|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Fersht A. Ч Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Dehydrogenases 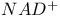 linked 32 458Ч472 linked 32 458Ч472
Dehydrogenases 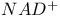 linked, A and B 250 linked, A and B 250
Dehydrogenases 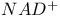 linked, domains 32 linked, domains 32
Dehydrogenases 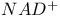 linked, evolution 32 linked, evolution 32
Dehydrogenases 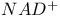 linked, rate determining product release 167 linked, rate determining product release 167
Dehydrogenases 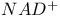 linked, stereospecificity 249 250 linked, stereospecificity 249 250
Denaturation of proteins 508Ч537
Denaturation of proteins, acid denaturation 516
Denaturation of proteins, cold unfolding 511
Denaturation of proteins, denaturants 509
Denaturation of proteins, solvent denaturation 513Ч517 522
Denaturation of proteins, specific heat 510Ч513
Denaturation of proteins, thermodynamics 509Ч513
Denatured state, molecular dynamics simulation 589
Denatured state, structure 518Ч521 578 589
Deoxynucleoside monophosphates 402
Deoxythymidine kinase 294
Detailed balance see УMicroscopic reversibilityФ
Deuterium tracer experiments 250 256Ч258
Diagonal plot 33
dielectric constant 6 73 74 160 325 326
Difference energy diagrams 427 428 431
Differential binding energy change 351 352
Differential binding energy change, protein engineering and 438 439
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 207 512 513
Diffusion-collision model 575 576
Diffusion-controlled reactions 158Ч166
Diffusion-controlled reactions, effects of viscosity on 161
Diffusion-controlled reactions, limited by equilibria 368
Dihedral angle 16Ч18
Dimethylsuberimidate 276
Discrimination among substrates 377
Dispersion forces see УVan der WaalsФ
Dissociation constants of acids and bases see УIonization constantsФ
Dissociation rate constants of protein-ligand complexes, determination 202Ч207
Dissociation rate constants of protein-ligand complexes, kinetic analysis 158 164 167
Dissociative mechanism 259
Distortion of enzyme or substrate 372Ч374
Distributive polymerization 410
Disulfide bridges 4 603
Disulfide bridges as probes in protein folding 574 575
Disulfide bridges, configurational entropy of loops 535
Disulfide bridges, effects on stability 534 535
Divergent evolution 26Ч28
DNA ligase 393 405Ч407
DNA ligase, blunt end ligation 407
DNA polymerases 37Ч38 124 404 405 408 409
DNA polymerases, editing mechanism 389Ч393 405
DNA polymerases, molecular mechanism of editing 392Ч394
DNA polymerases, mutator and antimutator mutants 391
DNA polymerases, Уtwo-metal-ionФ mechanism 392Ч394
DNA, cDNA 411
DNA, cloning 410Ч413
DNA, hybridization 413
DNA, mutagenesis 410 413Ч416
DNA, properties 401Ч404
DNA, repair 393Ч395
DNA, replication 404 405
DNA, restriction 406 407
DNA, RF 414
DNA, structure 401Ч404
DNA, Watson Ч Crick base pairing rules 401Ч404
Domain swapping 33
Domain theory of enzyme evolution 32 33
domains 20 32 33
Domains, analysis by protein engineering 445Ч449
Domains, folding 595
Double mutant cycles see УThermodynamic cyclesФ
Double-displacement mechanism 236 254 256 267
Double-sieve editing mechanisms 387Ч389 398 399
Eadie Ч Hofstee plot 112 114
Editing mechanisms 384Ч399
Editing mechanisms, cost of editing 395Ч399
Editing mechanisms, editing in DNA replication 389Ч395
Editing mechanisms, editing in protein synthesis 385Ч389
Ef-Tu 315 316
Elastase 26Ч30 40
Elastase, acylenzyme 27 40
Elastase, binding energies of subsites 356 357
Elastase, binding site 26Ч30
Elastase, kinetic constants for peptide hydrolysis 357
Elastase, specificity 27
Electrophiles 276
Electrophilic catalysis 61
Electrophilic catalysis, metal ions 74Ч77
Electrophilic catalysis, pyridoxal phosphate 79Ч82
Electrophilic catalysis, Schiff bases 77Ч82
Electrophilic catalysis, thiamine pyrophosphate 82Ч84
Electrostatic catalysis 61 73 74 498
Electrostatic effects on enzyme-substrate association rates 159Ч161
electrostatic forces 179Ч181 325Ч327
Electrostatic strain and stability 74
Enamines 76 77
Enantiomer 245
Encounter complex 159
Encounter frequency 164 166
Enediols 251 252
Energy landscapes 575 598
Energy landscapes, rough 598
Energy landscapes, smooth 598
Energy landscapes, versus pathways 600 601
Energy of activation 56 58 546 547
Ensembles 600
Enterokinase 480
Enthalpy 55
Enthalpy versus entropy in protein folding 509Ч512 587 599
Enthalpy, activation 56 545Ч547
Enthalpy, protein folding 509Ч512
Enthalpy, specific heat effects 511 545Ч547
Enthalpy-entropy compensation 346
entropy 55 68Ч72
Entropy, activation 56 545Ч547
Entropy, binding 324 345
Entropy, Boltzmann equation 510
Entropy, chelate effect 345
Entropy, configurational 510
Entropy, configurational entropy of loops 535
Entropy, effective concentration 68Ч72
Entropy, equilibria on enzyme surface 118
Entropy, hydrogen bond 338
Entropy, hydrophobic bond 332 510
Entropy, importance in enzyme catalysis 72
Entropy, importance in enzyme-substrate binding 72
Entropy, importance in protein folding 510
Entropy, specific heat effects 511 545Ч547
Entropy, transition state analogues 360
Entropy-enthalpy compensation 346
Enzyme-activated irreversible inhibitors see УSuicide inhibitorsФ
Enzyme-substrate complexes 38Ч44
Enzyme-substrate complexes, association rate constants 143 144 152Ч154
Enzyme-substrate complexes, binding energies 324Ч347
Enzyme-substrate complexes, dissociation constants, determination of 202Ч207
Enzyme-substrate complexes, dissociation rate constants 153 162 167
Enzyme-substrate complexes, methods for study by x-ray diffraction 39Ч40
Epoxides 274 276 280
EPR 46
Equatorial 260
Equilibria on enzyme surface see УInternal equilibriaФ
Equilibrium constants, apparent 109 110
Equilibrium constants, linked 127Ч129
Equilibrium constants, macroscopic 127Ч129 179
Equilibrium constants, microscopic 127Ч129 179
Equilibrium dialysis 202 203
Equilibrium gel filtration 203 204
Ergodic principle 589
Errors of observation see УStatisticsФ
Ester hydrolysis 57 59 62Ч64 86Ч90
Evolution of enzymes 25Ч34
Evolution of enzymes, fine tuning 439Ч442
Evolution of enzymes, probing by reverse genetics and protein engineering 438Ч442
| Evolution of maximum rate 362Ч364 440Ч442
Exon 25 26 32 33
Extein 25 26
Extinction coefficient 191 192 194
Extrathermodynamic relationships 600
Eyring equation 545
Ficin 482
Filter assays 198 205
First-order transition 521
Fischer projection formula 247
FKBP12,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
FKBP12, folding kinetics 552
Flash photolysis 136Ч137
Flavoproteins 285 286
flexibility 44Ч51
Fluorescence 46 47 192 193
Fluorescence, anisotropy 46
Fluorescence, labels 276
Fluorescence, polarization 46
Fluorescence, quenching 193
Folding funnel 598Ч600
Folding of proteins see УDenaturationФ
Folding of proteins, folding kinetics 541Ч570
Folding pathways 573Ч602
Folding pathways, optimization of rates 600
Folding pathways, pathways versus landscapes 600 601
Folding pathways, proteins with two-state kinetics 551Ч553
Folding problem 508
Foldon 577 593 596
Force fields 331
Framework model 575 576 583
Fructose 6-phosphate 252 254 309Ч311
Frustration 598
Fumarase 250 252 257
Furin 453
Furolisin 453
Furylacryloyl group 220 221
Fyn SH3 domain, folding kinetics 552
G proteins 315Ч317
Gaussian distribution 210
Gel filtration 203 204
Gene fusion 32 33 37
Gene library (bank) 412 417
General-acid-base catalysis 61Ч66 72 76
General-acid-base catalysis, examples with enzymes 85 310 311 466 472 484 488 490 493 494 497 498
General-acid-base catalysis, kinetically equivalent mechanisms 94Ч96
General-acid-base catalysis, principle of microscopic reversibility and 93 94
genetic engineering 401
Genome sequences 25
Gibbs free energy 55
Glucose 6-phosphate 279
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase 459
Glucose 6-phosphate isomerase 279
Glucosidases see УLysozymeФ
Glutamate dehydrogenase 167
Glutamine synthetase 298
Glyceraldehyde 3Чphosphate dehydrogenase 23 32 45 167 281 296 297 303 469Ч472
Glycerol, viscogenic effects 160
Glycerophosphate dehydrogenase 367
Glycogen phosphorylase see УPhosphorylaseФ
Glycogenolysis 312Ч314
Glycolysis 309 310
Glycolysis, substrate concentrations in 365Ч367
Glycosidases 233Ч235 243
Golf course analogy of folding 598
Greek key 20 21
GroEL 296 604Ч610
Group 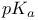 179 179
Guggenheim method 200
Haldane equation 117 118 229
Half-chair conformation 359
Half-life (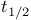 ) 140 ) 140
Half-of-the-sites activity 297 298 382 468 471
Half-of-the-sites activity, analysis by protein engineering 448 449
Hammond effect 57Ч58 375 442 582 591 599
Hammond effect, internal equilibria and 375 472
Hammond effect, protein folding 582
Hansch equation 335
Hard and soft centers 88Ч91 276 277
heat capacity see УSpecific heatФ
Heat shock proteins 603
Heme-chemical models 307
Hemoglobin 289 304Ч307
Hemoglobin, allosteric interactions 289Ч292 302
Henderson Ч Hasselbalch equation 170
Heterotropic 290
Hexokinase 23 51 364
Hill constant 299 300Ч302 304
Hill equation 297Ч300
Hinge motions 48
HIV protease 486
Holoenzyme 458
Homology 8 9
Homology modeling 537
Homotropic 290
Hpr (histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein), folding kinetics 552
Hydride transfer 97 98 249 250 256 257 276 458Ч472
Hydrogen bond 11 13 22 24 329Ч331
Hydrogen bond, inventory 337Ч339
Hydrogen bond, low barrier 330 331 475
Hydrogen bond, specificity and 340 345 347
Hydrogen exchange kinetics 7 48 518 563Ч569
Hydrogen exchange kinetics, effects of mutation 566
Hydrogen exchange kinetics, EX1 limit 565
Hydrogen exchange kinetics, EX2 limit 565
Hydrogen exchange kinetics, intrinsic rate constant 565
Hydrogen exchange kinetics, protection factor 564 565
Hydrogen exchange kinetics, quenched flow 567Ч569
Hydrophobic bond (УeffectФ) 22 332Ч336
Hydrophobic bond (УeffectФ), dispersion energies 343 344
Hydrophobic bond (УeffectФ), hydrophobic core 532Ч534
Hydrophobic bond (УeffectФ), specific heat 510 546
Hydrophobic bond (УeffectФ), surface area dependence 334 335 524 525
Hydrophobic bond (УeffectФ), surface tension and 334
Hydrophobic collapse 575 576 596
Hydrophobic core 24 532Ч534
Hydrophobic zipper model 596
Hydrophobicity constant (77) 335 336
Hydroxyethylthiamine pyrophosphate 83Ч84
IgG binding domain of streptococcal protein L,  -value analysis 594 -value analysis 594
IgG binding domain of streptococcal protein L, folding kinetics 552
IgG binding domain of streptococcal protein L, radius of gyration of denatured state 520 521
In-line mechanism 259
Incremental binding energy 335 339Ч344 435
Induced fit 295 369Ч371 432
Induced fit, specificity 372 381
Infrared spectroscopy 475
Infrared spectroscopy, determination of ionization constants 186
Infrared spectroscopy, resonance Raman spectra and strain 476
Inhibition of enzyme activity 112Ч115
Inhibition of enzyme activity, competitive 113Ч115
Inhibition of enzyme activity, irreversible 112 273Ч283
Inhibition of enzyme activity, mixed 113 114
Inhibition of enzyme activity, noncompetitive 113Ч115
Inhibition of enzyme activity, slow, tight binding 286 287
Inhibition of enzyme activity, uncompetitive 115
Initial rate for pre-steady state kinetics 140 142 145
Initial rate in steady state kinetics 103 104 106
Intein 25 26
Intermediates, accumulation 374 375
Intermediates, definition 55
Intermediates, detection by kinetics 216Ч214 547 549Ч551 554Ч556
Intermediates, detection by stereochemical criteria 253Ч255
Intermediates, pre-steady state kinetics 132 144Ч149 154Ч157 543 547 549Ч551 554Ч556
Intermediates, proof of on pathway 217 218 553Ч556 566 567
Intermediates, steady state kinetics 107 108 116 117 121Ч123 543 547 549Ч551 554Ч556
Intermediates, undesirability of accumulation 375 600 602
Internal equilibria 118 375
Intramolecular catalysis 65Ч72
Intramolecular catalysis, effective concentrations in 65Ч72
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



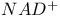 linked
linked  -value analysis
-value analysis 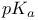
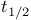 )
)