|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Fersht A. Ч Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 helix 13 18 helix 13 18
 see УLabel-free optical detectionФ see УLabel-free optical detectionФ
 326 327 326 327
 -atpase 318Ч321 -atpase 318Ч321
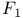 -ATPase 318Ч321 -ATPase 318Ч321
 see УCatalytic constantФ see УCatalytic constantФ
 inhibitors see УSuicide inhibitorsФ inhibitors see УSuicide inhibitorsФ
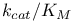 see УSpecificity constantФ see УSpecificity constantФ
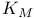 see УMichaelis constantФ see УMichaelis constantФ
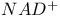 , , 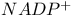 249 250 458Ч472 249 250 458Ч472
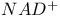 , , 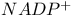 , ,  466 466
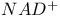 , , 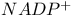 , , 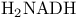 394 394
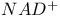 , , 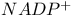 , binding energy and , binding energy and 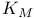 365 365
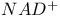 , , 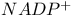 , fluorescence 458 , fluorescence 458
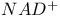 , , 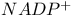 , kinetic isotope effects and hydride transfer 97 98 463Ч465 , kinetic isotope effects and hydride transfer 97 98 463Ч465
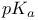 see УIonization constantsФ see УIonization constantsФ
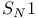 , , 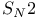 reactions 235 254 255 498 reactions 235 254 255 498
 helix 10Ч13 18 22Ч24 helix 10Ч13 18 22Ч24
 helix, amphipathic 13 helix, amphipathic 13
 helix, caps 12 525Ч527 helix, caps 12 525Ч527
 helix, circular dichroism 195 helix, circular dichroism 195
 helix, dipole 13 helix, dipole 13
 helix, kinetics of formation 541 569 570 helix, kinetics of formation 541 569 570
 helix, stability see УProtein stabilityФ helix, stability see УProtein stabilityФ
 -effect 89 -effect 89
 -Lytic protease 357 -Lytic protease 357
 -Spectrin SH3 domain, -Spectrin SH3 domain,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
 -Spectrin SH3 domain, folding kinetics 552 586 -Spectrin SH3 domain, folding kinetics 552 586
 -value see УBronstedФ -value see УBronstedФ
 Bend 13 16 Bend 13 16
 Hairpin 20 Hairpin 20
 Hairpin, kinetics of formation 541 570 Hairpin, kinetics of formation 541 570
 sheet 10 13 15 19 sheet 10 13 15 19
 value see УBronsted TanfordФ value see УBronsted TanfordФ
 -Aspartate decarboxylase 81 285 -Aspartate decarboxylase 81 285
 -Galactosidase 233Ч235 243 255 -Galactosidase 233Ч235 243 255
 -Hydroxy-decanoyl dehydrase 283 -Hydroxy-decanoyl dehydrase 283
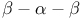 Hairpin 22 Hairpin 22
 -repressor folding kinetics 551 -repressor folding kinetics 551
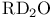 , solvent effects on kinetics 99 , solvent effects on kinetics 99
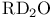 , solvent effects on pKa 185 , solvent effects on pKa 185
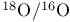 tracer experiments 262Ч266 488Ч490 tracer experiments 262Ч266 488Ч490
 -value analysis 558Ч563 574 590 593 -value analysis 558Ч563 574 590 593
 -value analysis, compared with Bronsted -value analysis, compared with Bronsted  562 562
 -value analysis, fractional values 579Ч582 -value analysis, fractional values 579Ч582
 -value analysis, implicating intermediate on pathway 556 -value analysis, implicating intermediate on pathway 556
 -value analysis, introduction 558Ч563 -value analysis, introduction 558Ч563
 -value analysis, molecular dynamics simulation 583 591 -value analysis, molecular dynamics simulation 583 591
 -value analysis, nucleation-condensation mechanism 583 -value analysis, nucleation-condensation mechanism 583
 -value analysis, versus quenched-flow hydrogen exchange 568 569 -value analysis, versus quenched-flow hydrogen exchange 568 569
 see УHydrophobicity constantФ see УHydrophobicity constantФ
 Helix 18 Helix 18
 domain, domain,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
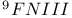 domain, folding kinetics 552 domain, folding kinetics 552
(-)Deprenyl 286
1,2-Anhydro-D-mannitolphosphate 279
2,5-Anhydro-D-glucitolphosphate 254
2,5-Anhydro-D-mannitolphosphate 254
Absolute configuration 246
Abzyme see УCatalytic antibodyФ
Acetoacetate decarboxylase 78 189 298
Acetyl coenzyme A: arylamine acetyl-transferase 121
Acetylcholinesterase 84 108 166
Acid phosphatase 233 374
Acid proteases see УCarboxyl proteasesФ УPepsinФ
Acid-base catalysis see УGeneral-acid-base catalysisФ
Actinidin 482
Activation energy 56 58 546 547
Activation energy, interconversion of activation and binding energies 350Ч355
Active-site directed irreversible inhibitors see УAffinity labelsФ
Active-site titration 155Ч158 423
Acylbinding proteins,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
Acylbinding proteins, folding kinetics 551
Acylphosphatase (muscle), folding kinetics 552
Adair equation 290 291
Adjacent mechanism 260 263 267
Affinity labels 277Ч280 474
AGADIR 529 530 532
Alanine racemase 285
Alcohol dehydrogenase 23 32 40 61 86 97 460Ч465
Alcohol dehydrogenase, protein engineering of specificity 465
Alcohol dehydrogenase, stereospecificity 250
Aldolase 79 296 366
Aldose-ketose isomerases 251 252
Alkaline phosphatase 225 231Ч233
Allosteric interactions 289Ч315 604Ч606
Allosteric interactions, activators and inhibitors 290 293 300 310Ч315
Allosteric interactions, feedback 290 309
Amino acids 2 3
Amino acids, absolute configuration 247
Amino acids, chemical reactivity of side chains 273Ч277
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases 92 235Ч242
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, determination of binding energies by 341 342
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, editing mechanism 239Ч242
Amyloidosis 1 575
Angiotensin converting enzyme 483
Anilinyl-naphthalene sulfonic acid (ANS) 520
Annealing mechanism 607
Anti-cooperativity see УNegative cooperativityФ
Anti-Hammond effect 591
Antimutator strain of T4 phage 390 391
Apical position 260
Apoenzyme 458
Apparent 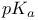 173 175 177 178 180 183 173 175 177 178 180 183
Apparent binding energies 428
Apparent binding energies, relationship with incremental binding energies 435
Apparent equilibrium constants 109 110
Arc repressor (dimer),  -value analysis 595 -value analysis 595
Arc repressor (single chain),  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
Arc repressor (single chain), folding kinetics 552
Arom complex 36 37
Arrhenius equation 544Ч555
Arrhenius equation, breakdown 555
Aspartate aminotransferase 284 285
Aspartate transcarbamoylase 298 360
Aspartyl proteases see УCarboxyl proteasesФ
Aspirin 66 67
Association rate constants, collision theory 54 158 159
Association rate constants, electrostatic enhancement 159Ч161
Association rate constants, examples 153 164Ч166
Association rate constants, kinetic analysis 143 144 152 153
Associative mechanism 259
Asymmetry 245
ATP synthase 318Ч321
Automatic titration 196
Bacteriophage, 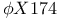 391 391
Bacteriophage, fd 414 416
Bacteriophage, M13 414 416
Bacteriophage, phage display 416Ч418
Bacteriophage, phagemid 416
Barnase,  Barrel 30Ч32 Barrel 30Ч32
Barnase, association kinetics with barstar 159Ч161
Barnase, crystal structure 588
Barnase, electrostatic interactions in 326
Barnase, folding kinetics 544 550 589
Barnase, folding pathway 588Ч592
Barnase, fragments 589 595
Barnase, GroEL binding 604Ч606
Barnase, helix stability 524Ч529
Barnase, helix structure 12
Barnase, hydrogen exchange 566
Barnase, hydrophobic core stability 533 544
Barnase, kinetics of folding 550 551
Barnase, mechanism 492Ч496
Barnase, solution structure 8
Barnase, solvent denaturation 515 516
Barnase, structure 588
Barnase, subsites and binding energies 495 496
Barnase, thermal denaturation 512
Barstar, association kinetics with barnase 159Ч161
| Barstar, mechanism of folding 591Ч593
BeerТs law 191 192
Bequerel 196
Binding energy versus specificity 339
Bohr effect 305
Borohydride reduction 78 274 276
Bovine seminal ribonuclease 33
Bradford assay 214
Breathing motion 47
Briggs Ч Haldane kinetics 106Ч108 166 167 183
Briggs Ч Haldane kinetics, evolutionary aspects 368
Briggs Ч Haldane kinetics, pH dependence 178 179
Briggs Ч Haldane kinetics, specificity and 166 167 384
Bromelain 482
Bronsted  and and  58 58
Bronsted  and and  , compared with , compared with  562 562
Bronsted  and and  , general-acid-base catalysis and 62Ч65 , general-acid-base catalysis and 62Ч65
Bronsted  and and  , interpretation of 58 87 88 , interpretation of 58 87 88
Bronsted  and and  , kinetic equivalence and 95 , kinetic equivalence and 95
Bronsted  and and  , nucleophilic catalysis and 86Ч89 , nucleophilic catalysis and 86Ч89
Bronsted  and and  , protein engineering of binding energy changes and 442Ч444 , protein engineering of binding energy changes and 442Ч444
Bronsted equation 58
Bronsted equation in protein folding 579Ч582 590
Burst kinetics 155Ч158 218
Caged ATP or GTP 137
Calorimetry see УDifferential scanning calorimetry isothermal
Capillarity 598
Carbonic anhydrase 10 108 163 166
Carbonic anhydrase, chemical models 76 77
Carbonic anhydrase, substrate concentrations in vivo 365
Carboxyl proteases 486Ч491
Carboxypeptidases 23 30 75 482Ч486
Carboxypeptidases, chemical modification 420
Catalase 108 162Ч164 166
Catalysis, binding energy factors 349Ч375
Catalysis, catalytic power of enzymes 59 60
Catalysis, chemical 54Ч102
Catalysis, classical factors in enzyme catalysis 100 101
Catalytic antibody 60 361
Catalytic constant ( ) 105Ч109 ) 105Ч109
Catalytic constant ( ), meaning of 108 109 ), meaning of 108 109
Catalytic constant ( ), pH dependence of 169 174 175 180 ), pH dependence of 169 174 175 180
Cathepsin D 486
CD2 domain 1
CD2 domain,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
CD2 domain, folding kinetics 552
Central complex 120
Cerenkov radiation 197
Chair conformation 359
Chaperonins 604
Chelate effect 345 346
Chemical modification of proteins 273Ч288
Chemical modification of proteins, pH dependence 187 278 279 468 487
Chemiosmotic hypothesis 318 319
Chevron plot 543
CheY protein 596
CheY protein,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
Chiral methyl group 256Ч259
Chiral phosphate group 259Ч266
Chirality 245
Chirality, rules for RS designation 246 247
Chymosin 473 486
Chymostatin 479
Chymotrypsin 4 26Ч30 60 100 218Ч231 472Ч482
Chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2), folding kinetics 544Ч577 577
Chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2), fragments 577 578 587 588 595
Chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2), GroEL binding 605
Chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2), mechanism of folding 576Ч588
Chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2), structure 576 577
Chymotrypsin, 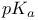 of active site 182Ч184 of active site 182Ч184
Chymotrypsin, active-site titration 157
Chymotrypsin, activity in crystal 45
Chymotrypsin, acylenzyme 37Ч40 107 218Ч231
Chymotrypsin, affinity labeling 278 279
Chymotrypsin, association rate constants with substrates 165
Chymotrypsin, binding energies of subsites 342 343 356Ч358
Chymotrypsin, catalytic factors 100
Chymotrypsin, catalytic triad 474 475
Chymotrypsin, enzyme-substrate complex 40Ч44
Chymotrypsin, estimation of binding energies 341
Chymotrypsin, hydrophobicity of active site 342
Chymotrypsin, indolylacryloyl-chymotrypsin 40 45
Chymotrypsin, intermediates 218Ч231
Chymotrypsin, kinetic constants for substrate hydrolysis 224 228 357 358 477
Chymotrypsin, kinetic equations for 107 110 116 226 227
Chymotrypsin, pH dependence of catalysis 182Ч184
Chymotrypsin, pre-steady state kinetics 146 148 149
Chymotrypsin, primary structure 5
Chymotrypsin, product partitioning 225Ч229
Chymotrypsin, reaction mechanism 41 100
Chymotrypsin, redesigning specificity by protein engineering 481 482
Chymotrypsin, rotational correlation time 46
Chymotrypsin, secondary structure 23
Chymotrypsin, specificity 27 40 481
Chymotrypsin, steady state kinetics 107 108 223Ч230
Chymotrypsin, stereochemical specificity 248
Chymotrypsin, stereoelectronic effects on mechanism 270
Chymotrypsin, tertiary structure 27 29
Chymotrypsin, tetrahedral intermediate 13 40 86
Chymotrypsin, zymogen 480
Chymotrypsin, Уcharge-relay systemФ 475
Chymotrypsinogen 480 481
Circular dichroism (CD) 193Ч195
Circular dichroism (CD), optimal absorbance for signal to noise 212Ч214
Circularly permuted proteins 586 587
Cloning genes 410Ч415
Clostripain 482
Cold-shock  -barrel proteins, folding kinetics 551 -barrel proteins, folding kinetics 551
Collision theory of kinetics 54 158 159
Competing substrates 116 117
Complementarity 332 334 354
Complementarity in enzyme-substrate interactions 356Ч362
Complementarity, analysis by transition state theory 354Ч356
Complementarity, base pairing in DNA 401Ч403
Complementarity, base pairing in RNA 345
Complementarity, basis of molecular recognition 332
Complementarity, lock-and-key 354
Complementation assay 412
Computer fitting of data 209
Configuration 246 249
Conformation 249
Conformational change 44
Conformational change, detection 242
Conformational mobility of proteins 44Ч51
Contact order 602
Continuous-flow method 133 134 541
Control analysis 308
Control enzymes 290
Control enzymes, allosteric interactions 293Ч296
Convergent evolution 29 30
Coomassie blue 214
Cooperativity, ligand binding 289Ч307
Cooperativity, nested 296
Coordinate expression 35 38
Coordinate regulation 3 8
Cost-selectivity equation 395Ч399
Coupled assays 196
Covalent catalysis 62 77Ч85
Creatine kinase 264 266
Crotonase 108 166
Cryoenzymology 40
Crystalline enzymes, activity 45
Crystalline enzymes, water content 39
Curie 196
Cyclophilin see УPeptidyl-prolyl isomeraseФ
Cysteine proteases 482
Cytidine deaminase 359
Cytidine triphosphate synthetase 298
Cytochrome c, folding kinetics 551
Debye Ч Hueckel theory 159
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



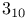 helix
helix 
 -atpase
-atpase 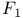 -ATPase
-ATPase 
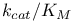
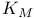
 ,
, 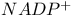

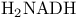
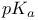
 ,
, 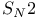 reactions
reactions  helix
helix  -value analysis
-value analysis  Bend
Bend 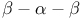 Hairpin
Hairpin  -repressor folding kinetics
-repressor folding kinetics 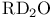 , solvent effects on kinetics
, solvent effects on kinetics 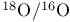 tracer experiments
tracer experiments 
 domain,
domain, 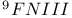 domain, folding kinetics
domain, folding kinetics 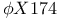
 Barrel
Barrel