|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lee T.H. Ч Design of CMOS Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Sequential phase detectors with extended range 457Ч458
Sequentiel Couleur avec Memoire (SECAM) 440
Series resonance, of parallel RLC tank 87
Series RLC network 91
Series-peaked RLC network 217
Set-reset (SR) flip-flop as phase detector 456Ч457
Set-reset (SR) flip-flop with cross-coupled NOR gates 457
Shockley, William 62
Short circuits, terminating ports in 139
Short-channel MOSFETs 73Ч77 240 362Ч363
Short-channel MOSFETs, linearity of 317
Short-channel MOSFETs, noise in 248 250
Short-channel MOSFETs, problem based on 73Ч77
Short-channel MOSFETs, transconductance in 300
Short-circuit time constants (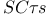 ) method for bandwidth estimation 161Ч166 ) method for bandwidth estimation 161Ч166
Short-circuit time constants (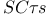 ) method, accuracy of 164 ) method, accuracy of 164
Short-circuit time constants (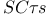 ) method, advantages of 174 ) method, advantages of 174
Short-circuit time constants (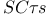 ) method, restrictions of 164Ч166 ) method, restrictions of 164Ч166
Shot noise 250Ч252
Shunt admittance 127
Shunt capacitance, equation for 50
Shunt peaking, design example for 183Ч184
Shunt-peaked amplifiers 179Ч191
Shunt-peaked RLC network 217
Shunt-series amplifiers 191Ч197 306
Shunt-series amplifiers, bandwith of 195Ч197
Shunt-series amplifiers, detailed design of 193Ч197
Shunt-series amplifiers, input-output impedances of 195Ч197
Shunt-series amplifiers, input-output resistances of 193Ч195
Shunt-series amplifiers, low-frequency gain of 193Ч195
Shunt-series amplifiers, noise figure of 278 279
Sichrome resistors 36
Sidebands of mixers 310
Sidebands of noise figures 311
Sigma-delta technique, for noise distribution 521
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), in calculation of noise figure 310
Signum function (sgn) 452
Silicided polysilicon, resistors from 35
Silicon detectors, first patent on 9
Silicon transistors, development of 580
Silicon, lack of piezoelectric activity in 504
Single-balanced mixers 319Ч322 342
Single-conversion receiver, architecture for 554Ч555
Single-diode mixers 337
Single-ended low-noise amplifier 288Ч292 304
Single-sideband noise figure (SSB NF) 310Ч311
Skin effect 49 142Ч143
Slope demodulation, of FM 20
Smith chart 127 134Ч138 259 379
Smith chart, problem set for 144Ч145
Solenoid, single-layer type 55
Solid-state amplifiers 20Ч21
Source followers, capacitively loaded 282
Source-coupled amplifiers, with single tuned load 204
Source-drain diffusions, resistors from 35
Soviet Union 20
Spark-gap detector, of Hertz 3
Spectrum analyzer, noise density determination by 263
SPICE 239
SPICE level-3 models 80Ч81 217 380
SPICE level-3 models, parameters for 82
SPICE MOSFET models 80
SPICE, IP3 estimation using 298
SPICE, mixer simulation using 324
SPICE, use for bandwidth estimation 149 152 155 157 158 159 160 175
Spiral inductors 47Ч52
Spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) 302Ч303
Square waves, as approximations of loop inputs 451Ч453 454
Square-law mixers 315Ч318
Squegging behavior 500
Stability, BIBO definition of 395
Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) 132
Static moduli, synthesizers with 517Ч519
Stationarity, in noise characterization 536
Stereo FM radio, phase-locked loop circuits in 441
Subsampling, architectures for 565
Substrate current, from hot electrons 76
Superbuffer, for 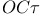 calculation 177 calculation 177
Superheterodyne AM radio, with heptode 32
Superheterodyne receiver 438 439
Superheterodyne receiver, block diagrams for 309 554
Superheterodyne receiver, invention and use of 15 17 21 308 574
Superheterodyne receiver, single-conversion type 554
Superheterodyne transmitter 550 566
Superregenerator amplifiers 131 211Ч213 218
Superregenerator amplifiers, Armstrong's invention of 574Ч575
Superregenerator amplifiers, interference from 212
Superregenerator detector, use in toy walkie-talkies 20 581 583
Superregenerator, invention of 18Ч20 211
Suppressor grid 31
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices, as resonators 503Ч504
Swallow counter, in integer-N synthesizer 518
Sweep oscillators, use in television 439
Switches, CMOS technology 319 331 335
synthesizers 514Ч524
Synthesizers with dithering moduli 519Ч521
Synthesizers with static moduli 517Ч519
Synthesizers, combination synthesizers 521Ч522 528
Synthesizers, direct digital synthesizer 521Ч522
Synthesizers, divider "delay" in 515Ч516
Synthesizers, integer-N synthesizer 517Ч519
Synthesizers, offset synthesizer 521 529
Synthesizers, phase-locked loop use in 478
Syntony and Spark (Aitken) 22
T-coil, bandwidth enhancement by 189 213 214 215 216
T-match circuit(s) 98 107 108
Tank circuit 86
Tank resistance, as noise source 531 532Ч533
Tantalum, in light bulbs 23
Tapped capacitor resonator 105Ч106 107
Tapped capacitor resonator as impedance matching network 99Ч101
Tapped inductor match circuit 102Ч103 106
Teal, Gordon 580
Tektronix 198 215
Telelfunken 579
Telephone repealer amplifier 12
Telephone transmission lines, signal-dispersion reduction in 124
Television, "snow" as noise in 243
Television, amplifier development for 179
Television, color television 439Ч440
Television, early amplifiers for 33
Television, gain-handwith amplifiers for 213
Television, mixers in UHF tuners for 337
Television, phase-locked loops in 439
Television, sweep oscillators in 439
Tellegen, B.D.H. 268
Temperature, on-chip measurement of 375
Terminations, of transmission lines 125Ч127
Tesla coil 91
Tesla, Nikola 7 91
Tetrode, characteristics of 30
Texas Instruments (TI) 578 580
Thackeray, D. 22
The Continuous Wave (Aitken) 22
The Empire of the Air (Bums) 22
The Father of Radio (de Forest) 22
The New York Times 389
Thermal noise 243Ч250 532
Thermal noise in MOSFETs 248Ч250
Thermal noise, epi noise as 291
Thomson, J.J. 9
Thoriated tungsten, in filaments 24
Three-point method, for IP3 estimation 298Ч299 300 303
Three-port mixers 314
Threshold reduction, in MOS devices 76
Threshold voltage, increases in 84
ThtHenin resistance 95 245
Tickler coil 13 18
| Time constants 181
Time constants, calculation of 91 147 148 149 150
Time invariance, assumption of 308
Time-dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB), in MOS devices 373
Time-division multiple-access (TDMA) systems 564
Time-domain simulators, simulation of mixer IP3 with 324Ч5
Time-varying theory 497
TITO oscillator 506 524
Token rings, peaking problem in 447
Toys, radio-controlled, coherer use in 4 8
Toys, superregenerator use in 19Ч20 see
Track-and-hold subsampling mixer 336
Transconductance of short-channel MOSFETs 300
Transconductance, equations for 29
Transconductance, temperature effects on 83
Transconductor, cross-quad type 327Ч328
Transconductor, large-signal type 488 489
Transcontinental telephone service, inauguration of 387
Transformers in passive RLC networks 86
Transformers, quarter-wave type 117
Transformers, upward and downward types 94
Transient impedance 120
Transistor amplifiers, 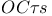 for 151Ч152 for 151Ч152
Transistor radio, history of 578Ч580
transistors 33
Transistors, behavior of 62Ч85
Transistors, invention of 1
Transistors, velocity saturation effect on 75Ч76
Transit time effects, in MOS devices 79Ч80
Transmission lines 119Ч124
Transmission lines as black holes for energy 119
Transmission lines with arbitrary terminations 125Ч127
Transmission lines, artificial lines 125Ч131
Transmission lines, attenuation constant of 142Ч143
Transmission lines, characteristic impedance of 88 89
Transmission lines, cutoff frequency of 128Ч129
Transmission lines, equations for 127
Transmission lines, exponentially tapered 117
Transmission lines, half-sections for termination of 129Ч130
Transmission lines, ideal, as infinite ladder network 118Ч119
Transmission lines, lossless type 132
Transmission lines, lossy type 119Ч122
Transmission lines, lumped lines 128Ч129
Transmission lines, RC diffusion lines 132
Transmission lines, with matched terminations 125
Transmitter(s) 6 7
Transmitter(s) of Hertz 2
Transmitter(s), architectures for 566Ч567
Transmitter(s), superregenerative receiver as 19
Triode vacuum tube 9 23 27
Triode vacuum tube, HF limitations of 29Ч30
Triode vacuum tube, incremental model for 29
Triode vacuum tube, invention of 11
Triode, structure and characteristics of 28 571
Tristate detectors 460
Triwave phase detector 462 463 464
Tuned amplifiers 199Ч203 218
Tuned input-tuned output oscillator see "TITO oscillator"
Tuned radio-frequency (TRF) receiver 15Ч16
Tungsten, in light bulbs 24
Two-diode mixers 338
Two-port bandwidth enhancement, of amplifiers 187Ч91
Two-port mixers 314 315Ч18
Two-port noise theory 256Ч60
Two-port variable definitions 138
Two-tone third-order intercept, of mixer linearity 312
Tyne, Gerald 11
U.S. Army Signal Corps 14
Unilateralization, of amplifiers 203Ч206
Unsilicided poly, resistivity of 35
Upconversion of noise 540
Upconversion, architecture for 555Ч556
V-I characteristics of MOSFETs 83
V-I characteristics of vacuum tubes 25Ч33
Vacuum tube computers 580
Vacuum tubes as amplifiers 387
Vacuum tubes as oscillators 385
Vacuum tubes in AM broadcast radios 205 575Ч578
Vacuum tubes, basic information on 22Ч33
Vacuum tubes, de Forest's work on 11
Vacuum tubes, describing function transconductance for 489 490
Vacuum tubes, development of 9Ч13 22 243
Vacuum tubes, distributed amplifier use with 215
Vacuum tubes, grid number in 32
Vacuum tubes, input impedance in 280 281
Vacuum tubes, V-I characteristics of 25Ч33
Van der Ziel, A. 249
Varactors 40 41 310
Varactors, junction capacitors as 59Ч60
Velocity saturation, effect on transistors 75
Very large-scale integration see "VLSI technologies"
Video amplifiers, shunt peaking derivation from 183
VLSI circuits, passive components of 86
VLSI technologies, source-drain diffusions in 35
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs) 468Ч469
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs) in 4046 CMOS device 471Ч472
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs) in phase-locked loop circuits 441Ч442 443
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), based on relaxation oscillator topology 449
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), control voltage for 463 465
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), design examples for 470Ч478
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), frequency of 459
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), noise in 483
Voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), ring oscillators 468Ч469
Voltage references 223Ч242
Voltage references, problem set for 237Ч242
Voltage, of diodes 223Ч224
Volterra series 295
Walkie-talkies (toy), development of 580Ч583
Walkie-talkies (toy), receive mode of 581Ч582
Walkie-talkies (toy), superregenerator use in 20 581
Walkie-talkies (toy), transmit mode of 581Ч582
Watson, Thomas, Jr. 580
Wave equation (Maxwell) 115
Weaver architecture 557 558
Webster, Roger 578
Well resistors 35
Westinghouse 16
Wheeler's formula 56
Wheeler, Harold 16 205 578
White noise 523 540
Whittier, John Greenleaf 5
Widlar, Bob 227
Wilson, Robert 247Ч248
Wing electrode 11 25
Wire loop, inductance of 56
Wireless communication, Marconi's invention of 4
Wireless World 9
Wollaston wire 8 11
Wood's metal, in detectors 5
Worcester Polytechnic Institute 387
World War I 7 14 15 21 579
World War II 337
X-ray tubes 24
X-rays, discovery of 10
XOR phase detector 455 478
XOR phase detector, use in design example 475Ч476
Year, seconds in 253
Yuan formula and method 41Ч42 43
Z-plane maps 135
Zener diode 227
Zero damping, of feedback systems 414
Zero-order hold (ZOH), transfer function of 515Ч516
Zero-peaked amplifier 219Ч220
Zero-power receivers 113
Zeros as bandwidth enhancers 178 179Ч191
Zeros in root-locus techniques 415 416Ч417 419Ч423 429 431
Zigzag wire electrode, in triode 11
Zincite crystal diodes 20
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



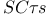 ) method for bandwidth estimation
) method for bandwidth estimation 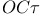 calculation
calculation 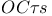 for
for