|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Fersht A. Ч Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Proton transfer rates 162 163
Pseudorotation 260
Pulsed quenched flow 136 567Ч569
Pyridoxal phosphate chemistry 62 79Ч82
Pyridoxal phosphate chemistry, stereoelectronic control 267
Pyridoxal phosphate chemistry, suicide inhibition 284 285
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex 37
Pyruvate kinase 267 294
Quaternary structure 9 24
Quenched flow 136 567Ч569
R state 292 293
Radioactive procedures 196Ч198
Ramachandran diagram 1Ч4 18 19 524 526
Raman scattering 192
Random mechanism 120
Rapid equilibrium mechanism 120
Rapid mixing techniques 133Ч136
Rapid quenching techniques 135Ч136
Ras protein 45 315 316
Rate limiting step of metabolic pathway 308
Rayleigh scattering 192
Re 247
Recombinant DNA technology 401Ч419
Reductive methylation 274
Regulation of enzymes and metabolic pathways 308Ч315
Relaxation methods 137 138
Relaxation methods, kinetics 139Ч155
Relaxation time 138
Renin 486
Rennin see УChymosinФ
Repertoire selection 415Ч418
Reporter group 276
Resonance Raman spectra 476
Restriction endonucleases 406Ч408
Restriction fragment 408
Retention of stereochemical configuration 253 254
Reverse genetic s 438Ч442
Reverse transcriptase 38
Rhizopus-pepsin 486 490
Ribonucease T1 492 495 528 529
Ribonuclease A 9
Ribonuclease A, stereochemistry of reaction 262
Ribonucleases 490Ч496
Ribozyme 26
RNA polymerase, Уtwo-metal-ionФ mechanism 393
Rotational correlation time 46
RS notation 246 247
S notation 246 247
S-Adenosyl methionine 90 91
Salt bridges 304 335 337Ч339 344 530Ч532
Saturation kinetics 104
Scatchard plot 208 303
Schiff bases 77Ч82
Second-order transition 521
Secondary structure 9 13 14 20Ч23
Secondary structure, 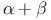 23 24 23 24
Secondary structure,  23 24 23 24
Secondary structure, all  23 23
Selectivity 397
Sequence identity 33 34
Sequential mechanism 119
Sequestration of reactive intermediates 432
Serine dehydratase 284
Serine proteases 7 26Ч30 40Ч43 473Ч482
Serine proteases, Protein engineering of specificity 452Ч454 481 482
SH3 domain of  -spectrin 552 586 594 -spectrin 552 586 594
Shear motion 48
Shikimate pathway 36 37
Si 247
Sigmoid binding curves 289
Single-turnover kinetics 139 146 147 219Ч222 242
Site-directed mutagenesis see УMutagenesis and protein engineeringФ
Slater Ч Kirkwood equation 328
Small angle x-ray scattering 520 521
Sofa conformation 358 496 500
Sofa conformation, structure 359
Solvation energies 336 337
Solvation energies, ions 74 344 426
Specific acid or base catalysis 61
Specific heat 510 511 513 545Ч547
Specific heat, activation 546 548 578 579
Specific heat, transition state 578 579
Specificity 372 377Ч400
Specificity constant (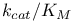 ) 104 105 116 ) 104 105 116
Specificity constant (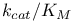 ), binding energy and 350Ч355 ), binding energy and 350Ч355
Specificity constant (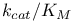 ), Briggs Ч Haldane kinetics and 166 167 384 ), Briggs Ч Haldane kinetics and 166 167 384
Specificity constant (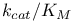 ), diffusion control and 106 368 ), diffusion control and 106 368
Specificity constant (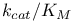 ), evolution of 362Ч364 368 ), evolution of 362Ч364 368
Specificity constant (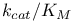 ), limits from Haldane equation 368 ), limits from Haldane equation 368
Specificity constant (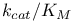 ), meaning of 110 ), meaning of 110
Specificity constant (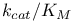 ), pH dependence of 169 174Ч176 ), pH dependence of 169 174Ч176
Specificity in protein-protein interactions 347
Specificity, competing substrates 117 377
Specificity, editing mechanisms see УEditing mechanismsФ
Specificity, induced fit 372 381
Specificity, intermediates 117 381 385
Specificity, nonproductive binding 116Ч117 372
Specificity, strain 372 377 379 384
Specificity, versus binding 339 340
Spectrofluorimetry 192 193 195
Spectrofluorimetry, determination of ionization constants by 186
Spectrophotometry 191 192 195
Spectrophotometry, optimal absorbance for signal to noise 212Ч214
Spin glass theory 598
Spliceosomal protein U1A, folding kinetics 552
splicing 26
Src SH3 domain,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
Src SH3 domain, folding kinetics 552
Staphylococcal IgG binding protein GB1 domain 529
Staphylococcal nuclease 23 47
Statistics 209Ч214
Statistics, combining errors 211 212
Statistics, standard deviation 210
Statistics, standard error 210
Steady state 103
Steady state approximation 106
Steady state kinetics 103Ч125 173Ч179 199Ч200 216 223Ч231
Steady state kinetics, induced fit, nonproductive binding, strain and 114Ч118 372 373
Stereochemistry 245Ч272
Stereoelectronic control 266 267 270 271
| Stereospecificity 247Ч250
Stopped-flow methods 134 135 243 520 541
strain 369Ч374 (see also УTransition state stabilizationФ)
Strain, electrostatic effects on protein stability 74
Strain, equilibria on enzyme surface and 118
Strain, specificity and 372 380
Strain, versus stress 372Ч374
Streptococcal proteinase 482
Stress 372Ч374
Structure of proteins-prediction 536Ч537
Structure-activity relationships 58 59 85Ч92
Structure-activity relationships, inductive effects on substrate 86
Structure-activity relationships, structural changes of enzyme 362 420Ч454
Structure-activity relationships, structural changes of substrate 356Ч358
Substrate channeling 38
Substrate concentrations in vivo 362Ч368
Subtilisin 27 28 30 450Ч454 476
Subtilisin, prosequence 540
Subtilisin, protein engineering specificity of 452Ч454
Subtilisin, protein engineering surface charge and 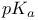 of 180 327 of 180 327
Subtiloloigase 453 454
Subunits 24 289Ч297
Subunits, construction of hetero-oligomers by protein engineering 446Ч449
Succinates 66 67
Suicide inhibitors 280Ч286
Superoxide dismutase 166
Supersecondary structure 9 20
Surface charge of protein 179Ч180 327
Surface plasmon resonance see УLabel-free optical detectionФ
T state 292 293
T4 lysozyme 33 497
T4 lysozyme, helix stability of 528 529
T4 lysozyme, hydrophobic core stability of 533 544
Tanford  value 544 555 578 582 value 544 555 578 582
Temperature jump 137 138 541
Temperature jump, protein folding 593
Terminal transferase 408 410
Ternary complex 120
Tertiary structure 22
Theorell Ч Chance mechanism 120
Thermodynamic cycles 125Ч131
Thermodynamic cycles, acid denaturation 516 517
Thermodynamic cycles, double mutant cycles 129Ч131 594
Thermodynamic cycles, mutant cycles 129
Thermodynamic cycles, specificity 381 383
Thermodynamic cycles, УalchemicalФ steps 129
Thermolysin 22 30 483Ч486
Thiamine pyrophosphate 62 83Ч84
Thiol proteases 473 482
Thionesters 478
TNfn3 domain,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
TNfn3 domain, folding kinetics 552
Torsion angle 16Ч18
Tos-L-phenylalanine chloromethyl ketone (TPCK) 278 475
Trans aldolase 79
Transit time 123Ч125
Transition state 47Ч49
Transition state analogues 49 317 356 358Ч361 474 495
Transition state in protein folding 556Ч558 573Ч575 578Ч583
Transition state stabilization 353 369 439
Transition state theory 54Ч61 86
Transition state theory, analysis of enzyme catalysis 349Ч355
Transition state theory, analysis of protein folding 545 558
Transition state theory, application to chemical catalysis 57Ч61
Transition state theory, application to enzyme specificity 380Ч383
Transition state, definition 55
Transition state, ensemble 600
Transketolase 83
Transmission coefficient 56 558
Triosephosphate isomerase 23 30 31 39 41 108 167
Tritium tracer experiments 47 257Ч259
Trojan horse inhibitors see УSuicide inhibitorsФ
Trypsin 26Ч30 42 43 474 476 480 482
Trypsin inhibitor (basic pancreatic) 286 575
Trypsin, specificity 28
Trypsinogen 480 481
Tryptophan synthase 35
Tunneling 97 98
Turnover number see УCatalytic constantФ
TWIg18 domain, folding kinetics 552
Two-state transitions 517 518
Two-state transitions, apparent 518 547
Two-state transitions, kinetics 543Ч553
Tyransducin- 315Ч317 315Ч317
Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase 51 118 242 296 297 420Ч450
Ubiquitin, folding kinetics 552
Ultracentrifugation 204 205
Unfolding of proteins see УDenaturationФ
Uniform binding energy change 351 352
Uniform binding energy change, protein engineering and 438 439
Uracil glycosidase 394
V system 294
Valyl-tRNA synthetase 239Ч242 379 386 389
Van der Waals contact distance 328
Van der Waals energies 329 331
Van der Waals forces 327Ч329
Van der Waals radii 328Ч329
Vanadate 495
VanТt Hoff enthalpy 512 513 517
VanТt Hoff equation 513
Vector 411 412
Walker consensus sequence 316 320
Warwicker Ч Watson algorithm 326
Watson Ч Crick base pairing 401Ч403
X-ray diffraction methods 4Ч7
X-ray diffraction methods, difference Fourier 39
X-ray diffraction methods, isomorphous replacement 4 5
X-ray diffraction methods, molecular replacement 6 39
X-ray diffraction methods, resolution 6
X-ray diffraction methods, static disorder and real motion 49 50
X-ray diffraction methods, time resolved 39
X-ray diffraction methods, von Laue method 39
Zero-point energy 96
Zinc proteases 482Ч486
УEffective concentrationФ 65Ч72
УEffective concentrationФ in general-acid-base catalysis 66
УEffective concentrationФ in nucleophilic catalysis 66
УEffective concentrationФ, entropy and 68Ч72
УOrbital steeringФ 72 73
УRidges-into-groovesФ 22
УRolloverФ 550
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте





 )
)  -value analysis
-value analysis 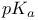 of
of  value
value