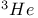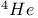|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Davies P. Ч The New Physics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Rosen bimetric theory of gravity 11 18
Rosen, Nathan 11 382 see
Rotation curves of galaxies 161Ч163
Rotations 383 470
RR-Lyrae stars 126
Ruby laser 300
Ruel, R.R. 221
Rutherford, E. 400
Rydberg atoms 295
Ryle, Martin 66
S-matrix 88
S-state 399 402 404Ч405
Sahkarov, A. 444
Salam, Abdus 39 436 474
Scale-invariance of configurations 246
Scale-invariance of effective couplings 255
Scaling 216 218 231Ч232
Scattering 397 410
Scattering and renormalisation group 209 211 217Ч219 222Ч224 229 231Ч233 244
Schroedinger, E. 369Ч370 377 391Ч392
Schwarz, John 489
Schwarzschild radius 25 144Ч145 169Ч170 175
Schwarzschild solution 25
Schwarzschild, Karl 25
Scorpius X-1 (Sco X-1) 178Ч180
Second harmonic generation 299
Selenium 228
Self-focusing of light 299
Self-organisation 5Ч6
Self-phase modulation 307
Semiconductors 210 214 228Ч235
Separatrix 332
Series expansion method 243
Seyfert galaxies 107 110 169Ч182
Seyfert galaxies, types I and II 170Ч174 177
Shadow matter 487 see
Shapiro time delay 12Ч14
Shapiro, Irwin 12
Shnirelman, A.I. 368
Short range forces 459 473
Shot noise 315
Shull, C. 392
Siggia, E. 226
Silicate features in interstellar dust grains 152Ч153
Silicon 228Ч230 232 235
Silicon burning in stars 121Ч122
Silicon dioxide 229Ч230
Silk damping 199
Simon, B. 391
Singularity (spacetime) 28Ч29 65Ч68 189
SLAC 410 414
Slow-rollover phase transition 45 48Ч49
Smarr, Larry 33
Smectic phases in liquid crystals 222Ч223
Smoothness problem 36 48Ч52
SO (10) 439
SOHO-Cluster mission 120 204
Solar neutrinos 118Ч121
Solar oscillations 119Ч121
Solar seismology 118Ч121
Solid-state devices 6
Solids 209Ч211 216 218 220Ч225 228Ч230 234
Solitons 308 489
Solomonov, R. 350
Sound 224 225Ч226
Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) 203Ч204
Spacetime 70 72 74Ч75 78 80 89Ч90 392 459
Spacetime, asympotic structure of 32
Spacetime, continuum 72 75 93
Spacetime, curved 8Ч9 11 63 66
Spacetime, relativistic 385 388
Spacetime, singularity of 28Ч29 65Ч68 189
SPEAR 415
Special relativity 7 9 81 459 464
Specific heat 211Ч212 214 217Ч218 220Ч222 226
Specker, E. 384
Spectroscopic binary of stars 127 139 145
Spectroscopy (hadrons) 400 420
Spectrum 397
speed of light 426 447 459 477
Spin 400 402 404 406 410 416 419
Spin (intrinsic) 210Ч220 223Ч225 232Ч233 433 447Ч448 465Ч467 484Ч487
Spin glass 263
Spin, singlet 407
Spin, triplet 407
Spin-up of neutron stars 138Ч139 141
Spiral structure of our Galaxy 146
Spontaneous decay of superfluidity 224 226
Spontaneous emission 289
Spontaneous magnetisation 212 224
Spontaneous symmetry breaking 39 41Ч43 435
Squarks 483
Squeezed states of light 313
SS433 178Ч180
SSC (superconducting supercollider) 482Ч483
Stability 389
Stability of supercurrent flow 278 283 286
Stability, analysis 335
Stability, asymptotic 317 322 331Ч332 334Ч335
Standard model 423
Stanford 410 414 421
Star clusters 123
Star formation 103 118 145Ч161
Star formation, contents of regions of 155Ч158
Star formation, problems of 158Ч160
Star formation, rate of 154Ч155 163Ч164
Starburst galaxies 172
Stark shift 294 302
Starobinsky, A.A. 48
Starquakes 136Ч137
Stars 110Ч113 118Ч129 see "White "X-ray
Stars, collapse of 67
Stars, dead 113 129Ч145
Stars, mass loss from 111Ч113 125Ч128 146
Stars, mass-luminosity relation 111
Stars, masses of 127 206
Stars, molecular discs around 158 160
Stars, population III 125 191
Stars, red giant 128
Stars, RR-Lyrae 126
Stars, spectroscopic binaries 127 139 145
Stars, symbiotic 128Ч129
Stars, unstable 126
Stars, visual binaries 127
States in quantum mechanics 78Ч80 92 374 378 380 429
States in quantum mechanics, complete 382 384Ч386
States in quantum mechanics, mixed 374 390
States in quantum mechanics, neutral 390
States in quantum mechanics, polarisation 386
States in quantum mechanics, pure 374 390
States in quantum mechanics, quantum 374 382Ч383 389 391Ч392
States in quantum mechanics, relative 393
Stationary nonequilibrium state 320
Steady-state cosmology 7 31 66
Stein, H. 393
Steinhardt, Paul J. 45 48
Stellar coronae 125
Stellar evolution 110Ч113 118Ч129
Stellar evolution in globular clusters 123Ч125
Stellar evolution in radio galaxies 190Ч191
Stellar populations in galaxies 165
Stellar structure 118Ч129
Stellar winds 125Ч127 140Ч141
Stimulated emission 289
Stimulated transitions 295
Stormer, H. 233
Strange Attractor 311
Strange particles 401 450
Strange quark 402 414Ч415 420 422 472
Strangeness 401Ч403 484
| Streaming velocities of galaxies 184 200Ч201
Strings, cosmic 164 491
Strong coupling 431
Strong force 1Ч3 71 85 401 458 472 475 482 487 489 491
SU (2) 87 433 482
SU (3) 430 482
SU (5) 439
Subharmonics 315
Sublattice 211 217 221
Sublattice magnetisation 217 219
subspace 375 378 380 384Ч385 389Ч390
Substrate 217Ч219 221Ч222 225Ч226
Sulphur 228
Sun 118Ч121
Sun, oblateness of 14Ч15
Sunyaev Ч Zeldovich effect 168 191
Superclusters (of galaxies) 107 163Ч164 183Ч184 199Ч201
Superconducting levitation 280 286
Superconductivity 3Ч5 209 216 226Ч228 230 234 274 279Ч284 286Ч288 393 479
Superconductivity at high temperatures 5
Superconductivity at room temperature 286 288
Supercurrents 225Ч227
Superfluid density 225Ч227
Superfluidity 4Ч5 209 216Ч217 225Ч228 274
Superfluidity in neutron stars 135 137
Superfluidity of 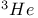 284Ч286 284Ч286
Superfluidity of 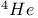 275Ч279 275Ч279
Superfluidity, anisotropic 284Ч285
Supergravity 39 87Ч88 482 485Ч490
Superluminal communication 388
Superluminal velocities 175Ч176 179Ч181
Superluminal velocities, relativistic ballistic model for 179
Superluminal velocities, screen model for 179
Supermassive black holes 110 169Ч170 176 194
Supernova 1987A 130
Supernovae 3 98 111Ч114 116Ч117 128Ч133 147
Supernovae and neutron star formation 24
Supernovae as cosmological distance indicators 191
Supernovae as source of gravitational waves 20
Supernovae as X-ray sources 132
Supernovae, remnants 129Ч133 148 see dead"
Supernovae, Type I and Type II 130
Superposition in quantum mechanics 379 387 389Ч390 392Ч393
Superstring theory 3 39 41 49 88Ч89 92Ч93 482 489Ч491
Supersymmetry 87 482 484Ч490
Surface phenomena 209 214 218Ч221 225Ч226 229Ч232 234
Susceptibility of dielectrics 298 304
switch 229
Symbiotic stars 128Ч129
Symmetry 389 428
Symmetry of wave function 405Ч406
Symmetry, breaking 318Ч319 323 328Ч330 336
Symmetry, role in critical phenomena 262
Synchrotron radiation 96Ч99 117Ч118 132 175 177Ч182 222 224 234
Synchrotron radiation from cosmic ray electrons 101
Tantalum 228
TASSO 417
Tau lepton 399
Tau particle 472
Taylor, G.I. 292
Taylor, Joseph 17
Temperature scale, Kelvin 268
Temperature scale, Kelvin, logarithmic 1 268
Temporal evolution in quantum mechanics 379Ч380 390Ч392
Tensor product 377 379
Theoretical astronomy 103Ч104
Theories of Everything 3 489Ч491
Thermal convection 316Ч317 320
Thermal disorder 268 285
Thermal excitations 224 228
Thermal history of universe 195Ч201
Thermal motion 230
Thermodynamic potential 331Ч332
Thermodynamics 5 76 78 317 320 330Ч331 337Ч338 358 361
Thermonuclear flashes in accreting X-ray sources 143
Thin films 209 214Ч215 217Ч218 221Ч222 225Ч227 232 234Ч235
Things-in-themselves 394
Third harmonic frequency 298
Third sound 225Ч226
Thorne, Kip 8
Thouless, D.J. 224 231
Three-dimensional systems 209Ч210 212 214Ч218 220Ч222 224 228 234Ч235
Tidal interactions between galaxies 166
Time, beginning and end of 65Ч66 68
Top quark 399 420 484
Topological conservation law 278Ч279 283 287
topology 63 75 82 84 90 93 209 211Ч212
Topology of hadron decay 408
Topology of space 490
Transition metal 210
Transition probability 337
Transition temperature 221Ч222 214Ч215 217 222 224 226Ч228 280 284 see
Trapping of electrons 209 214 229Ч230 234Ч235
Triangular lattice 220 229
Tritium 421
Truth quark 399
Tryon, Edward P. 53
Tsui, D.C. 233
tunnelling 288
Turbulence 264 319 351
Turbulence, chemical 323
Turner, Michael S. 48
Twistor theory 93
Two-dimensional systems 209Ч220 222Ч225 227Ч232 234Ч235
Two-photon decay 300
Two-point correlation function of galaxies 183Ч184
Twose, W.D. 230
U(1) 434 482
UHURU X-ray satellite observatory 100 139 204
Ulman, S. 364
Ultra-high energy gamma rays 100 144 205
Ultrarelativistic electrons, in active galactic nuclei 173Ч176
Ultrashort optical pulses 306
Ultraviolet astronomy 101
Ultraviolet astronomy, future of 204
Ultraviolet radiation of hot gas 148
Ultraviolet radiation of young stars 148
Uncertainty principle 67Ч69
Uncertainty principle, quantum (in theory of chaos) 352 370
Uncertainty relations 394 427 450
Uniaxial magnet 248
Unification (of forces and particles) 486 488 see "Grand
Unified electroweak theory see "Electroweak theory"
Unipolar induction 137Ч138
Universality 209 216 225
Universality class 216Ч218 220 222 225 248 262
Universality, meaning 236 241
Universality, origins in configuration flow 246
Universality, origins in effective coupling flow 253
Universe 393
Universe, age of 124 186 192Ч193
Universe, collapse of 61
Universe, creation of 61
Universe, critical density of 37Ч38 49Ч51 54Ч55 187
Universe, density of mass/energy 35Ч38 43Ч44 48Ч49 51 54Ч55 57Ч59
Universe, density of matter 65
Universe, density parameter of 187
Universe, distribution of matter and energy 35Ч36 48Ч52 104Ч107 198Ч201
Universe, dust-filled models of 186Ч189
Universe, expansion of 4 30 64
Universe, flatness of 37Ч38 44 48 59
Universe, Friedmann models 64Ч66
Universe, geometry of 187
Universe, homogeneity of 183Ч184
Universe, horizon problem 35 37 44Ч45 48 50
Universe, inflationary models see "Inflationary models of the early universe"
Universe, initial singularity of 189
Universe, isotropy of 183Ч184 201
Universe, matter-dominated 187Ч188
Universe, origin of 61Ч69 see
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте