јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Sattler K.D. Ч Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenesјвтор: Sattler K.D. јннотаци€: The field of nanoscience was pioneered in the 1980s with the groundbreaking research on clusters, which later led to the discovery of fullerenes. Handbook of Nanophysics: Clusters and Fullerenes focuses on the fundamental physics of these nanoscale materials and structures. Each peer-reviewed chapter contains a broad-based introduction and enhances understanding of the state-of-the-art scientific content through fundamental equations and illustrations, some in color. This volume covers free clusters, including hydrogen, bimetallic, silicon, metal, and atomic clusters, as well as the cluster interactions. The expert contributors examine how carbon fullerenes are produced and how to characterize their stability. They discuss the structure, properties, and behavior of carbon fullerenes, including the smallest possible fullerene: C20. The book also looks at inorganic fullerenes, such as boron fullerenes, silicon fullerenes, nanocones, and onion-like inorganic fullerenes. Nanophysics brings together multiple disciplines to determine the structural, electronic, optical, and thermal behavior of nanomaterials; electrical and thermal conductivity; the forces between nanoscale objects; and the transition between classical and quantum behavior. Facilitating communication across many disciplines, this landmark publication encourages scientists with disparate interests to collaborate on interdisciplinary projects and incorporate the theory and methodology of other areas into their work.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2011 оличество страниц: 912ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.07.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Carbon fullerenes, structure and properties, carbon onions 34-1Ч34-15 Carbon fullerenes, structure and properties, electron acceptors 36-1Ч36-12 Carbon fullerenes, structure and properties, molecular orbital treatment 33-1Ч33-18 Carbon fullerenes, structure and properties, plasmons 35-1Ч35-10 Carbon fullerenes, structure and topology 25-2Ч25-4 Carbon fullerenes, supported fullerenes, fundamental processes 39-1Ч39-2 Carbon fullerenes, supported fullerenes, metal surfaces 39-3Ч39-11 Carbon fullerenes, supported fullerenes, semiconductor and insulator surfaces 39-11Ч39-12 Carbon fullerenes, supported fullerenes, supporting medias 39-12 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, 38-5Ч38-9 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, 38-3 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, developments 38-10 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, fluid fullerenes 38-9Ч38-10 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, liquid crystalline assemblies 38-9 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, nanocarbon clusters 38-2 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, pristine 38-2Ч38-3 Carbon fullerenes, supramolecular assemblies, solid surfaces assemblies 38-3Ч38-5 Carbon fullerenes, suspensions, applications of 40-7 Carbon fullerenes, suspensions, endohedral fullerenes 40-6Ч40-7 Carbon fullerenes, suspensions, in water 40-3Ч40-6 Carbon fullerenes, suspensions, pristine fullerenes solubility 40-2Ч40-3 Carbon fullerenes, suspensions, solubility of 40-7Ч40-8 Carbon fullerenes, suspensions, structures of 40-1Ч40-2 Carbon fullerenes, suspensions, toxicity, health, and environmental issues 40-6 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, (5,7) type 28-10Ч28-12 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, convex polyhedra and planar graphs 28-1Ч28-2 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, icosahedral fulleroids 28-6Ч28-8 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, local restrictions 28-4Ч28-6 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, multi-pentagonal faces 28-8Ч28-10 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, octahedral, prismatic, or pyramidal 28-10 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, point symmetry groups 28-2 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, polyhedral symmetries and graph automorphisms 28-2Ч28-3 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, subgroups 28-8 Carbon fullerenes, symmetry of fulleroids, twofold rotational axis 28-6 Carbon nanotube (CNT), 41-9 41-14 Carbon nanotube (CNT), 46-19Ч46-20 Carbon nanotube (CNT), 46-3Ч46-4 Carbon nanotube (CNT), 46-12Ч46-13 Carbon nanotube (CNT), single-walled type, 31-6 Carbon nanotube (CNT), single-walled type, 31-5 Carbon nanotube (CNT), single-walled type, SW defect 31-3 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) 34-9 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, 24-12 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, catalytic disproportionation, CO 24-10Ч24-12 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, hollow carbon onion particles production 24-17Ч24-19 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, low-temperature synthesis 24-13Ч24-15 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, nitrogen incorporation, growth of 24-15Ч24-17 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, plasma enhanced 24-10 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, thermal 24-13 Carbon onions, chemical vapor deposition, vapor phase growth 24-12Ч24-13 Carbon onions, closed cage carbon structures, fullerene molecules 34-3 34-4 Carbon onions, closed cage carbon structures, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images 34-3 34-4 Carbon onions, closed cage carbon structures, icosahedral structure 34-4 Carbon onions, closed cage carbon structures, polyhedral OLC particles 34-5 Carbon onions, high-energy condition, preparation, arc discharge method 24-2Ч24-4 Carbon onions, high-energy condition, preparation, carbon ions implantation, metal particles 24-5Ч24-6 Carbon onions, high-energy condition, preparation, high-energy irradiation 24-4Ч24-5 Carbon onions, high-energy condition, preparation, thermal treatment 24-6Ч24-9 Carbon onions, hybridization, 34-2Ч34-3 Carbon onions, hybridization, orbital mixing 34-2 Carbon onions, hybridization, overlap of sp hybrid orbitals 34-2 Carbon onions, properties and applications, electrical resistivity 34-11 Carbon onions, properties and applications, electronic properties 34-10Ч34-11 Carbon onions, properties and applications, field emission 34-11Ч34-13 Carbon onions, properties and applications, optical properties 34-13Ч34-14 Carbon onions, properties and applications, tribological properties 34-14Ч34-15 Carbon onions, synthesis, alternative material 34-6Ч34-8 Carbon onions, synthesis, developments 34-8Ч34-10 Carbon onions, synthesis, electron beam irradiation 34-5Ч34-6 Carbon onions, TEM images of 24-2 Carbon onions, ultra-dispersed diamond (UDD) 34-10 34-11 Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS), gas-phase clusters 9-4 Charge migration 13-11Ч13-12 Charged fullerenes stability, 25-15Ч25-16 Charged fullerenes stability, 25-12 Charged fullerenes stability, 25-15Ч25-16 Charged fullerenes stability, 25-5Ч25-12 Charged fullerenes stability, bonding features, 25-5 Charged fullerenes stability, bonding features, 25-5 Charged fullerenes stability, bonding features, chemical bonds 25-4Ч25-5 Charged fullerenes stability, kinetic energy release 25-2 Charged fullerenes stability, nano-peapods 25-2 Charged fullerenes stability, negatively charged fullerenes 25-16Ч25-18 Charged fullerenes stability, rules of stability 25-5Ч25-6 Charged fullerenes stability, singly and doubly charged, 25-12Ч25-15 Charged fullerenes stability, structure and topology, definition and nomenclature 25-2Ч25-3 Charged fullerenes stability, structure and topology, nonclassical fullerenes 25-4 Charged fullerenes stability, structure and topology, Schlegel diagram 25-4 Charged fullerenes stability, structure and topology, sphericity 25-3Ч25-4 Charged fullerenes stability, structure and topology, Stone Ч Wales transformation 25-3 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), 24-12 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), carbon onion growth, nitrogen incorporation 24-15Ч24-17 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), catalytic disproportionation, CO 24-10Ч24-12 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), hollow carbon onion particles production 24-17Ч24-19 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), low-temperature synthesis 24-13Ч24-15 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), plasma enhanced 24-10 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), thermal 24-13 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), vapor phase growth 24-12Ч24-13 Chemisorption 18-3 Chloromethane clusters 7-19 Closed cage carbon structures, fullerene molecules 34-3 34-4 Closed cage carbon structures, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images 34-3 34-4 Closed cage carbon structures, icosahedral structure 34-3 34-4 Closed cage carbon structures, polyhedral OLC particles 34-5 Cluster beam formation, fundamentals aspects 19-2Ч19-3 Cluster beam formation, mass selection of 19-3Ч19-4 Cluster beam formation, sources, gas aggregation 19-3 Cluster beam formation, sources, spray sources 19-4 Cluster beam formation, sources, supersonic jet sources 19-3 Cluster beam formation, sources, surface erosion 19-3Ч19-4 Cluster calorimetry, mass spectra, clusters vs. internal energy 15-7 Cluster calorimetry, mass spectra, schematic representation 15-7 Cluster deposition 19-5Ч19-7 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, decay and source problems 16-8 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, definition 16-1 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, gelation transition, finite time gelation 16-9 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, gelation transition, gelation kinetics regularization 16-10Ч16-12 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, gelation transition, instantaneous gelation 16-10 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, modeling, lattice model 16-3 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, modeling, mean-field theory 16-5 see Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, modeling, Monte Carlo simulation 16-4 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, modeling, stochastic Smoluchowski equation 16-3Ч16-4 see Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, Smoluchowski equation, exact solution 16-6Ч16-7 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, Smoluchowski equation, scaling hypothesis 16-5Ч16-6 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, stationary state 16-8Ч16-9 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, strong fluctuations, multiscaling, decaying CCA 16-12Ч16-14 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, strong fluctuations, multiscaling, mass distribution 16-15Ч16-17 Cluster-cluster aggregation (CCA) kinetics, strong fluctuations, multiscaling, steady state, particle injection 16-14Ч16-15 Cluster-substrate interaction, electronic structure, change transfer 18-13Ч18-14 Cluster-substrate interaction, electronic structure, chemical reactivity 18-14Ч18-15 Cluster-substrate interaction, electronic structure, work function 18-11Ч18-13 Cluster-substrate interaction, kinetic aspects, cluster size effects 18-10Ч18-11 Cluster-substrate interaction, kinetic aspects, nucleation 18-10 Cluster-substrate interaction, kinetic aspects, sintering 18-10 Cluster-substrate interaction, kinetic aspects, surface diffusion 18-9 Cluster-substrate interaction, kinetic aspects, temperature effect 18-11 Cluster-substrate interaction, particle-surface interactions, adsorption sites 18-3Ч18-4 Cluster-substrate interaction, particle-surface interactions, physisorption and chemisorption, adsorption 18-2Ч18-3 Cluster-substrate interaction, particle-surface interactions, surface coverage effect 18-4Ч18-7 Cluster-substrate interaction, thermodynamic aspects, growth modes 18-8Ч18-9 Cluster-substrate interaction, thermodynamic aspects, reactivity 18-7 Cluster-substrate interaction, thermodynamic aspects, wetting 18-7Ч18-8 Cluster-surface collisions see also "Cluster-substrate interaction" Cluster-surface collisions, cluster beams formation, fundamental aspects 19-2Ч19-3 Cluster-surface collisions, cluster beams formation, mass selection of 19-3Ч19-4 Cluster-surface collisions, cluster beams formation, sources 19-3Ч19-4 Cluster-surface collisions, history of 19-2 Cluster-surface collisions, interaction, deposition 19-5Ч19-7 Cluster-surface collisions, interaction, implantation 19-8Ч19-10 Cluster-surface collisions, interaction, pinning 19-7Ч19-8 Cluster-surface collisions, interaction, surface erosion 19-10Ч19-13 CNT see "Carbon nanotube" Coarsening process 1-5 Computational methodology, Car Ч Parrinello scheme 32-3Ч32-4 Computational methodology, density functional theory 32-3 Computational methodology, ELF and localized orbitals method 32-4 Computational methodology, Nose Ч Hoover thermostats 32-5 Computational methodology, population analysis 32-4Ч32-5 Computational methodology, technical details 32-5Ч32-6 Coulomb explosion, fragmentation, fullerenes 26-7 Coulomb explosion, intense laser field, atomic clusters, pulse-profile and size-distribution effects 13-9Ч13-11 Coulomb explosion, intense laser field, atomic clusters, single-cluster explosion 13-8Ч13-9 Coulomb fragmentation, fissility parameter 15-12 Coulomb fragmentation, large fissilities and explosion regime 15-14 Coulomb fragmentation, low fissilities and fission channels 15-12Ч15-14 Cyclodextrins 41-2Ч41-3 Decahedral sphere packing, clusters 37-14 Density functional theory (DFT), alkali and noble metal clusters 6-6Ч6-7 Density functional theory (DFT), polyhydroxylated fullerenes 45-3 45-14Ч45-15 Density functional theory (DFT), silicon-doped fullerenes 32-3 Density functional theory (DFT), solid state structure of 30-1Ч30-2 Density-functional-based tight-binding (DFTB) method, 30-3 Density-functional-based tight-binding (DFTB) method, 30-4Ч30-6 Density-functional-based tight-binding (DFTB) method, 30-7Ч30-9 Derjaguin Ч Landau Ч Verwey Ч Overbeek (DLVO) theory 44-9 Deuterium, superfluidity 2-17 DFT see "Density functional theory" DFTB method see "Density-functional-based tight-binding (DFTB) method" Diamondoids 7-26 Dimers and clusters of fullerenes 27-20Ч27-25 Dimers and clusters of fullerenes, cage-cage distances 27-21 Dimers and clusters of fullerenes, DFT and model results for 27-24 Dimers and clusters of fullerenes, ionization energies, comparison of 27-25 Dimers and clusters of fullerenes, time-of-flight mass spectrum for 27-22 Dimers and clusters of fullerenes, van der Waals clusters of 27-22 Doped silicon cages, infrared spectroscopy 5-11Ч5-13 Doped silicon cages, mass spectrometry, anionic clusters 5-4Ч5-5 Doped silicon cages, mass spectrometry, cationic clusters 5-4 Doped silicon cages, mass spectrometry, neutral clusters 5-5Ч5-6 Doped silicon cages, photoelectron spectroscopy, Cr-doped silicon cluster 5-11 Doped silicon cages, photoelectron spectroscopy, HOMO-LUMO gaps 5-10 Doped silicon cages, photoelectron spectroscopy, terbium-silicon clusters 5-10 Doped silicon cages, quantum chemical calculations, advantages 5-9Ч5-10 Doped silicon cages, quantum chemical calculations, group-6-doped cluster 5-8Ч5-9 Doped silicon cages, quantum chemical calculations, shrinkage 5-8 Doped silicon cages, quantum chemical calculations, size, exo-to endohedrall transition 5-9 Doped silicon cages, quantum chemical calculations, Zr-doped silicon clusters 5-8 Doped silicon cages, reactivity and chemical-probe studies 5-6Ч5-7 Doped silicon cages, reactivity and chemical-probe studies, argon (Ar) probe 5-8 Doped silicon cages, reactivity and chemical-probe studies, mixed plasma 5-7Ч5-8 Doped silicon cages, reactivity and chemical-probe studies, silane and terbium 5-7 Doubly magic clusters (DMC) 4-9Ч4-10 Dynamical nucleation theory (DNT) 15-18Ч15-19 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, alkali halide clusters 10-7Ч10-8 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, beam broadening 10-4Ч10-6 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, beam deflection 10-3Ч10-4 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, definitions 10-1Ч10-2 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, ferromagnetism 10-9Ч10-11 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, forces and deflections, external field 10-2Ч10-3 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, helium nanodroplets 10-9 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, metal cluster ferroelectricity 10-8Ч10-9 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, metal-fullerene clusters 10-6Ч10-7 Electric and magnetic dipole moments, free clusters, water clusters 10-7 electron field Carbon onions, emission characteristics 34-13 Electron localization function (ELF), bonding features 32-9Ч32-10 Electron localization function (ELF), computational methodology 32-4 Electron-phonon coupling 29-6 Electronegative atoms 36-3Ч36-5 Electronic closed shell-geometric transition, electronic density of states (DOS) 17-13Ч17-14 Electronic closed shell-geometric transition, electronic ground-state properties 17-13 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, atomic structure influence 6-6 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, deformation, ellipsoidal 6-6 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, deformation, energy levels, spheroidal 6-4Ч6-5 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, deformation, Jahn Ч Teller effect 6-5 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, density functional theory (DFT) calculation, Hohenberg Ч Kohn theorem 6-6 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, density functional theory (DFT) calculation, Kohn Ч Sham equation 6-7 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, effective single-particle potential derivation, Hamiltonian 6-3 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, effective single-particle potential derivation, harmonic potential 6-3Ч6-4 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, effective single-particle potential derivation, Wood Ч Saxon potential 6-4 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, noble metal clusters, photoelectron spectra patterns 6-14Ч6-16 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, noble metal clusters, s-band intersection 6-14 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES) measurement, experimental setup 6-8Ч6-9 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, photoelectron spectroscopy (PES) measurement, principle 6-7Ч6-8 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, quantum size effect 6-1 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, size-dependence 6-1 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, sodium clusters, angle-resolved PES 6-16Ч6-17 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, sodium clusters, large 6-13Ч6-14 Electronic structure, alkali and noble metal clusters, sodium clusters, small 6-9Ч6-13 Electrophoretic mobility, fullerol clusters 44-8 44-9 elf see "Electron localization function" Encapsulation, 41-2Ч41-3 Encapsulation, 41-4Ч41-5 Encapsulation, 41-3 Encapsulation, 41-4 Encapsulation, 42-11 Encapsulation, 42-1 Encapsulation, 42-2 Encapsulation, 42-1Ч42-2 Encapsulation, 42-3Ч42-9 Encapsulation, 42-9Ч42-11 Encapsulation, 42-2Ч42-3 Encapsulation, 42-3 Encapsulation, 41-5Ч41-6 Encapsulation, 41-9 41-12 41-13 Encapsulation, 41-9 41-14 Encapsulation, 41-6 Encapsulation, 41-6Ч41-7 Encapsulation, 41-7Ч41-11 Encapsulation, 41-15 Endoatom 26-9Ч26-10 Endohedral doping method, encapsulation, molecules and clusters 48-8 Endohedral doping method, metal embedded cages 48-7Ч48-8 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, see " Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-13Ч33-14 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-16 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-16 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-14 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-15 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-17 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-14 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-15 33-16 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, 33-14 33-15 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, electron acceptors 36-8Ч36-9 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-12 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-10 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-11 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-10 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-11 33-12 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-9 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-12 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-12 33-13 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-11 33-12 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-10 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, hydrogenated 33-10 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, metallofullerenes ( 33-17Ч33-18 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, plasmons 35-9Ч35-10 Endohedrally doped fullerenes, suspensions 40-6Ч40-7 Evaporative ensemble, dissociation energy 15-6 Evaporative ensemble, dissociation rate 15-5 Exchange-correlation potential 32-3 Exohedral doping method, coating 48-11 Exohedral doping method, hydrogenation, binding energy 48-9 Exohedral doping method, hydrogenation, comparison, HOMO orbitals 48-10 Exohedral doping method, hydrogenation, frontier orbitals 48-9 Exohedral doping method, hydrogenation, icosahedral group 48-10 Exohedral doping method, hydrogenation, localization, HOMO orbital 48-8Ч48-9 Exohedral doping method, hydrogenation, structures 48-8Ч48-9 Exohedral doping method, latest developments 48-11Ч48-12 Ferroelectricity 10-8Ч10-9 Ferromagnetic cluster, definition of 10-9Ч10-10
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



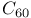 derivatives
derivatives 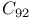
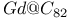
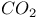 , catalytic reduction
, catalytic reduction 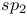 and
and 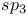 hybridization
hybridization 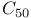 , negatively charged
, negatively charged 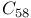 and
and 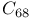 fullerenes
fullerenes 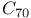 fullerenes, negatively charged
fullerenes, negatively charged  bond, electron derealization and spherical aromaticity
bond, electron derealization and spherical aromaticity  bonds, strain
bonds, strain 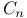
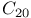
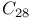
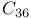
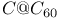 systems
systems 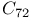 and
and 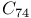
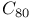 ,
, 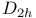 configuration, vibrational analysis
configuration, vibrational analysis 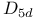 structure
structure 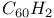 and
and 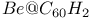 structural properties
structural properties 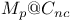 )
)