|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lee T.H. Ч Design of CMOS Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Open-circuit time constants (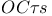 ) method for bandwidth estimation 147Ч161 163 178 ) method for bandwidth estimation 147Ч161 163 178
Open-circuit time constants (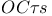 ) method, accuracy of 149Ч150 ) method, accuracy of 149Ч150
Open-circuit time constants (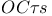 ) method, advantages of 167 174 178 ) method, advantages of 167 174 178
Open-circuit time constants (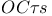 ) method, disadvantage of 178 ) method, disadvantage of 178
Open-circuit time constants (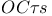 ) method, risetime addition and 173 ) method, risetime addition and 173
Open-circuit time constants (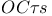 ) method, summary of 160Ч161 ) method, summary of 160Ч161
Open-circuit time constants (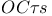 ) method, superbuffer for 177 ) method, superbuffer for 177
Open-loop system, with additive noise sources 394
Optical fiber systems, gain-delay tradeoff in 213
Optical phonons, scattering by 73
Optimum source admittance 259 260
Oscillator(s) 484Ч529
Oscillator(s), Clapp oscillator 505 506 512 513 526
Oscillator(s), Colpitis crystal oscillator 507 508 524Ч525
Oscillator(s), Colpitis oscillator 495Ч500 504Ч506 511 524 525Ч526 546 547
Oscillator(s), crystal oscillators 507Ч509 514 524
Oscillator(s), dependence on nonlinearities 485
Oscillator(s), describing function analysis of 492Ч493
Oscillator(s), function generator 491Ч495
Oscillator(s), Hartley oscillator 505 524
Oscillator(s), linear type 484Ч485
Oscillator(s), negative resistance oscillator 509Ч514 527
Oscillator(s), noise from 449
Oscillator(s), oscillation amplitude in 484
Oscillator(s), oscillation frequency in 530
Oscillator(s), oscillation startup in 498Ч500
Oscillator(s), Pierce crystal oscillator 508Ч509 511 525
Oscillator(s), problem set for 525Ч529
Oscillator(s), quadrature oscillator 509 525
Oscillator(s), RLC oscillator 531 532
Oscillator(s), root locus for 485
Oscillator(s), stability of 567Ч568
Oscillator(s), superregenerative amplifier as 19
Oscillator(s), TITO oscillator 506Ч507
Oscillator(s), tuned type 504Ч509
Oscilloscopes, phase distortion in 182
Oscilloscopes, probe of 184 185
Oscilloscopes, vacuum tube distributed amplifiers in 215
Output compression point 312
Output third-order intercept point (OIP3) 312
Overlap capacitances 68
Oxides, trap formation in 373
p-n-p parasitic substrate, in CMOS 226 227 234
Parallel plate capacitors 37Ч47
Parallel resonance, of parallel RLC tank 87
Parallel resonant lank circuit, problem on 59
Parallel RLC tank 86Ч89
Parallel RLC tank, admittance of 86Ч87
Parallel RLC tank, bandwidth of 90
Parallel RLC tank, characteristic impedance of 88
Parallel RLC tank, network energy of 88
Parallel RLC tank, quality factor of 88Ч89
Parameters, for SPICK level-3 models 82
Parametric converters (parametric amplifiers) 310 338
Parasitic capacitances and inductances, effect on amplifier performance 178
Parasitic transistors, bias circuits made from 223
Parseval's theorem 541
Passive mixers 331Ч335
Passive RLC networks 86Ч113
Passive RLC networks, problem set for 106Ч113
Path transfer function, derivation of 435
Patterned ground shield, in spiral inductors 51Ч52
Peaking problem, in phase-locked loops 446Ч447
Pentode, characteristics of 31
Penzias, Arno 247Ч248
Percival, W.S. 214
Perveance 26 28
Phase detector constant 453 456
Phase detector gain 450Ч451 455
Phase detector in phase-locked loop circuits 441 442
Phase detector, analog multiplier as 450Ч451
Phase detector, exclusive-OR gate as 453Ч455 479
Phase detector, frequency detector vs. 459
Phase detector, Hogge's phase detector 460Ч463
Phase detector, quadrature type 451 453
Phase detector, sequential type 455Ч463
Phase detector, XOR phase detector 455 475Ч476 478
Phase detectors, triwave detector 462 463 464
Phase distortion, errors caused by 182
Phase margin, computation of 424
Phase noise 448 484 530Ч549
Phase noise of ideal oscillator 532Ч536
Phase noise, equation for 534
Phase noise, Hajimiri model for 536Ч544
Phase noise, Leeson model for 535 536 541 547
Phase noise, linear time-invariant analysis of 537 539
Phase noise, problem set for 545Ч549
Phase noise, theory of 532Ч536
Phase shift 182
Phase transfer function, derivation of 444 446
Phase-alternating line (PAL) system 441
Phase-locked loops (PLLs) 409 438Ч483
Phase-locked loops (PLLs) as sampled-data systems 448
Phase-locked loops (PLLs) as synthesizers 515 516 517 518 522 524
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), architecture of 441
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), history of 438Ч441
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), linearized 441Ч447
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), loop filters in 463Ч468
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), noise input into 447
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), noisy 481Ч482
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), problem set for 478Ч483
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), quartz-controlled oscillator combined with 514
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), second-order type 435 444Ч447 475Ч478
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), use as FM demodulators 472Ч473
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), uses of 438 439
Phase-locked loops (PLLs), VCO output in 480
Philips Electronics N.V. 268
Phillips, V. 22
Phosphor, designation for 33
Photoelectric effect, of Einstein 20
Pickard, Greenleaf Whittier 4 6
Pierce crystal oscillator 508Ч509 511 525
Pinched-off channels 67
Pink noise see "Flicker noise"
Planck's constant 247
PLLs see "Phase-locked loops"
PMOS devices, high-field effects of 76
PMOS devices, noise in 248Ч249 255
PMOS devices, threshold reductions in 77
Poisson's equation 26
Pole-zero doublet 186
Poly resistors 35
Polysilicon resistor, problem on 60Ч61
Popcorn noise 255Ч256
Positive feedback amplifiers 386 390
Positive feedback systems, root-locus rules for 403Ч404
Potentiometric mixers 329Ч331
Poulsen Tikker 14
Poulsen, Valdemar 7 14
Power amplifiers 344Ч384
Power amplifiers, breakdown phenomena in 372Ч374
Power amplifiers, characteristics of 364Ч365
Power amplifiers, Class A amplifiers 346Ч349 362Ч363 364 365Ч369 381 382 384 578
Power amplifiers, Class AB amplifier 354 362Ч363 369Ч370
Power amplifiers, Class B amplifiers 349Ч351 362Ч363 364 369Ч370
Power amplifiers, Class C amplifiers 351Ч354 362Ч363 365 369Ч370
Power amplifiers, Class D amplifiers 355Ч357 365
Power amplifiers, Class E amplifiers 357Ч359 362Ч363 365 370Ч371
Power amplifiers, Class F amplifiers 359Ч363 365
Power amplifiers, design examples for 365Ч371
Power amplifiers, design summary for 379Ч380
Power amplifiers, general model for 345
Power amplifiers, instability of 372
Power amplifiers, large-signal impedance matching in 375Ч376
Power amplifiers, load-pull characterization of 376
Power amplifiers, load-pull contour example of 378Ч379
Power amplifiers, modulation of 362Ч363
Power amplifiers, power-added efficiency of 372
Power amplifiers, problem set for 380Ч384
Power amplifiers, pulsewidth modulation of 364
| Power amplifiers, push -pull amplifiers 351 356 383
Power amplifiers, thermal runaway in 374Ч375
Power gain, at low frequencies 93Ч104
Power RF oscillators, invention of 13
Power transfer 86
Power, DC transmission of 10
Power, dissipation of 530
Power, handled by coaxial cable 141
Power, published gain figures for 316
Power, units for 140Ч141
Power-constrained optimization of noise 284Ч288
Preselector, of single-conversion receiver 554
Problem sets for architectures 568Ч570
Problem sets for bandwidth estimation 174Ч177
Problem sets for biasing and voltage references 237Ч242
Problem sets for distributed systems 131Ч133
Problem sets for feedback systems 432Ч437
Problem sets for high-frequency amplifier design 217Ч222
Problem sets for IC components 58Ч61
Problem sets for low-noise amplifiers 304Ч307
Problem sets for mixers 340Ч343
Problem sets for MOS devices 81Ч85
Problem sets for noise 266Ч271
Problem sets for oscillators 525Ч529
Problem sets for passive RLC networks 106Ч113
Problem sets for phase noise 545Ч549
Problem sets for phase-locked loops 478Ч483
Problem sets for power amplifiers 380Ч384
Problem sets for Smith chart and S-parameters 144
Propagation constant ( ) 119 ) 119
Propagation constant ( ), relationship to line parameters 122Ч124 ), relationship to line parameters 122Ч124
Proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT) 228 229 230
Pulse impedance 120
Pulsewidth modulation (PWM), of power amplifiers 364 365
Pupin coils 124
Pupin, Michael 124
Push-pull amplifiers, crossover distortion in 383
Push-pull amplifiers, power capability of 351 356
q see "Quality factor"
Quadrature generators, for image-reject receivers 559Ч561 562
Quadrature oscillators 509 525 560
Quadrature phase detector 451 479Ч480
Quality factor (Q) 90 95 285
Quality factor (Q) of parallel RLC tank 88Ч89
Quality factor (Q) of tapped capacitor resonator 100
Quality factor (Q), ringing and 90Ч91
Quantum effect, in carborundum LEDs 20
Quarter-wave resonators 500Ч501
Quartz crystals as resonators 501
Quartz crystals, fabrication of 503
Quartz crystals, symbol and model for 501
Quench oscillator, in early superregenerative receiver 575
Quinn, Pat 327
Radar, microwave diodes for 337
Radio astronomy, sideband information in 311
Radio circuits 15Ч18
Radio Corporation of America (RCA) 15 19 21 31 33 212 576
Radio electronics, developments in 15
Radio, history of 1Ч33
Radio-frequency (RF) carriers, sine-wave type 7
Radio-frequency (RF) signals 8 15
Radioactivity, discovery of 10
Radiotelegraphy 8 22
Radiotelegraphy, transition to radiotelephony 9
Radiotelephony 9 29
Radius of gyration 169
Random telegraph signals (RTS) see "Popcorn noise"
RC low-pass filter, step response in 171
Reactance tube 269
Read-only-memory (ROM) lookup table 523 524 568
Receiver with coherer 3
Receiver, "universal" 562
Receiver, direct-conversion type 562Ч563
Reflection coefficient 126 127 134Ч135
Reflection coefficient, admittance relation to 270
Reflex circuits 17Ч18
Regency TR-1 transistor radio, history of 578Ч580
Regenerative amplifier/detector/oscillator, invention of 13 17 18 386 573Ч574 577
Regenerative radios, de Forest's sale of 17
Regenerative receiver 13 18
Resistances, of shunt-series amplifiers 193Ч195
resistors 34Ч37
Resistors, flicker noise in 253Ч254
Resistors, layout of 36Ч37
Resistors, thermal noise of 245Ч246 265
Resonance, branch currents at 89
Resonant circuits, amplifier function in 107
Resonant frequency, of parallel RLC tank 87
Resonant voltage, magnification of 91
Resonators 500Ч504
Resonators, quarter-wave resonators 500Ч501
Resonators, quartz-crystal resonators 501
Resonators, SAW devices 503Ч504
RETMA 33
RF circuits and systems, history of 571Ч583
RF circuits and systems, noise in 251
RF circuits and systems, superregenerators in 212Ч213
RF circuits and systems, units in 140Ч141
RF rectifiers 10
RF signals 17
RF transconductors, for mixers 321
Ring oscillator, impulse sensitivity function for 538 539
Ring oscillator, uses of 544
Ripple components, in loop filters 466
Risetime addition rule 171 173
Risetime of cascade systems 169Ч171
Risetime, bandwidth relations with 171Ч173 175 213
RLC networks as impedance transformers 93Ч104 180
RLC networks, lossy type 110
RLC networks, passive components in see "Passive RLC networks"
RLC networks, resonators in 501 530
RLC oscillator, "perfectly efficient" 531 532
RLC tank circuits 202 496
RLC tank circuits in series 91
RLC tank circuits, admittance of 203
RLC tank circuits, not-quite-parallel type 92
Roenlgen, Wilhehn Konrad 10
Root-locus techniques for feedback systems 398Ч403
Root-locus techniques for positive feedback systems 403Ч404
Root-locus techniques, compensation and 415Ч422 432
Root-locus techniques, summary of 422Ч423
Rosenstark, S. 167
Round, Henry J. 9 14 20
S-parameters 134 138Ч140
S-parameters, problem set for 144Ч145
Sakurai equation and method 42 43 45 46 47
Sample-and-hold action, of synthesizers 515
Sample-and-hold circuit 270
Sarnoff, David 15 19 22
Satellite communications, phase-locked loops in 441
Saturating amplifier, describing function for 487
Saturation, definitions for MOS and bipolar devices 346
SAW see "Surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices"
Sawtooth generators, use in television 439
Scattering parameters see "S-parameters"
Schmitt trigger 487 488 492
Scholtky diode 5
Schotlky, Walter 243 250 252 308
Searle, C.L. 166
Second-order low-pass systems, formulas for 413Ч414
Second-order phase-locked loops 444Ч447 479
Second-order phase-locked loops in design examples 446Ч447 475Ч478
Second-order phase-locked loops, jitter peaking in 446Ч447
Seconds, number in year 253
Self-biased circuits, start-up network in 226 227
Self-resonant properties, of spiral inductors 51
Self-restoring device, barretter as 8
Semiconductor detector, first patent for 5
Semiconductor, early types of 6
Sequential phase detectors 455Ч463
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



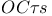 ) method for bandwidth estimation
) method for bandwidth estimation  )
)