|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Prigogine I. (ed.), Rice S.A. (ed.) Ч Advances in Chemical Physics. Volume 118 |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Interatomic tunneling currents and paths, many-electron tunneling 18Ч21
Interatomic tunneling currents and paths, many-electron tunneling, Mulliken population operators 18Ч20
Interatomic tunneling currents and paths, many-electron tunneling, population dynamics 20Ч21
Interatomic tunneling currents and paths, one-electron long-distance tunneling 9Ч12
Intermolecular dipole interaction, environmental decoherence effects, molecular clusters 168Ч170
Intramolecular interaction 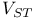 , singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism 49Ч50 , singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism 49Ч50
Iron molecular clusters 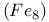 , environmental decoherence effects 165Ч176 , environmental decoherence effects 165Ч176
Iron molecular clusters 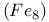 , environmental decoherence effects, hole digging analysis of dipolar distribution and hyperfine coupling 166Ч168 , environmental decoherence effects, hole digging analysis of dipolar distribution and hyperfine coupling 166Ч168
Iron molecular clusters 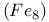 , environmental decoherence effects, hyperfine interaction 170Ч171 , environmental decoherence effects, hyperfine interaction 170Ч171
Iron molecular clusters  , environmental decoherence effects, intermolecular dipole interaction 168-170 , environmental decoherence effects, intermolecular dipole interaction 168-170
Iron molecular clusters  , environmental decoherence effects, Landau Ч Zener tunneling probability 171Ч175 , environmental decoherence effects, Landau Ч Zener tunneling probability 171Ч175
Iron molecular clusters  , environmental decoherence effects, Prokof'ev Ч Stamp theory 165Ч166 , environmental decoherence effects, Prokof'ev Ч Stamp theory 165Ч166
Iron molecular clusters  , magnetic quantum tunneling, anisotropy 150Ч154 , magnetic quantum tunneling, anisotropy 150Ч154
Iron molecular clusters  , magnetic quantum tunneling, Landau Ч Zener tunneling 154Ч160 , magnetic quantum tunneling, Landau Ч Zener tunneling 154Ч160
Iron molecular clusters  , magnetic quantum tunneling, quantization techniques, single-domain nanoparticles 181Ч183 , magnetic quantum tunneling, quantization techniques, single-domain nanoparticles 181Ч183
Iron molecular clusters  , magnetic quantum tunneling, splitting oscillations 160Ч165 , magnetic quantum tunneling, splitting oscillations 160Ч165
Ishchenko, V.N. 46(13) 47Ч49(37Ч41) 62(39) 77(39Ч41) 82(41) 83Ч84(39Ч41 128) 85(37Ч38) 86Ч87(37Ч41) 88(39 41) 91Ч92(41) 93Ч94 96
Ishii, Y. 131(71) 187
Ishimoto, H. 150(124) 176(124) 189
Ito, M. 88(139) 89(141) 97
J-coupling scheme, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism, triplet-state structure 55Ч56
J-dependence, oxalylfluoride, magnetic field influence on excited-state dynamics 84
Jacobs, I.S. 147(103) 188
Jahnes, C. 104(30) 186
Jamet, M. 104(39) 109(39) 121(39 61) 123(61) 142(39) 186Ч187
Jamet, R. 103(17) 185
Jang, S. 195Ч196(31) 227(31) 238(31) 268
Jaso, M. 104(41) 161(41) 186
Jensen, R. 121(60) 187
Jibril, I. 151Ч152(125) 189
Johns, J.W.C. 54Ч55(105) 96
Johnson, B.G. 26(66) 44
Johnston, R. 49(73) 51(73) 95
Jonkman, H.Th. 91(162Ч164 175) 97Ч98
Jordan, K.D. 11(55) 44
Jorgensen, W.L. 239(102) 270
Jortner, J. 2Ч3(10) 41 49(55Ч57 59 75) 51(55Ч57 59 75) 52(75) 82(118) 91(166 172) 94Ч97 206(78) 218(78) 269
Josephson effect, micro-SQUID magnetometry configuration 104Ч105
Jost, R. 46(3 20Ч21) 47(3 20Ч21 24 32 34Ч36) 88(137) 93Ч94 97
Judd, B.R. 55(115) 96
Kaiser, W. 192(1 3 6) 267
Kalmykov, Yu.P. 136(89Ч90) 137(89Ч91) 188
Karplus, M. 6(39) 43
Karrlein, R. 206(85) 270
Kato, S. 205(74) 269
Katsnelson, M.I. 165(157) 176(171) 190
Katz, D.J. 7(43) 43
Kececioglu, E. 163(150) 190
Keith, T.A. 26(66) 44
Keldish, L.V. 213(93) 270
Kelly, D. 104(25 31) 185Ч186
Kemp, M. 3(16) 6(42) 42Ч43
Kenkre, V.M. 206(81) 269
Kennedy, E.C. 136(90) 137(90Ч91) 188
Kent, A.D. 104(26) 150(120) 151(26) 154(120) 173(120 167) 186 189Ч190
Keszei, E. 233(97) 270
Ketchen, M. 104(41) 161(41) 186
Keyes, T. 206(82) 270
Khmelinskii, I.V. 46(13) 47Ч49(39Ч41) 53(93) 62(39) 77(39Ч41) 82(41) 83Ч84(39Ч41 128) 86Ч87(39Ч41) 88(39 41) 91Ч92(41) 93Ч96
Kim, G.-H. 177Ч178(177) 190
Kim, H. 15(60) 44
Kim, J. 5(34) 9Ч11(34) 17(64) 34(34) 43Ч44
Kimura, Y. 203(65) 269
King, G.W. 82(122Ч123) 88(130 132) 96
King, H. 15(60) 44
Kinsey, J.L. 55(110) 88(138) 96Ч97
Klein, M.L. 205(73) 238(100) 239(73 102) 269Ч270
Kleinsasser, A.W. 104(41) 161(41) 186
Klik, I. 137(92Ч93) 188
Kliner, D.A.V. 201(55) 269
Knowles, J.E. 103(12) 185
Kochubei, S.A. 46(13) 47Ч49(37Ч41) 62(39) 77(39Ч41) 82(41) 83Ч84(39Ч41 128) 85(37Ч38) 86Ч87(37Ч41) 88(39 41) 91Ч92(41) 93Ч 96
Kodama, R.H. 147(105Ч106) 188
Kohl, C. 101(5) 185
Kohn Ч Sham equations, tunneling current calculations 39
Kommandeur, J. 91(161Ч164 175) 97Ч98
Kono, H. 49(82) 51(82) 95
Kubo O. 104(37) 109(37) 111(37) 121(37) 142(37) 144(37) 180(37) 186
Kuhn, I.H. 49(84) 51(84) 95
Kuhn, L.T. 104(27) 186
Kuki, A. 6(40) 43
Kurkijaervi, J. 141(96) 188
Kurnikov, I. 8(44) 11(44) 39(80) 43Ч44
Kurnikova, M.G. 39(80) 44
Kuttner, H.G. 47(25 31) 94
Kuznetsov, A.M. 2Ч3(9) 40(9) 41
Ladanyi, B.M. 198(45 47) 202(61) 269
Lahmani, F. 49(77) 51Ч52(77) 91(165) 95 97
Lahut, J.A. 147(103) 188
Lambert, W.R. 47(42) 90(42) 94
Lamelas, F.J. 126(62) 187
Landau Ч Zener tunneling, environmental decoherence effects, intermolecular dipole interaction 169-170
Landau Ч Zener tunneling, environmental decoherence effects, temperature dependence 171Ч175
Landau Ч Zener tunneling, iron  molecular clusters 155Ч160 molecular clusters 155Ч160
Landau Ч Zener tunneling, iron 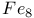 molecular clusters 154Ч160 molecular clusters 154Ч160
Landau Ч Zener tunneling, tunnel splitting oscillations 160Ч165
Landau, L. 154(130) 189
Langen, R. 2Ч4(6) 26(6) 33(6) 41
Langevin equation, thermal-dependent magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model 135Ч136
Langevin equation, vibrational energy relaxation 193Ч194
Langevin equation, vibrational energy relaxation, classical approaches 201Ч203
Langevin equation, vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 234Ч237
Langhof, S.R. 90(148) 97
Laplace transformation, vibrational energy relaxation, Langevin equation 202Ч203
Larsen, R.E. 203(66 68) 269
Larsson, S. 4(21) 36(21) 42
Laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) spectra, oxalylfluoride, magnetic field influence on excited-state dynamics 82Ч83
Laubereau, A. 192(1) 267
Laviolette, R.A. 237(98) 241(98) 270
Lavrik, N.L. 46(5 7) 47(5) 93
Ledermann, M. 103(19) 133(78) 142(19) 185 187
Lee, C.H. 126(62) 187
Lee, S.-F. 104(29 32) 186
Lee, S.-Y. 163(153) 190
Lee, Y.T. 90(149) 97
Leggett, A.J. 149(107) 188 207(89) 211(89) 218(89) 220(89) 225(89) 270
Leighton, R.B. 163(147) 190
Lelievte-Berna, E. 151Ч152(109) 188
Lennard-Jones potential, vibrational energy relaxation Hamiltonians 199Ч200
Lennard-Jones potential, vibrational energy relaxation, influence functional theory 208Ч209
Lerme, J. 121(60) 187
Leuenberger, M.N. 155(138) 171(138) 173(138) 176(174) 189Ч190
Level anticrossing mechanism (LAM), singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism 52Ч53
Level anticrossing mechanism (LAM), theoretical background 46Ч49
Levine, R.D. 82(118) 96
Levinson, L.M. 147(103) 188
Levy, D.H. 46(2) 93
Levy, R.M. 205(69) 269
Liang, C.X. 33(74) 44
Liang, j.-q. 163(152) 190
Lim, E.C. 91(167Ч168) 92(168) 97
Lim, E.S. 49(69) 51(69) 91(172 174) 95 97
Lim, M. 192(9) 196(9) 238(9) 245(9) 267
Lin, S.H. 49(82) 51(82) 82(117) 91(170) 95Ч97 206(77) 218(77) 269
Lindelof, P.E. 104(27) 186
Lionti, F. 150(115 123) 154(115) 176(123) 189
Lipinski, M. 104(28) 186
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation, vibrational energy relaxation, mean field approximation 231Ч232
Liu, D.S. 54Ч55(102) 96
Liverman, M.G. 82(120) 96
Livingstone, J.D. 135(85) 141(85) 188
Lobaugh, J. 239(103) 270
Loiseau, A. 104(36) 109(36) 111(36) 121(36) 142(36) 144(36) 180(36) 186
Lok, J.G.S. 104(27) 186
Lombardi, M. 46(3 20Ч21) 47(3 20Ч21 24 32 34Ч36) 49(89) 51(89) 88(137) 93Ч95 97
Long-distance electron tunneling, analytic techniques, future development 37
Long-distance electron tunneling, density functional theory (DFT) calculations 38Ч39
Long-distance electron tunneling, Gaussian basis vs. real-space (grid) calculations 37Ч38
Long-distance electron tunneling, many-electron formulation, current density operator 12Ч13
Long-distance electron tunneling, many-electron formulation, Hartree Ч Fock approximation 15Ч18
| Long-distance electron tunneling, many-electron formulation, interatomic tunneling currents 18Ч21
Long-distance electron tunneling, many-electron formulation, spatial distribution of current density 13Ч15
Long-distance electron tunneling, one-electron theory, interatomic currents and paths 9Ч12
Long-distance electron tunneling, one-electron theory, protein pruning 8Ч9
Long-distance electron tunneling, one-electron theory, tunneling matrix element, very large systems 6Ч8
Long-distance electron tunneling, polarization cloud dynamics 36Ч37
Long-distance electron tunneling, protein dynamic effects 39Ч40
Long-distance electron tunneling, theoretical background 2Ч6
Long-distance electron tunneling, tunneling current calculations, exchange effects 34Ч36
Long-distance electron tunneling, tunneling current calculations, pruned His-125 molecule 24Ч27
Long-distance electron tunneling, tunneling current calculations, quantized vortices in tunneling flow 27Ч32
Long-distance electron tunneling, tunneling current calculations, Ruthenium-modified copper protein electron transfer 21Ч24
Long-distance electron tunneling, tunneling current calculations, transfer matrix element 32Ч33
Long-distance electron tunneling, tunneling current calculations, transition state analysis 33Ч34
Loss, D. 155(138) 161(145) 171(138) 173(138) 176(174) 189Ч190
Louisell, W.H. 225(95) 270
Low-field limit, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, Zeeman interaction operator 63Ч65
Low-temperature behavior, vibrational energy relaxation, one-harmonic-oscillator bath model 258Ч260
Lowther, J.E. 206(75) 269
Lu, L. 103(20) 185
Lu, Y. 104(30) 186
Maan, J.C. 104(27) 186
MacElroy, R.D. 237(98) 241(98) 270
Madura, J.D. 239(102) 270
Magnetic fields, excited-state dynamics, acetylene 88Ч90
Magnetic fields, excited-state dynamics, anisotropic spin-spin constants 92Ч93
Magnetic fields, excited-state dynamics, diazines 90Ч92
Magnetic fields, excited-state dynamics, oxalylfluoride 82Ч88
Magnetic fields, perturbation effects, theoretical background 46Ч49
Magnetic fields, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, interaction schemes and 68Ч78
Magnetic fields, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, triplet-state wave functions 78Ч82
Magnetic quantum tunneling see "Quantum tunneling"
Magnetic quenching (MQ), acetylene fluorescence 89Ч90
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry 104Ч114
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, array schematics 113
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, blind mode three-dimensional switching field measurements 111Ч113
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, cold mode magnetization switching measurements 109Ч111
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, critical current magnetization measurements 105Ч109
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, fabrication techniques 105
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, future applications 114
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, hysteresis loop measurement feedback 109
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, scanning microscopy 114
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, micro-SQUID mangetometry, SQUID configuration selection 104-105
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, quantum tunneling 149Ч183
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, quantum tunneling, environmental decoherence effects 165Ч176
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, quantum tunneling, individual single-domain particles 176Ч183
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, quantum tunneling, molecular clusters 150Ч165
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, research background 100Ч102
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, single-particle measurement techniques 102Ч114
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, temperature effects 135Ч149
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, temperature effects, Neel Ч Brown model 136Ч138
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, zero Kelvin reversal 114Ч135
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, zero Kelvin reversal, nonuniform magnetization reversal 129Ч135
Magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, zero Kelvin reversal, uniform rotation (Stoner Ч Wohlfarth model) 115-129
Magnetocrystalline anisotropy (MC), zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model 118Ч120
Magnetoelastic (ME) anisotropy, zero Kelvin magnetization reversal, Stoner Ч Wohlfarth uniform rotation model 118Ч120
Mailly, D. 103(22) 104(22 34Ч39) 105Ч106(43Ч44) 109(36Ч39) 111(35Ч39) 113(48) 114(43Ч44 50Ч51) 120(22 59) 121(36Ч39) 128(65) 131Ч132(35 74) 133(79) 134(22 59 79) 142(36Ч39 59) 144(36Ч37) 146(35 74) 147(59 74 79) 148(59 74) 151(126) 155(129) 159(129) 168(129) 173(126) 179(22 35) 180(36Ч37) 185Ч187 189
Makarov, V.I. 46(7 13 19) 47Ч48(19 37Ч41) 49(37Ч41) 53(93Ч94 96) 62(39) 67(19) 77(19 39Ч41) 79(19) 82(19 41) 83(39Ч41 128) 84(19 39Ч41 128) 85(37Ч38 40) 86(37Ч41) 87(19 37Ч41) 88(39 41) 89(143 145) 90(143) 91Ч92(41) 93Ч97
Manganese molecular clusters, environmental decoherence effects, hyperfine couplings 170Ч171
Manganese molecular clusters, magnetic quantum tunneling 150Ч151
Manganese molecular clusters, magnetic quantum tunneling, anisotropy measurements 1564
Mangin, S. 113(48) 186
Maniero, A.L. 150(124) 176(124) 189
Manny, M. 104(41) 161(41) 186
Many-electron formulation, long-distance election tunneling, current density operator 12Ч13
Many-electron formulation, long-distance election tunneling, Hartree Ч Fock approximation 15Ч18
Many-electron formulation, long-distance election tunneling, interatomic tunneling currents 18Ч21
Many-electron formulation, long-distance election tunneling, spatial distribution of current density 13Ч15
Many-electron formulation, Ruthenium-modified copper protein, His/Met residue tunneling transition 26Ч27
Many-electron formulation, vibrational energy relaxation, theoretical background 196Ч197
Mao, Y. 3(16) 42
Marchal, G. 113(48) 186
Marcus Ч Levich Ч Dogonadze expression, protein dynamics, electron-phonon coupling 40
Marcus, R.A. 2Ч4(8) 6(41) 8(41 48) 26(8) 32(8) 40(8) 41 43
Marley, A. 104(30) 186
Maroncelli, M. 200(51) 269
Martet, C. 121(60) 187
Martin, R.L. 26(66) 44
Martinis, J.M. 104(40) 186
Matrix elements see also "Tunneling matrix element"
Matrix elements, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, first-order perturbations 58Ч61
Matrix elements, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, magnet field interaction 68Ч78
Matrix elements, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, second-order perturbations 61Ч62
Matrix elements, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, triplet-state wave functions, magnetic field 78Ч82
Matrix elements, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion, Zeeman perturbation 62Ч68
Matrix elements, tunneling flow calculations 32Ч33
Matsuda, T. 103(13) 185
Matsumoto, Y. 46(14) 47(14 43Ч45) 90(14 43Ч45) 91(43Ч45 169) 93Ч94 97
Matsuzaki, A. 46(6 22) 47(22 27) 62(22) 64(22) 93Ч94
Matsuzaki, M. 46(4) 47(4 26) 93Ч94
Maude, D.K. 103(23) 179(23) 185
Maurice, J.L. 104(32) 186
Maxwell equations, tunneling flow vortices 31Ч32
McConnell, H.M. 4(20) 36(20) 42
McCormick, S. 39(76) 44
McCullough, E.A.Jr. 26(69) 44
McDonald, I.R. 194(14) 205(73) 238(100) 239(73) 268Ч270
McDonald, J.R. 82(126) 96
McFadyen, I. 103(16) 185
McHugh, A.J. 47(28) 94
McLaughlin, I. 49(59) 51(59) 94
McNiff, E.J. 147(105) 188
McVitie, S. 103(15) 185
Mean field approximation, 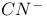 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation times 240Ч241 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation times 240Ч241
Mean field approximation, vibrational energy relaxation, mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics 229Ч232
Mean field approximation, vibrational energy relaxation, theoretical background 196
Medvedev, D. 8(50) 9(50Ч951) 11(50) 24(50) 36(50) 38(50) 43
Medvedev, E.S. 8(45Ч47) 31(45) 34(45Ч47) 39Ч40(45Ч46) 43
Meerts, W.L. 90(151) 97
Megy, R. 103(17) 185
Meier, J. 104(35) 1 131Ч132(35 74) 146(35 74) 147Ч148(74) 179(35) 186Ч187
Meiweis-Broer, K.H. 103(20Ч21) 185
Melinon, P. 104(39) 109(39) 121(39 60Ч61) 123(61) 142(39) 186Ч187
Merer, A J. 54Ч55(98) 95
Mesoscopic effects, quantum tunneling magnetization reversal 149Ч150
Met residue, Ruthenium-modified copper protein, tunneling transition 24Ч27
Metiu, H. 202(59) 269
Metz, F. 49(84) 51(84) 95
Meyer, P. 103(17) 185
Michel, C. 46(3 20Ч21) 47(3 20Ч21 24 30 34 36) 93Ч94
Michel-Beyerle, M.E. 4(17) 42
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetic quantum tunneling, iron molecular clusters 151Ч152
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters 104Ч114
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, array schematics 113
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, blind mode three-dimensional switching field measurements 111Ч113
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, cold mode magnetization switching measurements 109Ч111
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, critical current magnetization measurements 105Ч109
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, fabrication techniques 105
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, future applications 114
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, hysteresis loop measurement feedback 109
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, scanning microscopy 114
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, SQUID configuration selection 104Ч105
Micro-SQUID magnetometry, thermal-dependent magnetization reversal, nanometer-sized particles and clusters, Neel Ч Brown model 142Ч144
Miguel, M.C. 177(176) 190
Mihama, K. 103(13) 185
Mikami, T. 238(99) 270
Miller, A. 176(169) 190
Mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, 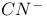 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation times 240Ч241 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation times 240Ч241
Mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, vibrational energy relaxation, applications 232Ч237
Mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, vibrational energy relaxation, direct simulation 228Ч237
Mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, vibrational energy relaxation, future research applications 266Ч267
Mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, vibrational energy relaxation, mean field approximation 229Ч232
Mixed quantum-classical molecular dynamics, vibrational energy relaxation, theoretical background 195Ч196
Miyashita, S. 155(133Ч134) 189
Molecular clusters, environmental decoherence effects 165-176
Molecular clusters, environmental decoherence effects, hole digging analysis, dipolar distribution and hyperfine coupling 166Ч168
Molecular clusters, environmental decoherence effects, hyperfine interaction 170Ч171
Molecular clusters, environmental decoherence effects, intermolecular dipole interaction 168-170
Molecular clusters, environmental decoherence effects, Landau Ч Zener tunneling probability 171Ч175
Molecular clusters, environmental decoherence effects, Prokof'ev Ч Stamp theory 165Ч166
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



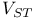 , singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism
, singlet-triplet (S-T) conversion mechanism 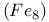 , environmental decoherence effects
, environmental decoherence effects 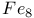 molecular clusters
molecular clusters 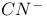 ions in aqueous solution, relaxation times
ions in aqueous solution, relaxation times