, surface-plasmon 13-1 Laser-cluster interactions, time-resolved particle and photon emission, CREI concept 13-15Ч13-16 Laser-cluster interactions, time-resolved particle and photon emission, pulse duration 13-15 Laser-cluster interactions, time-resolved particle and photon emission, x-ray yield 13-16 Laser-induced photon absorption 26-7 Lattice dynamics theory 46-6Ч46-7 Lead (Pb) clusters, Si(111)7 17-4 Lead (Pb) clusters, Si(111)7 17-4 Lead (Pb) clusters, Si(111)7 17-5 Lead (Pb) clusters, Si(111)7 17-5 Lead (Pb) clusters, Si(111)7 17-2Ч17-3 Lead (Pb) clusters, Si(111)7 17-4 Leary's Tetrahedron structure 37-9 37-11 Lennard Ч Jones potential 18-2 Liposomes 41-4Ч41-5 Local density approximation (LDA) 32-3 Macrocyclic compounds 41-6Ч41-7 Magic clusters, atomic shells model 4-6Ч4-7 Magic clusters, definition 4-5 Magic clusters, electronic closed shell-geometric transition 17-13Ч17-14 Magic clusters, electronic shells model 4-5Ч4-6 Magic clusters, first-principles calculations 17-11Ч17-13 Magic clusters, size and shape distributions, spatially averaged tunneling spectra 17-11 Magic clusters, size and shape distributions, STM image 17-9Ч17-10 Magic clusters, substrate effect, adsorption 17-16 Magic clusters, substrate effect, Moire pattern 17-14Ч17-15 Magnetic bottle PE spectrometer 8-7 Magnetic dipole moments see "Electric and magnetic dipole moments" "Free Mayer bond order (MBO) 32-5 Mercury clusters, band gap closure 3-1 Mercury clusters, bond length 3-1Ч3-2 Mercury clusters, dissociation energies ( 3-1 Mercury clusters, electron localization function (ELF) 3-3 Mercury clusters, global minimum structures 3-4 Mercury clusters, ionization potentials and static dipole polarizability 3-2 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, ab initio potential 3-5 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, electronic distribution 3-5 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, electrowetting, crystal structure 3-6 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, gas-liquid coexistence curve 3-5Ч3-6 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, inelastic x-ray scattering measurements 3-6 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, Langmuir monolayer substrate 3-7 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, surface layering 3-6Ч3-7 Mercury clusters, liquid mercury, M-NM transition, threebody potentials 3-5 Mercury clusters, low melting point 3-1 Mercury clusters, medium- to large-sized structures 3-4 Mercury clusters, relativistic and electron correlation effects 3-2 Mercury clusters, solid mercury, mean-field (Hartree Ч Fock) treatment 3-7 Mercury clusters, solid mercury, pressure changes 3-8 Mercury clusters, solid mercury, rhombohedral lattice structure 3-7 Mercury clusters, solid mercury, wavefunction-based correlation treatment 3-8 Mercury clusters, spectroscopic properties 3-3 Mercury clusters, transition, chemical bond 3-2 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, copper surfaces Cu(111), Cu(110) and thin films, carbon 1s core-level photoemission spectra 39-4 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, copper surfaces Cu(111), Cu(110) and thin films, densities of states (DOS) 39-5 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, copper surfaces Cu(111), Cu(110) and thin films, sheet resistance measurement 39-4 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, copper surfaces Cu(111), Cu(110) and thin films, zero angle orientation 39-3 39-4 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, gold surface Au(110) and Au(111), EELS measurements 39-8 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, gold surface Au(110) and Au(111), frequency Shifts 39-9 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, gold surface Au(110) and Au(111), optimized interface structure 39-7 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, other metal surfaces 39-9Ч39-11 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, silver surfaces, Ag(111), and Ag(100), adsorption energies 39-6 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, silver surfaces, Ag(111), and Ag(100), Raman frequencies comparison 39-6 Metal surfaces, fullerenes, silver surfaces, Ag(111), and Ag(100), Raman spectra 39-6 39-7 Metal-coated fullerenes, alkali earth metals 43-3 Metal-coated fullerenes, alkali metal atoms 43-2Ч43-3 Metal-coated fullerenes, applications 43-5Ч43-6 Metal-coated fullerenes, coating mechanisms 43-5 Metal-coated fullerenes, synthesis and characterization 43-1Ч43-2 Metal-coated fullerenes, transition metal atoms case 43-3Ч43-5 Metal-coated fullerenes, vanadium coating 43-4 Metal-fullerene clusters, electric and magnetic dipole moments 10-6Ч10-7 Metallofullerenes 31-5Ч31-6 42-1Ч42-2 Methane clusters 7-18Ч7-19 Microreversibility, fragmentation, average kinetic energy release, evaporation 15-11 Microreversibility, fragmentation, phase space theory (PST) vs. molecular dynamics trajectories 15-10 Molecular beam deflection technique 10-11 Molecular orbital treatment, endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-1Ч33-9 Molecular orbital treatment, endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-13Ч33-14 Molecular orbital treatment, endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-14Ч33-17 Molecular orbital treatment, endohedrally doped fullerenes, endohedrally doped hydrogenated 33-9Ч33-13 Molecular orbital treatment, fullerenes definition 33-1 Molecular orbital treatment, metallofullerenes ( 33-17Ч33-18 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, group three metal atom, 42-3Ч42-5 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, group three metal atom, 42-5Ч42-6 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, group two metal atom 42-6Ч42-7 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, lanthanide elements, 42-7 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, lanthanide elements, 42-8Ч42-9 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, lanthanide elements, 42-7 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, lanthanide elements, 42-8 Mono metal atom-entrapped fullerenes, lanthanide elements, overview 42-7 Monte Carlo calculation, cluster-cluster aggregation kinetics 16-4 Monte Carlo calculation, quantum melting, hydrogen clusters 11-8 Monte Carlo calculation, superfluidity, helium clusters 12-2Ч12-3 Mulliken population analysis, boron nitride fullerenes and nanocones 49-9 Mulliken population analysis, cluster-substrate interaction 18-14 Mulliken population analysis, silicon-doped fullerenes 32-8 Multilayer icosahedral (MIC) 2-4 Multiphoton ionization (MPI), barrier-suppression ionization (BSI) 13-3 Multiphoton ionization (MPI), Keldysh adiabaticity parameter 13-2 Multiphoton ionization (MPI), nanoplasma and Inverse Bremsstrahlung (IBS) 13-3Ч13-4 Multiple atoms-entrapped fullerenes, 42-10Ч42-11 Multiple atoms-entrapped fullerenes, 42-9 Multiple atoms-entrapped fullerenes, 42-10 Multiple atoms-entrapped fullerenes, 42-9Ч42-10 Multiple atoms-entrapped fullerenes, nitride-entrapped fullerenes 42-10 Multiple atoms-entrapped fullerenes, overview 42-9 Multiply charged clusters, appearance size, theoretical calculations 37-12Ч37-13 Multiply charged clusters, hot clusters dynamics 37-13 Multiply charged clusters, liquid-drop model 37-11Ч37-12 Multiply charged clusters, production of 37-11 Multiscaling aggregating particles, cluster, decaying state 16-12Ч16-14 Multiscaling aggregating particles, cluster, mass distribution, higher order correlation functions 16-16 Multiscaling aggregating particles, cluster, mass distribution, inverse Laplace transform 16-15 Multiscaling aggregating particles, cluster, steady state 16-14Ч16-15 Nanocarbon clusters 38-2 Nanopeapods see also "Carbon nanotube" Nanopeapods, charged fullerenes 25-2 Nanopeapods, defective fullerenes 31-5Ч31-6 Neutral and charged clusters 37-8 Nitrogen clusters 7-17 Nonadiabatic dynamics, fragmentation, tight-binding method 15-4 Nonadiabatic dynamics, fragmentation, time-dependent density-functional theory (TDDFT) 15-4 Nonadiabatic dynamics, fragmentation, trajectory surface hopping (TSH) method 15-5Ч15-6 Nonequilibrium plasma method 21-7Ч21-8 Nose Ч Hoover thermostats 32-5 Nucleation and growth, clusters, coarsening process 1-5 Nucleation and growth, clusters, kinetics, compound NCs sythesis 1-4Ч1-5 Nucleation and growth, clusters, kinetics, stability 1-4 Nucleation and growth, clusters, kinetics, two-stage anneal 1-4 Nucleation and growth, clusters, narrow size distribution, cryogenic plasma systems 1-10 Nucleation and growth, clusters, narrow size distribution, general considerations 1-9 Nucleation and growth, clusters, narrow size distribution, nonequilibrium conditions 1-9Ч1-10 Nucleation and growth, clusters, narrow size distribution, short thermal anneal 1-10 Nucleation and growth, clusters, phase separation, Binder's derivation 1-6 Nucleation and growth, clusters, phase separation, long-term behavior, scaling 1-7Ч1-8 Nucleation and growth, clusters, phase separation, short-term behavior, nucleation 1-6Ч1-7 Nucleation and growth, clusters, phase separation, size distribution shape 1-8Ч1-9 Nucleation and growth, clusters, precipitation 1-2 Nucleation and growth, clusters, thermodynamics, Gibbs Ч Thomson relation 1-3 Nucleation and growth, clusters, thermodynamics, metastable region 1-3 Nucleation and growth, clusters, thermodynamics, spinodal curve 1-2Ч1-3 Nucleation and growth, clusters, thermodynamics, transition probabilities 1-4 Oligoacene cluster anions, isomer, characteristics, 8-9Ч8-10 Oligoacene cluster anions, isomer, characteristics, isomer I, disordered cluster anions 8-10 Oligoacene cluster anions, isomer, characteristics, isomer II-1, 2D crystal-like cluster anions 8-10Ч8-11 Oligoacene cluster anions, isomer, characteristics, isomer II-2, multilayered crystal-like cluster anions 8-11Ч8-12 Oligoacene cluster anions, isomer, coexistence 8-8Ч8-9 Onion-like inorganic fullerenes, computational techniques and stability, atomization energies 51-11 Onion-like inorganic fullerenes, computational techniques and stability, molecular electronic structure calculations 51-10 Onion-like inorganic fullerenes, definition 59-1 Onion-like inorganic fullerenes, experimental realizations 51-9Ч51-10 Onion-like inorganic fullerenes, geometric properties 51-2Ч51-5
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



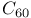 and
and 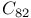
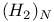 clusters formation
clusters formation 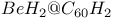 systems, HOMO and LUMO
systems, HOMO and LUMO 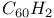 and
and 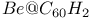 structural properties
structural properties  )
)  sheet structure
sheet structure 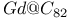
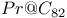
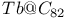
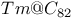
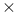 7 surface, 3D cluster and 2D island surface
7 surface, 3D cluster and 2D island surface 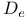 )
) 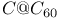 systems
systems 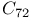 and
and 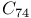
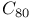
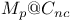 )
) 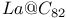
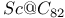
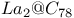
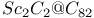 (
(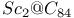 )
) 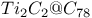
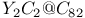 and
and 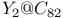
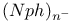 ,
, 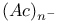 and
and