|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lee T.H. Ч Design of CMOS Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
"A Method for the Determination of the Transfer Function of Electronic Circuits" (Cochrun and Grabel) 167
"All-American" 5-tube superhet (radio), development of 32 575Ч578 583
"Duck test" version, of Occam's razor 116
"Four sevens" patent (#7777), of Marconi 7
"Motorboating", low-frequency oscillation as 434 435
"Subhistories of the Light-Emitting Diode" (Loebner) 22
"The Crystal Detector" (Douglas) 22
"Ultraviolet catastrophe" 247
"Universal" equations, for impedance transformation 94 95
"When Tubes Beat Crystals: Early Radio Detectors" (Thackeray) 22
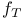 doubler, bandwith enhancement with 197Ч199 doubler, bandwith enhancement with 197Ч199
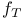 doubler, Battjes type 198Ч199 217 doubler, Battjes type 198Ч199 217
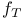 doubler, Darlington pair as 197 217 doubler, Darlington pair as 197 217
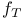 doubler, differential pair as 197 doubler, differential pair as 197
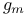 cell 329 cell 329
 -plane 135 -plane 135
 -match circuit 95Ч98 105 107 -match circuit 95Ч98 105 107
 -match circuit with transformed right-hand L-section 97 -match circuit with transformed right-hand L-section 97
4046 CMOS phase-locked loops, use in design examples 470Ч478
AC power, for filament tube 24
Active inductors, noise properties of 269
Adler, R.B. 148
Admittance of infinitesimal capacitance 110
Admittance of parallel RLC tank 86Ч87 90
Admittance of tapped capacitor resonator 99 100
Admittance relation, reflection coefficient relation to 270
Admittance, correlation admittance 258 275
Admittance, optimum source admittance 258 260
Advanced Mobile Phone Service 344
AF signals 17
Ailken, Hugh 12 22
Alexanderson alternator 8
Alexanderson, Ernst F.W. 7
Alternator technology, history of 22
Aluminum interconnect 36
AM broadcast band 15
AM broadcast radios, neutralization for 205
AM broadcast radios, standard IF for 316Ч317
AM broadcast, first by Fessenden 8 9
AM demodulator, Armstrong's explanation of 572
AM demodulator, envelope detector as 111 112
AM radio, preselector in 554 555
AM radio, static in 21
AM receiver, upconversion in design of 556
AM table radio, early model ("All-American") 32 575Ч578 583
AM, bandwidth of 21
AM, FM signal conversion into 20
America's Cup yacht race 7
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) 141
American Telephone and Telegraph Co. 12 390
American Wireless Telephone and Telegraph 7
Ampere's law 115
Amplifiers with voltage-sensitive capacitance 83
Amplifiers, cascaded 206Ч216
Amplifiers, common source type 200Ч201
Amplifiers, common-gate type 176
Amplifiers, design example for 153Ч160
Amplifiers, distributed type 191Ч197 214Ч216
Amplifiers, feedback-biased 176
Amplifiers, feedforward amplifiers 386Ч389
Amplifiers, gain of 180
Amplifiers, high-frequency type 178Ч222
Amplifiers, inverting amplifiers 85 406 407
Amplifiers, narrowband type 179
Amplifiers, negative feedback amplifiers 389Ч390
Amplifiers, neutralization of 203Ч206
Amplifiers, noise performance of 268
Amplifiers, noninverting amplifiers 405
Amplifiers, positive feedback amplifiers 386
Amplifiers, shunt and series peaking of 188Ч189
Amplifiers, shunt-peaked 184
Amplifiers, shunt-series type 191Ч197
Amplifiers, solid-state type 20Ч21
Amplifiers, superregenerative type 211Ч213
Amplifiers, tuned typed 199Ч203
Amplifiers, two-port bandwidth enhancement of 187Ч191
Amplifiers, unilateralization of 203Ч206
Amplitude modulation see "AM"
analog circuits 36
Analog Devices 264
Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) 562 568
Antiresonant frequency, of parallel RLC tank 87
Arc technology for industrial illumination 7
Arc technology, history of 22
Architectures 550Ч570
Architectures for dual-conversion receivers 556
Architectures for image-reject receiver 556Ч561
Architectures for single-conversion receiver 554Ч555
Architectures for subsampling 565
Architectures for transmitters 566Ч567
Architectures for upconversion 555Ч556
Architectures in dynamic range 551Ч565
Architectures, direct conversion in 562Ч565
Architectures, problem set for 568Ч570
Armstrong regenerative receiver 13
Armstrong, Edwin Howard 1 12 13Ч15 17 19 21Ч22 211 212 308 386 390
Armstrong, Edwin Howard, grid-leak AM demodulator of 572Ч573
Armstrong, Edwin Howard, history of inventions of 571Ч575
Armstrong, Edwin Howard, in legal battle 21Ч22
Armstrong, Marian 22
Asymptotic angle rule 401
Atmospheric noise 577
Attenuation constant, of transmission lines 142Ч143
Audions, as de Forest vacuum tubes 11Ч13 23 27 571
Audiophonics, power consumption in 348
Auditory system, of humans 6
Autodyne circuit, of "All-American" 5-tube superhet 577
Automatic gain control (AGC), in "All-American" 5-tube superhet 578
Automatic volume control (AVC), in "All-American" 5-tube superhet 578
Autotransformer 205
Available noise power 244
Back-gate bias effect 77 240
Ballasting 375
Bandgap reference principle 229
Bandgap references, classic 229Ч237
Bandgap references, design example for 230Ч233
Bandgap voltage references, in CMOS technology 227 233Ч235
Bandpass filters, for interference reduction 7
Bandwidth estimation 146Ч177
Bandwidth estimation, open-circuit time constants (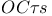 ) method 147Ч161 163 ) method 147Ч161 163
Bandwidth estimation, problem set for 174Ч177
Bandwidth estimation, short-circuit time constants (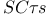 ) method 161Ч166 ) method 161Ч166
Bandwidth for noise 246
Bandwidth of shunt-series amplifiers 195Ч197
Bandwidth, 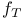 doubler enhancement of 197Ч199 doubler enhancement of 197Ч199
Bandwidth, channel capacity related to 124
Bandwidth, negative feedback and 392Ч393
Bandwidth, quality factor and 90
Bandwidth, risetime and delay 167Ч174
Bandwidth, risetime relations with 171Ч173 175
Bandwidth, shrinkage of 173 207Ч209
Bandwidth, T-coil enhancement of 190
Bandwidth, zeros as enhancers of 178 179Ч191
Bandwidth-delay tradeoff 189
Bardeen, John 62
Barretter 8
Battjes 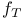 doubler 198 217 doubler 198 217
Battjes, Carl 198Ч199
Beam-forming electrode 31Ч32
Bell Laboratories 21 62 247 387 501 580
Bell, Alexander Graham 387
Bias circuits, supply-independent 225Ч227
Bias loop, in low-noise amplifier 294
Biasing 223Ч242
Biasing, problem set for 237Ч242
Big Bang, echoes of 248 311
Bilinear transformation 135
Bipolar circuits, biasing based on 223
Bipolar circuits, CMOS version of 198Ч199
Bipolar common-emitter amplifier 306
| Bipolar devices 62 75Ч76
Bipolar technologies, poly emitters for 35
Bipolar transistor mixer, conversion gain of 318
Bipolar transistors, bistable noise see "Popcorn noise"
Bipolar transistors, breakdown phenomena in 374
Bipolar transistors, describing functions for 488Ч491
Bipolar transistors, Dicker noise in 254
Bipolar transistors, Early effect in 77
Bipolar transistors, gold doping of 255
Bipolar transistors, incremental model of 485
Bipolar transistors, noise model for 266
Bipolar transistors, thermal runaway in 375
Black hole, for energy, transmission line as 119
Black, Harold S., feedforward amplifier of 387Ч389
Black, Harold S., negative feedback amplifier of 389Ч390
Blackbody radiation, noise associated with 247
Bode plots 176 392 397 398 424 436 446
Body effect see "Back-gate bias"
Body-effect coefficient 84
Boltzmann's constant 244 245
Bond wire inductors 34 52 60
Bose, J.C. 5
Bounded-input bounded-output (BIBO) definition, of stability 395
Branly coherer 3
Branly, Edouard 3
Brattain, John 62
Braun, Ferdinand 5
Bridging capacitance 189 190Ч191
Brightness signal, in color television 440
British Marconi 10
Brokaw cell 229 230 232
Brownian motion, noise and 243
Burns, Ken 22
Burst noise see "Popcorn noise"
Cady, W.G. 501
Calwhisker, as detector part 5 6 20
Capacitance of interconnect 41Ч47
Capacitance or MOSFETs 67Ч70
Capacitance, equations for 37 40 51 57Ч58
Capacitive degeneration 320
capacitors 34 37Ч47
Carbon resistors, dicker noise in 253
Carborundum detectors 6 9 11 20
Carson, John R. 21
Cartesian feedback 363
Cascade amplifiers 155 157 158 165 206Ч216
Cascade amplifiers with single tuned load 204
Cascade amplifiers, bandwidth shrinkage in 207Ч209
Cascade amplifiers, noise temperature of 260
Cascade amplifiers, optimum gain per stage in 209Ч211
Cascade systems for intercept calculation 553
Cascade systems for noise-figure computation 267 551Ч552
Cascade systems, delay in 167Ч169
Cascade systems, linearity of 552Ч554
Cascoding technique 29Ч30 291 327 328 500 577
Cascomp circuit 327
Cathodes, basic principles of 23Ч25
Cathodes, oxide-coated 24 25
Cellular telephones, channel spacing in 567
Cellular telephones, FM use by 344
Cellular telephones, lithium niobate filter use in 504
Channel capacity, bandwidth related to 124
Channel lengths in short-channel MOS devices 75Ч76
Channel lengths, modulation of 77Ч78 84
Channel-spacing counter, in integer-N synthesizer 518
Charge pump, as alternative for op-amp loop filter 465Ч466 479
Circadian rhythms, of humans, as injection locking 439
Circuit design, economics of 1
Circular capacitance, correction factors for fringing in 58
Clapp oscillator 505 506 512 513 524 532
Class A amplifiers 346Ч349 364 380 381 382 384 578
Class A amplifiers, design example for 365Ч369
Class A amplifiers, drain efficiency of 347
Class A amplifiers, load-pull characterization of 376Ч378
Class A amplifiers, modulation of 362Ч363
Class AB amplifiers 354
Class AB amplifiers, design example for 369Ч370
Class AB amplifiers, modulation of 362Ч363
Class B amplifiers 349Ч351 364
Class B amplifiers, design example for 369Ч370
Class B amplifiers, drain efficiency of 350
Class B amplifiers, modulation of 362Ч363
Class C amplifiers 351Ч354 365 382
Class C amplifiers, design example for 369Ч370
Class C amplifiers, drain efficiency of 354
Class C amplifiers, iterations of 376
Class C amplifiers, modulation of 362Ч363
Class D amplifiers 355Ч357 365
Class D amplifiers, design example for 370Ч371
Class E amplifiers 357Ч359 365
Class E amplifiers, design example for 370Ч371
Class E amplifiers, modulation of 362Ч363
Class F amplifiers 359Ч362 365
Class F amplifiers, modulation of 362Ч363
Clocked circuits 460 462 524 560Ч561
Closed-loop systems, stability of 398
Clutches, loop transmissions and 407
CMOS circuit blocks, dimensions of 116
CMOS technology, bandgap voltage references in 227 233Ч235 241
CMOS technology, bias circuits of 223
CMOS technology, bipolar circuit in 198Ч199
CMOS technology, bipolar transistors in 225
CMOS technology, diodes in 225
CMOS technology, distributed amplifier use in 216
CMOS technology, implanted diffusions in 231
CMOS technology, inferiority of 183
CMOS technology, inverters in 469 509
CMOS technology, junction capacitors in 513
CMOS technology, mixers 324Ч325 331 332
CMOS technology, noise figures of 278
CMOS technology, phase detectors in 456
CMOS technology, resistor options in 34 35
CMOS technology, RF integrated circuit design 134
CMOS technology, switches in 319 331 335 453
Coaxial cable, power-handling capacity of 141Ч142
Cochrun, B.L. 167
Coherer, Branly's 3
Coherer, replacement of 8
Color television, PLL-like circuit in 439Ч440
Colpitts crystal oscillator 507 508 524Ч525
Colpitts oscillator 504Ч506 511 524 525Ч526 543 546 548
Colpitts oscillator, describing function analysis of 495Ч500
Colpitts oscillator, startup model of 499
Colpitts oscillator, waveforms for 544
Columbia University 124
Common-gate amplifiers 220 222 279 306
Common-gate transconductor 340
Common-source (CS) amplifier 154
Common-source (CS) amplifier with shunt input resistor 278 305
Common-source (CS) amplifier with single tuned load 200Ч201
Common-source (CS) amplifier, inductively degenerated 282
Common-source (CS) amplifier, neutralization of 205 206
Common-source (CS) amplifier, zero-peaked 187
Communications systems, oscillators for 492
Commutating multipliers, as phase detectors 451Ч453
Comparator, describing function for 486
Comparator, oscillator with 545
Compensating capacitance, in neutrodyne amplifier 16
Compensation, root-locus examples and 415Ч422 432
Compensation, through gain reduction 423Ч426
Complementary metal-oxide silicon processes see "CMOS processes"
Complementary to absolute temperature (CTAT) 224 225 228 229
Computers, use of network analysis 146
Computers, vacuum tubes in 580
Conductors, three adjacent wires in 45Ч47
Conductors, wire sandwiched in 44Ч45
Conductors, wire-over-ground plane 41Ч43
Constant-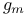 bias 235Ч237 238 241 bias 235Ч237 238 241
Constant-envelope amplifiers 344 362
Constant-k lines 118
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



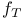 doubler, bandwith enhancement with
doubler, bandwith enhancement with 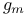 cell
cell  -plane
-plane  -match circuit
-match circuit 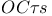 ) method
) method 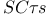 ) method
) method