|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Prigogine I. (ed.), Rice S.A. (ed.) Ч Advances in Chemical Physics. Volume 118 |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Richards, J.H. 2Ч3(6Ч7) 4(6) 26(6Ч7) 33(6Ч7) 41
Richardson, J.T. 147(104) 188
Richter, H.J. 103(14) 185
Rick, S.W. 267(109) 270
Riedle, E. 91(170Ч171) 97
Rishcon, S.A. 104(30) 186
Ritvold, P.A. 142(97) 188
Robb, M.A. 26(66) 44
Roberta, R. 155(129) 159(129) 168(129) 189
Robinson, G.W. 49(60Ч61 63 68) 51(60Ч61 63 68) 95
Roche, K.P. 104(30) 186
Roitberg, A.E. 3(16) 6(42) 42Ч43
Rose, G. 155(135Ч136) 160(136) 170(136) 189
Rossky, P.J. 195(33 35) 232(33 35) 233(97) 268 270
Rotational-orbit-spin-orbit (ROSO) perturbation, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism 49Ч50
Rotational-orbit-spin-orbit (ROSO) perturbation, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, magnet field interaction 69Ч78
Rotational-orbit-spin-orbit (ROSO) perturbation, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, second-order matrix elements 61Ч62
Rothschild W.G. 206(79) 218(79) 269
Rousseaux, E. 103(17) 185
Rubin J.J. 49(71) 51(71) 95
Ruehrig, M. 133(82) 187
Ruge, J. 39(76) 44
Ruiz, D. 150(120) 154(120) 173(120) 189
Rutel, I. 176(173) 190
Ruthenium complexes, Ruthenium-modified copper protein, electron transfer 21Ч24
Ruthenium complexes, Ruthenium-modified copper protein, His/Met residue tunneling transition 24Ч27
Ruthenium complexes, transition metals, tunneling mechanisms 24Ч27
Rutter, P. 103(23) 179(23) 185
s-Triazine, anisotropic spin-spin constants 92Ч93
s-Triazine, magnetic field influence on excited-state dynamics 92
Saigusa, H. 91(167Ч168) 92(168) 97
Sailing, C. 103(16) 185
Sand, M. 163(147) 190
Sander, S.P. 90(158) 97
Sangregorio, C. 150(116 118 121) 155(118 129) 159(129) 165(116 118) 168(118 129 161) 176(121) 189Ч190
Sarachik, M.P. 150(1 14 120) 154(114 120) 173(120) 188Ч189
Satoh, M. 239(101) 270
Scanning microscopy, micro-SQUID magnetometry 114
Schafer, R. 101(1) 185
Schawlov, A.L. 55(111) 96
Schelp, L.F. 104(32) 186
Schlag, E.W. 47(25 31) 54Ч55(108) 57Ч58(108) 91(170) 94 96Ч97
Schlegel, H.B. 26(66) 44
Schmidt, A. 207(88) 211(88) 218(88) 220(88) 225(88) 270
Schofield, S.A. 197(44) 251(44) 253(44) 255(44) 269
Schroeder, J. 201(58) 269
Schroedinger equation, Landau Ч Zener tunneling, iron 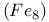 molecular clusters 155Ч160 molecular clusters 155Ч160
Schroedinger equation, transfer matrix element 32Ч33
Schroedinger equation, vibrational energy relaxation, mean field approximation 229Ч232
Schroedinger equation, vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 228Ч229
Schroedinger equation, vibrational energy relaxation, theoretical background 193Ч196
Schultz, S. 103(16 19) 133(78) 142(19) 185 187
Schulz, C.E. 150(112) 152(112) 163(112).188
Schwarzer, D. 201(58) 269
Schweinboeck, T. 104(28) 186
Schweizer, J. 151Ч152(109) 188
Schwinger, J. 213(92) 270
Second-order perturbations, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, matrix elements 61Ч62
Second-order perturbations, vibrational energy relaxation, influence action 223Ч226
Second-order perturbations, vibrational energy relaxation, perturbative influence functional, nonlinear couplings 214Ч217
Selzle, H.L. 47(25 31) 94
Semiclassical theory, magnetic quantum tunneling, splitting oscillations 163
Senz, V. 103(20) 185
Sessoli, R. 113(47) 150(111Ч113 115Ч116 121) 151(109Ч110 126) 152(109Ч110 112 127) 154(113 115) 158(140) 160(144) 163(110 112 155) 165(116) 168(144) 169(47) 170(144 164) 171(140) 172(166) 173(126 140) 175(47 140) 176(121 170) 186 188Ч188
Shaw, T.M. 104(30) 186
Shephard, M. 11(55Ч56) 44
Shiga, M. 195(28) 196(41Ч43) 207(28) 210(28) 233(43) 238(41Ч43 99) 241(41Ч42 99) 246(28) 268 270
Shklovskii, B. 3(12) 42
Sholl, D.S. 195(39) 268
Shtrikman, S. 129(66) 131(66) 187
Siddarth, P. 6(41) 8(41) 43
Sides, S.W. 142(97) 188
Siebrand, W. 49(64Ч66) 51(64Ч66) 95
Silbey, R.J. 206(84) 270
Singer, K.E. 103(23) 179(23) 185
Single tunneling orbital approximation (STOA), tunneling flow vortices 28Ч32
Single-domain particles, magnetic quantum tunneling 176Ч183
Single-domain particles, magnetic quantum tunneling, nanoparticles 177Ч178
Single-domain particles, magnetic quantum tunneling, quantization techniques 181Ч182
Single-domain particles, magnetic quantum tunneling, very-low-temperature measurements 179Ч181
Single-domain particles, magnetization reversal and 101Ч102
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters 102Ч114
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry 104Ч114
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, array schematics 113
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, blind mode three-dimensional switching field measurements 111Ч113
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, cold mode magnetization switching measurements 109Ч111
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, critical current magnetization measurements 105Ч109
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, fabrication techniques 105
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, future applications 114
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, hysteresis loop measurement feedback 109
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, scanning microscopy 114
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID magnetometry, SQUID configuration selection 104-105
Single-particle measurement techniques, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, theoretical background 103Ч104
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms 56Ч62
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, Coriolis interaction operator 56Ч62
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, coupling mechanisms, first-order perturbation matrix elements 58Ч61
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, electron-spin wave functions 58
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, magnetic and nonmagnetic interaction schemes 68Ч78
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, second-order perturbation matrix elements 61-62
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, spin-orbit perturbation operator 62Ч63
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, triplet-state wave functions, magnetic field presence 78Ч82
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, vibronic interaction operator 56
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, Zeeman perturbation matrix elements 62Ч68
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, Zeeman perturbation matrix elements, high-field limit 65Ч67
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, Zeeman perturbation matrix elements, interaction operator 62Ч63
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, Zeeman perturbation matrix elements, low-field limit 63Ч65
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, coupling mechanisms, Zeeman perturbation matrix elements, nuclear angular momentum 67Ч68
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, excited-state magnetic field dynamics, acetylene 88Ч90
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, excited-state magnetic field dynamics, anisotropic spin-spin constants in diazine and triazine 92Ч93
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, excited-state magnetic field dynamics, diazines 90Ч92
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, excited-state magnetic field dynamics, oxalylfluoride 82Ч88
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, theoretical background 47Ч53
Singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, triplet-state structure 53Ч56
Skinner, J.L. 194(21Ч25) 206(21Ч25 83) 225Ч226(83) 246(22 25 83) 268 270
Skourtis, S.S. 3(15) 4(23) 5(23) 7(23) 9(23) 11(23) 36(23) 42
Skubnevskaya, G.I. 46(5 7) 47(5) 93
Smalley, R.E. 82(120) 96
Smirnov-Rueda, R. 142(98) 188
Solarz, R. 46(2) 93
Solute/solvent degrees of freedom, 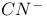 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation 244Ч247 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation 244Ч247
Solute/solvent degrees of freedom, vibrational energy relaxation, Hamiltonians 197Ч200
Solute/solvent degrees of freedom, vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 232Ч237
Solute/solvent degrees of freedom, vibrational energy relaxation, theoretical background 195Ч196
Solvated electrons, vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 232Ч237
Sorace, L. 150(121) 176(121) 189
Sorokin, N.I. 46(50) 47(5 33) 93Ч94
Space, B. 195(36) 232(36) 268
Spangler, L.H. 46(14) 47(14 43Ч45) 90(14 43Ч45) 91(43Ч45 169) 93Ч94 97
Spatial distribution, electron vs. hole transfer 34Ч36
Spatial distribution, many-electron tunneling 13Ч15
Spectral density, 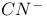 ions, aqueous solution 242Ч243 ions, aqueous solution 242Ч243
Spectral density, vibrational energy relaxation, perturbative influence functional, nonlinear couplings 215Ч217
Spin-orbit perburbation (SO), magnetic quantum tunneling, iron 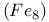 molecular clusters 152Ч154 molecular clusters 152Ч154
Spin-orbit perburbation (SO), singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion 49Ч50
Spin-orbit perburbation (SO), singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, coupling operators 57Ч58
Spin-orbit perburbation (SO), singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, magnet field interaction 71Ч78
Spin-orbit perburbation (SO), singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, triplet-state structure 54Ч56
Spin-orbit perburbation (SO), singlet-triplet (S-T) coupling, first-order perturbation matrix elements 60Ч61
Spin-spin interaction, triplet states 48Ч49
Srinivasan, R. 49(70) 51(70) 95
Stamp, P.C.E. 155(135) 160(143) 165(143 159Ч160) 166(143) 168(143) 176(172) 189Ч190
Stannard, P.R. 46Ч47(23) 62(23) 64(23) 93
Stanton, J.F. 90(154) 97
Stanton, R.E. 15(60) 44
Stawiaasz, K. 104(41) 161(41) 186
Steepest descent method, time-dependent transition probability, vibrational energy relaxation 218Ч223
Stefanov, B.B. 26(66) 44
Stein, K. 104(41) 161(41) 186
Stephenson, J.C. 192(2) 267
Steubing, W. 46(1) 93
| Stevens, C.G. 54Ч55(97) 95
Stewart, J.R. 26(66) 44
Stole, R.H. 194(15) 202(15) 268
Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model, magnetic quantum tunneling, quantization techniques, single-domain nanoparticles 181Ч183
Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model, zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters 115Ч129
Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model, zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, cubic anisotropy 126Ч129
Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model, zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, experimental data 120Ч126
Stoner, C. 115(52) 187
Stratt, R.M. 198(45Ч47) 202(61) 203(66Ч68) 269
Stuart, S.J. 267(109) 270
Stuchebrukhov, A.A. 5(25Ч34) 6(36Ч38) 7(37 43) 8(36 38 45Ч50) 9(25Ч29 34 38 49Ч51) 10(25Ч34 36Ч37) 11(26 34 49Ч50) 13(28) 17(64) 24(26 50) 26(31) 31(31 45) 34(45Ч47) 36(50) 38(33 50) 39(33 45Ч46) 40(45Ч46) 42Ч44
Stueckelberg, E.C.G. 154(132) 189
Suhl, H. 133(81) 187
Sulpice, A. 113(48) 133Ч134(79) 147(79) 186Ч187
Sumitani, M. 46(12) 93
Superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) see "Micro-SQUID mangetometry"
Superexchange mechanisms, long-distance electron tunneling 2Ч4
Suran, G. 103Ч104(22) 120(22) 134(22) 179(22) 185
Surface hopping approximation, vibrational energy relaxation, theoretical background 195Ч196
Survival probability estimation, 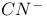 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation 243Ч247 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation 243Ч247
Sutin, N. 2Ч4(8) 26(8) 32(8) 40(8) 41
Suzuki, T. 89(142) 97
Switching measurements, magnetic quantum tunneling, single-domain nanoparticles and wires, very low temperatures 179Ч181
Switching measurements, micro-SQUID magnetometry, blind mode method, three-dimensional switching 111Ч113
Switching measurements, micro-SQUID magnetometry, cold mode techniques 109Ч111
Switching measurements, nonuniform zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nucleation and annihilation of domain walls 134Ч135
Switching measurements, thermal-dependent magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model 140Ч141
Switching measurements, zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model 121Ч126
Sykes, G. 2Ч3(4) 7(4) 33(4) 41
Szabo, A. 13(58) 15(58) 19(58) 44
Szarka, A.Z. 203(62) 269
Takahashi, K. 49(80) 51(80) 95
Takemura, T. 46(15) 47(15Ч16 47Ч50) 48(16 47 49Ч50) 90(15Ч16 47Ч50) 92(16 50 176Ч179) 93Ч94 98
Tamai, N. 53(95) 95
Tartarskii, V. 255(107) 270
Taskin, T. 103(23) 179(23) 185
Tayler, P.R. 90(148) 97
Taylor expansion, time-dependent transition probability, vibrational energy relaxation 218Ч223
Tejada, J. 150(114) 154(114) 176(173) 188 190
Telegraph noise measurements, magnetic quantum tunneling, single-domain nanoparticles and wires, very low temperatures 179Ч181
Telegraph noise measurements, thermal-dependent magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model 141Ч142
Temperature effects, Landau Ч Zener tunneling, environmental decoherence 171Ч175
Temperature effects, magnetic quantum tunneling, single-domain wires, very low temperatures 179-181
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters 135Ч149
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model 136Ч138
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model, cobalt cluster applications 144Ч146
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model, deviations from 147Ч149
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model, nanoparticle applications 142Ч144
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model, nickel wire applications 146Ч147
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model, switching field measurements 140Ч141
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model, telegraph noise measurements 141-142
Temperature effects, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model, waiting time measurements 138Ч140
Temperature effects, vibrational energy relaxation, one-harmonic- oscillator bath model 257Ч260
Terashima, T. 196(43) 233(43) 238(43) 268
Terazima, M. 91(172) 97
Thiavilie's calculation, zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model 118Ч120
Thiaville, A. 104(38) 105(46) 109(38) 111(38) 114(46) 115(54Ч55) 117(54Ч55) 119(54) 121(38) 122(54) 126(54Ч55) 138(55) 142(38) 186Ч187
Thirion, C. 104(39) 109(39) 121(39) 142(39) 186
Thomas, L. 103Ч104(22) 120(22 59) 133(79) 134(22 59 79) 142(59) 147(59 79 102) 148(59) 150(115) 154(115) 179(22) 185 187Ч189
Thorwart, M. 155(137) 189
Three-dimensional switching measurements, micro-SQUID magnetometry, blind mode techniques 111Ч113
Three-dimensional switching measurements, zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model 120Ч126
Tildesley, D.J. 193(10 12) 194(10) 268
Time-dependent transition probability, 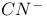 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation 243Ч247 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation 243Ч247
Time-dependent transition probability, vibrational energy relaxation, mean field approximation 229Ч232
Time-dependent transition probability, vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 232Ч237
Time-dependent transition probability, vibrational energy relaxation, perturbative influence functional, nonlinear couplings 217Ч223
Time-resolved pump-probe spectroscopy, vibrational energy relaxation 192Ч193
Tinti, D.S. 82(121) 96
Tokmakoff, A. 206(81Ч82) 269Ч270
Tonomura, A. 103(13) 185
Total atomic currents, one-electron longdistance tunneling, interatomic currents and paths 10Ч12
Townes, C.H. 55(111) 96
Trajectory calculations, vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 232Ч237
Tramer, A. 46(3 20Ч21) 47(3 20Ч21 24 34 35) 49(77) 51Ч52(77) 91(165) 93Ч95 97
Trans configuration, oxalylfluoride, magnetic field influence on excited-state dynamics 82
Transition metal complexes, tunneling mechanisms 24Ч27
Transition state, tunneling calculations 33Ч34
Transverse field dependence, Landau Ч Zener tunneling, environmental decoherence 175
Transverse field dependence, magnetic quantum tunneling, splitting oscillations 161Ч165
Trapezoidal numerical integration, vibrational energy relaxation, time-dependent transition probability 222Ч223
Traverse, A. 121(61) 123(61) 187
Treilleux, M. 121(60) 187
Treves, D. 129(66) 131(66) 187
Trie, C. 47(30) 49(77 87) 51Ч52(77 87) 91(165) 94Ч95 97
Triechel, M. 203(62) 269
Triplet-state structure, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism 53Ч56
Triplet-state structure, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, wave functions in magnetic field 78Ч82
Tronc, E. 103(8) 138(8) 141(8) 185
Trucks, G.W. 26(66) 44
Tsuchiya, S. 88(136) 89(146) 96Ч97
Tuaillon, J. 104(34) 120(60) 186Ч187
Tucker, S.C. 203(63) 269
Tuckerman, M. 194(16) 202(16) 268
Tully, J.C. 195(32 37Ч39) 196(32) 201(52) 268Ч269
Tunnel splitting oscillations, magnetic quantum tunneling, iron 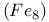 molecular clusters 160Ч165 molecular clusters 160Ч165
Tunnel splitting oscillations, magnetic quantum tunneling, numerical diagonalization 163Ч165
Tunnel splitting oscillations, magnetic quantum tunneling, semiclassical descriptions 163
Tunneling currents, calculations, Gaussian-type functions (GFT) vs. real-space (grid) calculations 37Ч38
Tunneling currents, calculations, new analytical techniques 37
Tunneling currents, calculations, protein dynamic effects 39Ч40
Tunneling currents, calculations, Ruthenium-modified copper protein electron transfer 21Ч24
Tunneling currents, long-distance electron tunneling, theoretical background 5Ч6
Tunneling matrix element see also "Matrix elements"
Tunneling matrix element, many-electron tunneling, Hartree Ч Fock approximation 15Ч18
Tunneling matrix element, many-electron tunneling, interatomic currents and paths 21
Tunneling matrix element, many-electron tunneling, spatial distribution of current density 13Ч15
Tunneling matrix element, one-electron long-distance tunneling, interatomic currents and paths 10Ч12
Tunneling matrix element, one-electron long-distance tunneling, very large systems 6Ч8
Tupitsyn, I. 160(142) 189
Turk, B. 147(104) 188
Twigg, M.V. 147(104) 188
Two-level fluctuations (TLF), magnetic quantum tunneling, single-domain nanoparticles and wires, very low temperatures 179Ч181
Tyrrell, J. 82(125) 96
Tyulin, V.I. 82(119) 96
Uher, C. 126(62) 187
Ungar, L.W. 39(79) 44
Uniform rotation (Stoner Ч Wohlfarth model), zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters 115Ч129
Uniform rotation (Stoner Ч Wohlfarth model), zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, cubic anisotropy 126Ч129
Uniform rotation (Stoner Ч Wohlfarth model), zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, experimental data 120Ч126
Uniform rotation (Stoner Ч Wohlfarth model), zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, generalization 116Ч119
Vaille, J.L. 121(60) 187
Valentine, R.W. 31(73) 44
Van Craen, J.C. 88(135) 96
van den Berg, H.A.M. 133 134(80) 187
van der Meer, B.J. 91(162Ч164) 97
Van Uitert, L.G. 49(71) 51(71) 95
Van Vleck theory, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism 49Ч50
Van Vleck, J.L. 49(90Ч92) 54Ч55(90Ч92) 58(90Ч92) 95
Vaures, A. 104(32) 186
Vavrn, W. 126(62) 187
Veillet, P. 103(17) 185
Velev, P. 206(87) 270
Velocity operator, many-electron tunneling, interatomic currents and paths 20Ч21
Vernon, F.L. 165(158) 190 195(26) 207Ч208(26) 211(26) 217(26) 268
Vibrational energy relaxation, 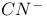 in aqueous solution 237Ч247 in aqueous solution 237Ч247
Vibrational energy relaxation, 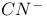 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism 241Ч247 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism 241Ч247
Vibrational energy relaxation, 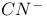 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, bath mode analysis 247 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, bath mode analysis 247
Vibrational energy relaxation, 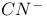 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, spectral densities 242Ч243 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, spectral densities 242Ч243
Vibrational energy relaxation, 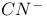 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, state densities 241Ч242 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, state densities 241Ч242
Vibrational energy relaxation, 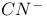 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, survival probabilities 243Ч247 in aqueous solution, relaxation mechanism, survival probabilities 243Ч247
Vibrational energy relaxation, 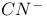 in aqueous solution, relaxation time 238Ч241 in aqueous solution, relaxation time 238Ч241
Vibrational energy relaxation, classical Langevin equation 201Ч203
Vibrational energy relaxation, classical molecular dynamics 200Ч201
Vibrational energy relaxation, Fermi's golden rule, classical force autocorrelation function 203Ч206
Vibrational energy relaxation, Hamiltonian parameters 197Ч200
Vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 228Ч237
Vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, applications 232Ч237
Vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, mean field approximation 229Ч232
Vibrational energy relaxation, path integral approach 206Ч227
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



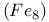 molecular clusters
molecular clusters 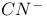 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation
ions in aqueous solution, relaxation