|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Sedgewick R. Ч Algorithms |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
2-node 188
2D (two-dimensional) trees 343 346
2Ч3 trees 198
2Ч3Ч4 tree 188
3-node 188
4-node 188
abacus 528
Abstract data structures 30 88 128 136
adapt (integration, adaptive quadrature) 85
add (polynomials represented with linked lists) 27
add (sparse polynomials) 28
Additive congruential generator (randomint) 38Ч40
Adjacency lists 378Ч381 382 383 391Ч392 410Ч411 435
Adjacency matrix 377Ч378 384 410Ч411 425 435 493 515
Adjacency structure see УAdjacency listsФ
adjlist (graph input, adjacency lists) 379
adjmatrix (graph input, adjacency matrix) 378
Adleman, L. 301 304
Aho, A.V. 304
Algorithm machines 457Ч469
All-nearest-neighbors 366
All-pairs shortest paths 492 494
Analysis of Algorithms 12Ч16 19
Approximation algorithms 522 524 533
Arbitrary numbers 33
Arithmetic 23Ч30
Arrays 24
Articulation points 390Ч392 430
Artificial (slack) variables 503 509
Attributes 335
Average case 12Ч13
AVL trees 198
B-trees 228Ч231 237
Backtracking 517Ч522
Backward substitution 60 64
Backward substitution (substitute) 62
Balanced multiway merging 156Ч161
Balanced trees 187Ч199 237 355
Basis variables 504
Batcher, K.E. 463Ч465
Bayer, R. 228
Bentley, J.L. 370
Biconnectivity 390Ч392 429
Binary search 175Ч177 336
Binary search (binarysearch) 176
binary search trees 169 178Ч185 204 210 336 343Ч346 353 356Ч359
Binary search trees, array representation 184Ч185
Binary search trees, indirect representation 184Ч185 353
Binary search trees, optimal 489Ч492
Binary search trees, standard representation 178Ч179
Binary search trees, weighted internal path length 490
Binary trees 179 237
Binomial queues 167
Bipartite graphs 444Ч447
Bitonic merge 463Ч465
bits 116 118 122 214 215 221 222
Bland's method (for cycle avoidance in simplex) 509
Bland, R.G. 507
Borodin, A. 88
Bottom-up parsing 275Ч276
Boyer Ч Moore string searching 250Ч251
Boyer, R.S. 242 304
Branch-and-bound 519Ч520
Breadth-first search 395 397Ч398 439
Brown, M.R. 167
brutesearch (brute-force string searching) 243
bstdelete (binary search tree deletion) 185 355
bstinsert (binary search tree insertion) 184 353 355
bstrange (one-dimensional range search) 337 355
Bubblesort 99
Caesar cipher 297
Catalan numbers 487
Chi-square (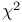 ) test (chisquare) 41Ч42 ) test (chisquare) 41Ч42
ciphers 297Ч300
Ciphers, Caesar 297
Ciphers, product 300
Ciphers, Vernam 299
Ciphers, Vigenere 298
Ciphertext 297
Clancy, M. 19
Closest-pair problem 362Ч366 368
Closest-point problems 361Ч368 370
Closure 258 261
Clustering 207
Comer, D. 237
Compare-exchange 93 460Ч465
Compilers 247 269 276Ч279 304
Complete binary tree 130
Complete graphs 376
complex numbers 473Ч478
Complex roots of unity 473Ч477
Computational accuracy 61 63 86 504
Concatenation 258 261
Connected components 375
Connected graph 375
Connectivity 389Ч405 454
Conquer-and-divide 152
Constant running time 14
Constraints 498
Context-free grammars 270Ч272
Contextrsensitive grammars 272
Convex hull 321
Convex hull algorithms 321Ч333 368 370
Convex hull algorithms, divide-and-conquer 368
Convex hull algorithms, Floyd-Eddy method 331Ч332
Convex hull algorithms, Graham scan 326Ч330 332
Convex hull algorithms, Graham scan (grahamscan) 329
Convex hull algorithms, hull selection 331Ч332
Convex hull algorithms, package wrapping 323Ч326 325
Convex hull algorithms, package wrapping (wrap) 332
convex polygons 321
Convexity 321
Conway, L.C. 536
Cook's theorem (satisfiability is NP-complete) 532Ч533
Cook, S.A. 242 532
Cooper, D. 19
Counting 455
Cross edges 423 430
Cryptanalysis 295Ч296
Cryptography 295Ч296
Cryptology 295Ч302 304
Cryptosystem 296
Cryptovariables 299
Cubic running time 15
Curve fitting 67Ч76
CYCLE 375 384
Cycling in the simplex method 506Ч507 509
Dags (directed acyclic graphs) 426Ч428
Data fitting 67Ч76
Data structures, abstract 30 128 136
Data structures, adjacency lists 378Ч381
Data structures, adjacency matrix 377Ч378
Data structures, adjacency structure 378Ч381
Data structures, array 24
Data structures, B-tree 228Ч231 237
Data structures, binary search tree 178Ч185
Data structures, deque 263Ч267
Data structures, heap 129Ч140
Data structures, indirect binary search tree 184Ч185
Data structures, indirect heap 138Ч139
Data structures, linked list 27Ч28 202Ч203 379
Data structures, priority queue 127Ч140
Data structures, queue 264 395
Data structures, red-black tree 192Ч199
Data structures, sorted list 129
Data structures, stack 109Ч110 264 394 428 429
Data structures, string 241
Data structures, top-down 2Ч3Ч4 tree 187Ч199
Data structures, unordered list 129
Database 226 237 335
| decryption 297 301
Deletion in binary search trees 183Ч184
Deletion in hash tables 208
Dense graphs 376 378 397Ч398 411 413 415Ч417
densepfs (priority graph traversal) 416 439Ч440
Deo, N. 536
Depth-first search 371 381Ч387 391Ч395 397Ч399 422Ч423 428Ч430 454 515
Depth-first search forest 382 384 394 422Ч423
Derivation 270
Deterministic algorithm 528
dfs (recursive depth-first search) 382Ч385
Dictionaries 171
Diffie, W. 301
Digital search trees 213Ч216
Digital search trees, digitalinsert 215
Digital search trees, digitalsearch 214
Dijkstra's algorithm (for finding the shortest path) 415
Dijkstra, E.W. 410 415 454
Directed acyclic graphs (dags) 426Ч428
Directed cycle 428
Directed graphs 376 380 421Ч430
Directed path 423
Directory 233
Discrete mathematics 19
Disk searching 225Ч235
Distribution counting 99Ч101 116 122Ч123
Divide-and-conquer 48 51 104 152 175 362 474 477Ч480 483
Divide-and-conquer recurrence 51 108 149 475 363
Dot product 74
Double buffering 161
Double hashing 207Ч210
Double rotation 198
Down edges 423
downheap (top-down heap repair) 134
drawing lines 311
Drawing lines (draw) 310
Dual of Voronoi diagram 367Ч368
Dummy node see УzФ
duplicate keys see УEqual keysФ
Dynamic programming 483Ч494 536
Eddy, W.F. 331 370
Edges 374
Edges, backward 437
Edges, capacities 435
Edges, cross 423 430
Edges, down 423
Edges, forward 437
Edges, negative weight 494
Edges, up 423 430
Edmonds, J. 439Ч440
eliminate (forward elimination) 62
Encryption 297 301
eof 9
Equal keys 172 177 193 204 214 227Ч228 234
escape sequence 286
Euclid's algorithm (for finding the gcd) 10Ч11 19 302
Euclidean minimum spanning tree 417
Euclidean shortest path problem 418
Euclidean traveling salesman problem 522Ч524
eval (fast Fourier transform) 479
eval (spline evaluation) 72
Even, S. 454
Exception dictionary 210
Exhaustive graph traversal (visit) 515
Exhaustive search 513Ч524 536
Exponential running time 15 513 520 528 534
exponentiation 46Ч47 301
expression (top-down compiler) 277
expression (top-down parser) 273
Extendible hashing 231Ч235 237
External nodes 180 230 289 490
External searching 225Ч235
External sorting 155Ч165
factor (top-down compiler) 278
factor (top-down parser) 274
Fagin, R. 231 237
Fast Fourier Transform 465 471Ч480 536
Fast Fourier transform (eval) 479
fastfind (union-find with compression and balancing) 403 411
Feasible basis 509Ч510
file compression 283Ч293
File compression, Huffman encoding 286Ч293
File compression, run-length encoding 284Ч286
File compression, variable-length encoding 286Ч293
find 399
find (union-find, quick union) 401
findinit (fastfind initialization) 403 411
Finite-state machine, deterministic 248 259
Finite-state machine, nondeterministic 259Ч267
Flow 435
Floyd, R.W. 331
Ford, L.R. 435
Forecasting 161
Forest 375
Forsythe, G.E. 88
Forward elimination 59 60Ч62 64
Forward elimination (eliminate) 62
Fourier transform 471Ч480
Fredkin, E. 216
Friedman, J.H. 370
Fringe vertices 393 410
Fulkerson, D.R. 435
Garey, M.R. 536
Gauss Ч Jordan method 63 65 508
Gaussian elimination 57Ч65 71 76 504 508
Gaussian elimination (gauss) 60
gcd (greatest common divisor, Euclid's algorithm) 11 12
General regular-expression pattern matching 279
General regular-expression pattern matching (match) 265
Geometric algorithms 307Ч370
Geometric algorithms, 2D-trees 343Ч346
Geometric algorithms, closest pair 362Ч366
Geometric algorithms, convex hull 321Ч333 368
Geometric algorithms, elementary 307Ч319
Geometric algorithms, grid method 339Ч342
Geometric algorithms, inside polygon test 316Ч318
Geometric algorithms, intersection 349Ч359
Geometric algorithms, line drawing 310Ч311
Geometric algorithms, range searching 336Ч347
Geometric algorithms, simple closed path 313Ч315
Gerrymandering 307
Gold, B. 536
Gosper, R.W. 242
Graham scan 326Ч330
Graham scan (grahamscan) 329
Graham, R.L. 326 370
grammars 270Ч272
Graph algorithms 373Ч454
Graph algorithms, all-pairs shortest paths 492Ч494
Graph algorithms, biconnectivity 390Ч392
Graph algorithms, bipartite matching 444Ч447
Graph algorithms, breadth-first search 395
Graph algorithms, connected components 384
Graph algorithms, cycle testing 384
Graph algorithms, depth-first search 381Ч387
Graph algorithms, elementary 373Ч387
Graph algorithms, exhaustive search for cycles 515Ч520
Graph algorithms, maximum flow in a network 439Ч440
Graph algorithms, minimum spanning tree 408Ч413
Graph algorithms, priority traversal 395Ч397
Graph algorithms, shortest path 413Ч415
Graph algorithms, stable marriage 447Ч452
Graph algorithms, strongly connected components 428Ч430
Graph algorithms, topological sorting 426Ч428
Graph algorithms, transitive closure 423Ч426
Graph algorithms, union-find 398Ч405
Graph input, adjacency lists (adjlist) 379
Graph input, adjacency matrix (adjmatrix) 378
Graph isomorphism 387
Graph traversal 393Ч398
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



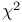 ) test (chisquare)
) test (chisquare)