|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Chvatal V. — Linear programming |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Muir, F. 221
Multicommodity flow problems 435
Multiple optimal solutions 22—23
Multiple pricing 115
Multiplication of matrices 79—82
Multipliers 55—56 144
Multistage problems see "Scheduling production and inventory"; "Personnel training example"; "Caterer problem"
Mulvey, J. M. 312
Munkres, J. 400
Murtagh, B. A. 115
Murty, K. G. 165
n-dimensional space 252
Negative cycle 362 402
Neighbor 278
Nemhauser, G. L. 207
Nemirovskii, A. S. 9 451
Network 292 369
Network flow problem see "Upper-bounded transshipment problems"
Network simplex method 297—310
Network simplex method, algebraic description 300—303
Network simplex method, computer implementations 311—317
Network simplex method, economic motivation 297—299
Network simplex method, initialization 303—306
Network simplex method, number of iterations 311
Network, acyclic 296
Network, auxiliary 296
Network, connected 296
Network, incidence matrix of 294
Network, layered see "Core"
Network, working 399
Nishizeki, T. xiii
Node 292
Node numbers 306—307
Node wet 393
Node, balanced 393
Node, dry 393
Node, dummy 322
Node, intermediate 292 369
Node, transshipment see "Intermediate"
Node,depth of 313
Node-arc matrix see "Incidence matrix of a network"
Nonbasic activity 104
Nonbasic variable 20
Nondegeneracy see "Degeneracy"
Nonnegativity constraints 6
Nonsingular matrix 93
Nonzero tolerances see "Zero tolerances"
Norm 218 269
Normal basic feasible solution 134 244
Normal distribution 220
Null vector see "Zero vector"
Number of iterations in the Dantzig — Wolfe decomposition algorithm 441
Number of iterations in the network simplex method 311 335
Number of iterations in the primal-dual method 398 400
Number of iterations in the simplex method 45—51
Number of vertices of a polyhedron 272—273
Nutrirtion problem see "Diet problem"
Nutritive values of foods 185—187
o-notation 380
Objective function 6
Objective function, parametric 162
Oil refinery example 10—11 69 70
On-the-job training example 11—12 168
Open pit problem 373
Operation count in Gaussian elimination 73 77
Operation count in the simplex method 112—114
Operations on matrices 79—82 84
Optimal certificate 61—62
Optimal solution 7
Optimal solution, uniqueness of 22—23
Optimal strategy 231
Optimal value 7
Optimum cover problem 388
Orchard — Hays, W. 97 105
Orden, A. 34 291
Order, partial 340 373
Oresme, N. 251
Origin 28
Origin in a transportation problem see "Source"
Outgoing variables see "Leaving variable"
Outliers 220
Overdetermined systems of linear equations 213—227
Overtime production 189 323
Packed form of sparse matrices 82 110
Paige, C. C. xiii
Paper recycling example 347—350
Paper trim problem see "Cutting-stock problem"
Parametric linear programming 162—166
Partial order 340 373
Partial pivoting 74
Partial pricing 115
Partitioned preassigned pivot procedure (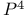 ) see "Hellerman — Rarick procedure" ) see "Hellerman — Rarick procedure"
Path 296
Path, alterable 375
Path, augmenting 375
Path, directed 391
Path, shortest 391
Payoff matrix 230
Peripheral memory 113—115 406 408 410 413
Permutation matrix 83 86—87 90—91 406—407
Perold, A. F. xiii 194 440 441
Personnel training example 11—12 168
Perturbation method 34—37 258—260 319
Phase one, phase two see "Two-phase simplex method"
Phelps, K. T. xiii
Picard, J. C. 373
Pivot column 24
Pivot element 73
Pivot row 21 24
Pivot stem 315
Pivoting in Gaussian elimination 74 78 89—92
Pivoting in the network simplex method 301
Pivoting in the simplex method 21
Pivoting rule 51 311—312
Pivoting strategy in Gaussian elimination 78 89—92
Planning, decentralized 436
Player 230
Pointers 408
Poker 235—237 238—239
Polyhedron 252 331
Polyhedron with no vertices 275—277
Polyhedron, facets of 252
Polyhedron, separation theorem for 267
Polyhedron, vertices of 253 271—273 287—288 331
Polytope 287
Postoptimality analysis see "Sensivity analysis"
Prager, W. 324
Pratt, A. W. 221
Predecessor 312—313
Prekopa, A. 273
Preorder 314
Price, shadow 67 104 437
Pricing 114—115
Pricing out a nonbasic activity 104
Primal problem 56 139
Primal-dual method 392—400
Product form of the inverse (PFI) xi 105 117
Product matrix 81
Product, scalar 269
Production and inventory scheduling 188—193 322—323
Proll, L. G. 282
Pure strategy 229
Quandt, R. E. 46
Queyranne, M. xii
Rank see "Full row rank"
Rarick, D. C. 91
Raws 195
Reciprocal 94
Recommended daily dietary allowances 182—183
Recycled paper example 347—350
| Redundant inequalities 242 247
Refactorization 111—113
Region of feasibility 252
Regular matrix see "Nonsingular matrix"
Regular-time production 189 323
Reid's method 412—413
Reid, J. K. xiii 115 406
Reinversion see "Refactorization"
Relationship between basic feasible solutions and vertices of polyhedra 253 274
Relationship between game theory and linear programming 232 239
Relationship between primal and dual problems 60—61 140
Relationship between spanning trees and bases in a transshipment problem 296—297 319
Renz, P. xiii
Representation of a tree 312—314
Resource 104 173
Restricted primal problem 115
Restricted variable 119—120 138
restrictions see "Constrains"
Return arc 368
Reverse arc 300 361
Revised simplex method xi 97 100—102
Rhys, J., 373
Right-hand side, parametric 165
Riley, V. 9
Robustness of an approximation 220
Rockafellar, R. T. 269
Roedl, V. xiii
Root of a tree 201 308—309 312
Rose, D. J. 91
Rosenberg, I.G. xiii
Rounding errors 74
Row player 230
Row rank see "Full row rank"
Row singletons 413
Row vector 82
Rubin, D. S. 282
Ryser, H. J. 366
Saaty, T. 163
Samuelson, P. A. 68
Sargent, T. 221
Saturated arc 354
Saunders's method 413—414
Saunders, M. A. xiii 406 412
Savage, J. L. 234
Scalar product 269
Scaling in transshipment problems 400—401
Scaling systems of linear equations 76—77
Scheduling production and inventory 188—193 322 323
Schmidt, B. K. 282
Schrijver, A. 451
Score vector 366
Scrimshaw, N. S. 183
Search breadth-first 280
Search depth-first 314
Seneta, E. 227
Sensitivity analysis 148—149 158—162 176 181—182
Separation theorem for convex sets 269
Separation theorem for polyhedra 267
Set bounded 270 287
Set convex 263
Shadow price 67 104 437
Shannon, C. E. 371
Sharpe, W. F. 221
Shor, N. Z. 451
Shortest paths algorithm 391—392 402
simplex 452
Simplex tableau xi 23
Simplified poker 235—237 238—239
Simultaneous equations see "System of linear equations"
Singleton 413
Singular matrix 93
Sink 292 369
Size of a problem 51
Slab 270
Slack variables 14
Sleator, D. D. K. 380
Smale, S. 46
Smallest-subscript rule 37—38 125
Smith, D. E. 74
Smoothing production 188—193 322—323
Solow, R. M. 68
Solution, approximate 213 216—227
Solution, basic 120
Solution, basic feasible 19 100 120
Solution, degenerate 30 124
Solution, dual-feasible 157
Solution, feasible 6
Solution, feasible tree 296 354
Solution, normal basic feasible 134 244
Solution, optimal 7
Solvability of systems of linear inequalities 143—144 146
Source 292—369
Space see "n-dimensional space"
Spanning tree 296
Spanning tree and the basis matrix 296—297 319
Sparse matrix 82
Sparse system of linear equations 77
Sparsity xi 111—114 406 409 451—452
Special structure 92 see
Spectrophotometry 214—216
Sphere 446 see
Spike 91 413
Staircase structure 193—194
Standard form of linear programming problems 6
Standard simplex method 97
Standard simplex method vs. revised simplex method 113—114
Steepest edge 115
Steiger, W. L. xiii 227
Steinberg, D. I. 33
Stiemke, E. 248
Stochastic vector 230
Stone, R. E. 451
Storage of sparse matrices 82—83
Strategy, dominant 237
Strategy, mixed 231
Strategy, optimal 231
Strategy, pure 229
Strict linear inequalities 43 448—451
Strongly feasible tree 308—309 319 362
Structural variable see "Decision variable"
Structure, block-angular 434—435
Structure, block-diagonal 435
Structure, block-triangular 412
Structure, GUB 415
Structure, staircase 193—194
Struik, D. J. 74
Strum, J. E. 18
Subproblem in Dantzig — Wolfe decomposition 428
Substitution of an activity 105
Sum of matrices 84
Suurballe, J. W. 33
Swanson, E. R. 171 177
Swanson, H. S. xiii 179
Swine 180
Symmetric game 233
System of distinct representatives (SDR) 336
System of linear equations 143—146 240—249 444—454
System of linear equations, dense 77
System of linear equations, equilibrated 76
System of linear equations, matrix representation of 82
System of linear equations, overdetermined 213—227
System of linear equations, solution of see "Gaussian elimination"
System of linear equations, sparse 77
System of linear equations, well-scaled 76
System of linear inequalities 143—146 240—249 444—454
System of linear inequalities, characterizing solutions of 244
System of linear inequalities, inconsistent 144
System of linear inequalities, unsolvable 144
Tableau format 23—25
Tableau simplex xi 23
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 )
)