|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Chvatal V. — Linear programming |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
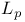 -approximation 218 -approximation 218
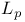 -norm 218 -norm 218
Absolute values 189—191 222—223
Absorbance 214
Absorption spectrum 214
Accumulated rounding errors 74
Activity 173
Activity new variable 158—159
Activity, basic 104
Activity, entering 105
Activity, nonbasic 104
Acyclic network 296
Adding new constraint 159—160
Addition of matrices 84
Affine transformation 446
Aho, A. V. 282
Aircraft scheduling example 352
Algebra of matrices 84
Algorithms, efficiency of 51—52
Ali, A. I. 317
Allocation of scarce resources 171—173
Almon, C. 436
Alterable path 375
Alternative optimal solutions 22—23
Analytic coordinates 250
Anderson, D. 227
Antichain 340
Antosiewicz, H. A. 193
Appolonius of Perga 251
Approximate solutions 213 216—227
ARC 292
Arc, artificial 304 363
Arc, dummy 322
Arc, endpoint of 292
Arc, entering 298 300 360
Arc, forward 300 361
Arc, head of 292
Arc, leaving 300
Arc, return 368
Arc, reverse 300 361
Arc, saturaated 354
Arc, tail of 292
Arc, zero 310
Arithmetic, floating point 74
Arrays representing a tree 312—314
Artificial arc 304 363
Artificial variable 125—126 130—132
Aspvall, B. 451
Assignment problem 343
Associative law of matrix multiplication 81
Augmenting path 375
Augmenting path method 374—380
Auxiliary network 393
Auxiliary problem 39 126 304 363
Avis, D. xiii 46 50
Away from a node 307
Back substitution 71—73
Backpath 315
Backward error analysis 75 409
Backward file 408
Backward transformation (BTRAN) 111 112 114 405—406
Balanced node 393
Balanced tree 282
Balinski, M. L. 373
Ball 270 see
Bartels — Golub method 409—410
Bartels, R. H. 406 409
Barth, G. 214
Basic activity 104
Basic feasible direction 242—243 278
Basic feasible partition 278
Basic feasible solution 19 100 120
Basic feasible solution, normal 134 244
Basic feasible solution, relationship with vertices of polyhedra 253 274
Basic solution 120
Basic solution, dual-feasible 157
Basic variable 20
Basis (=set of basic variables) 20 100 see
Basis heading 102
Basis matrix 100
Basis matrix, eta factorization of xi 105—106 109—100
Basis matrix, relationship with spanning trees 296—297 319
Basis matrix, triangular factorization of 405—406
Basis matrix, working basis 417
Beale, E. M. L. 33
Beer — Bouguer's law 215
Beer, A. 214
Belz, M. H. 211
Berge, C. 229—230 234
Best fit 213 216—221
Bicycle problem 12
Big M method 128
Big O notation 380
Bin-packing problem 198 208
Bipartite graph 332 372 388
Birkhoff G. 330
Birkhoff-von Neumann Theorem 330
Bland's rule see "Smalest-subscript rule"
Bland, R. G. 37 451
Blaschke, W. 267 270
Blattberg, R. 221
Block-angular problems 434—435 440—441
Block-triangular matrix 412
Blocking flow 383
Bloomfield, P. 227
Bluffing 235
Bogert, L. J. 185 187
Bonaparte, N. 227
Bonbon, T. 229—232 234
Bondy, J. A. xiii
Borel, E. 228—234
Borgwardt, K. H. 46
Boscovich, R. J. 227
Bottleneck assignment problem 344
Botts, T. 269
Bouguer, P. 214
Bounded set 270 287
Bounded variable see "Restricted variable"
Bounds on individual variables 119
Bowman, E. H. 323
Bradley, G. H. 312 317
Branch-and-bound method for the knapsack problem 206
Breadth-first search 280
Breakeven price 70
Briggs, G. M. 185 187
Brouwer, L. E. J. 228
Brunn, H. 262
BTRAN 111 112 114 405—406
Bump 91 412
Bunnenberg, E. 214
Calloway, D. H. 185 187
Capacitated transshipment problem see "Upperbounded transshipment problems"
Capacity of a cut 370
Caratheodory, C. 265
Cartesian coordinates see "Analytic coordinates"
Case study in forestry 171—176
Caterer problem 324—326
Cayley, A. 81
Center of ellipsoid 452
Center of simplex 446
Certificate of optimality 61—62
Chain 340 see
Changes in data see "Sensivity analysis"
Charnes, A. 10 34 193
Cheap, Middling or Dear 239
Chebyshev approximations see "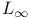 -approximations as a special case of -approximations as a special case of 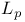 -approximation" -approximation"
Chvatal, V. 12 46 50 239
Circling see "Cycling"
Claerbout J. F. 221
Clark, D. xiii
| Column generation 198—200 428—429
Column player 230
Column singleton 413
Column vector 82
Column, entering 101
Column, eta 83
Column, leaving 102
Column, pivot 24
Combination, convex 330
Combination, linear 55 138
Comparison of the revised and the standard simplex methods 113—115
Complementary slackness 62—65 104—105 238
Complete pivoting 74
Component of a vector 82
Computer implementations of the network simplex method 311—317
Computer implementations of the simplex method 105—115 405—414
Connected network 296
Conservation law 369
Constrained variable see "Restricted variable"
Constraints, linear 6
Constraints, linking 435
Convex closure see "Convex hull"
Convex combination 330
Convex hull 263—265
Convex set 263
Convex set, separation theorem for 266
Cook, S. A. 336
coordinates see "Analytic coordinates"
Core (in Dinic's algorithm) 381
core memory 113—115 406 408 412 413—414
Corner-point theorem see "Fundamental Theorem of Linear Programming"
Cost vector 295
Cover 331 388
Cramer's rule 444
Cunningham's rule 307—310 335 365
Cunningham, W. H. 303 308
Cut 370
Cut, capacity of 370
Cutting-stock problem 195—212
CYCLE 296
Cycle, negative 362 402
Cycling 30—33 124 303
Dantzig — Wolfe decomposition algorithm 194 429—434
Dantzig — Wolfe decomposition algorithm, economic interpretation of 436—439 441
Dantzig — Wolfe decomposition principle 425—428 439—441
Dantzig, G. B. 7—9 34 37 45 46 57 97 105 119 193 194 228 291 336 339 391 416 435 436
Danzer, L. 267
de Buchet, J. 83
de Lucy, F. xiii
Decentralized planning 436
Decision variable 14
Decomposition of a transshipment problem 305—306
Decomposition, Dantzig — Wolfe 425—442
Decomposition, LU 88
Degeneracy 29—30 124 259 302 361 362
Delayed column generation 198—200 428—429
Demand vector 295
Dense systems of linear equations 77
Depth of a node 313
Depth-first search 314
Descartes, R. 250—251
Destination see "Sink"
Determinant 443—444
Devex 115
Dictionaries xi 17—19
Dictionaries, dual-feasible 149—152
Dictionaries, feasible 19
Dictionaries, matrix description of 98—100
Diet problem 3—5 182—184 185—187
Dijkstra's algorithm see "Shortest-paths algorithm"
Dijkstra, E. 391
Dilworth's Theorem 341
Dilworth, R. P. 340
DIMENSION see "n-dimensional space"
Dimension analysis 66
Dinic's algorithm 384 389
Dinic, E. A. 380 384
Directed path 391
Direction see "Basic feasible direction"
Displacement 398
Distance 269
Distinct representatives 336
Doig, A. G. 211
Domination between strategies 237
Dorfman, R. 68
Dot product see "Scalar product"
Doubly stochastic matrix 329
Dry node 393
Drysdale, R. S. xiii
Dual problem 56 139
Dual simplex method 152—157 175
Dual simplex method, revised format 153—157
Dual variables see "Dual problem"
Dual variables, economic significance of 65—68 136
Dual-feasible basic solution 157
Dual-feasible dictionary 149—152
Duality theorem 8 58 141 261—262
Duality theorem, weak 140
Duffin, R. J. 242 286
Dummy nodes and arcs 322
Dyer, M. E. 282
Dynamic programming 206—207
Economic interpretation of the decomposition algorithm 436—439 441
Economic interpretation of the revised simplex method 102 105
Economic significance of dual variables 65—68 136
Economy models 68
Edge of a network or a graph see "Arc"
Edge of a polyhedron 254—255
Edmonds, J. 51 331 336 380 391 400 444
Efficiency of algorithms 51—52
EFI see "Elimination form of the inverse"
Egervary, J. 334 374 390
Eisemann, K. 196
Eisenhart, C. 227
Elias, P. 371
Elimination form of the inverse(EFI) see "Triangular factorization"
Elimination of free variables 132—133
Elimination, Fourier — Motzkin 241—242
Elimination, Gauss — Jordan xii 79
Elimination, Gaussian xii 71—79 272 277 443—444
Ellipsoid 446
Ellipsoid method xii 52
Endpoint of an arc 292
Entering activity 105
Entering arc 298 300 360
Entering column 101
Entering variable 21 28 121 124
Entry of a matrix 81
Enumeration trees 201—202
Equations see "Linear equation"
Equilibrated systems of linear equations 76
Equivalence of game theory and linear programming 232 239
Equivalence of spanning trees and bases in a transshipment problem 296—297 319
Error analysis 75 409
Error tolerances see "Zero tolerances"
Eta column 83
Eta factorization of the basis xi 105—106 109—110
Eta file 110—112
Eta matrix 83
Euclidean norm see "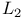 -norm as a special case of -norm as a special case of 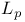 -norm" -norm"
Euclidean space see "n-dimensional space"
Eves, H. 74
Extreme points of a polyhedron see "Vertices of a polyhedron"
Facets of a polyhedron 252
Factorization of the basis, eta xi 105—106 109—110
Factorization of the basis, triangular 405—406
Fair game 233
Fama, E. P. 221
Farkas's lemma 248
Farkas, J. 248
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



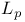 -approximation
-approximation 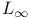 -approximations as a special case of
-approximations as a special case of  -norm as a special case of
-norm as a special case of