јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Tenenbaum M., Pollard H. Ч Ordinary differential equations: an elementary textbook for students of mathematics, engineering, and the sciences
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Ordinary differential equations: an elementary textbook for students of mathematics, engineering, and the sciencesјвторы: Tenenbaum M., Pollard H. јннотаци€: This book has been written primarily for you, the student. We have tried to make it easy to read and easy to follow.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1985 оличество страниц: 819ƒобавлена в каталог: 05.11.2010ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Legendre equation, functions of the second kind, 597 Legendre polynomials, 597Ч605 Legendre polynomials, properties of 598-605 Legendre polynomials, properties of, coefficients in binomial series expansion 598Ч600 Legendre polynomials, properties of, orthogonal property 602Ч604 Legendre polynomials, properties of, other integral properties 604Ч605 Legendre polynomials, properties of, recursion formula 601 Legendre polynomials, properties of, Rodrigue's formula 602 Legendre polynomials, properties of, values of 600Ч601 Libby, Dr. Willard F. 5 Line elements 39 Lineal element diagram 39 Lineal elements 39 Linear coefficients 62Ч69 Linear combinations, definition of 205 Linear dependence of functions 205 775-Comment 777-5 Linear dependence of solutions 781-Comment 64.15 Linear dependence, definition of 205 Linear differential equations, Bessel see "Bessel equation" Linear differential equations, characteristic equation of 212Ч220 Linear differential equations, characteristic equation of, definition 212 Linear differential equations, characteristic equation of, roots imaginary 217Ч220 Linear differential equations, characteristic equation of, roots real and distinct 213Ч214 Linear differential equations, characteristic equation of, roots real but some multiple 214Ч217 Linear differential equations, complementary function of 210 Linear differential equations, definition of 92 196 Linear differential equations, Euler 247 Linear differential equations, exact 248 Linear differential equations, existence theorem for see "Existence and uniqueness theorems" Linear differential equations, first order 91Ч95 Linear differential equations, first order, definition of 92 Linear differential equations, first order, general solution of 93 Linear differential equations, first order, integrating factor for 94 Linear differential equations, first order, solution of 92 Linear differential equations, form of solution of 211Ч220 Linear differential equations, fundamental theorems for 207 208 Linear differential equations, Gauss's 587 Linear differential equations, general solution of 93 210 788 Linear differential equations, Hermite 607 Linear differential equations, homogeneous with constant coefficients 211Ч220 Linear differential equations, homogeneous with nonconstant coefficients 241Ч246 Linear differential equations, homogeneous, definition of 196 Linear differential equations, hypergeometric 587 Linear differential equations, integrating factors for 94 248 Linear differential equations, Laguerre 624Ч630 Linear differential equations, Legendre see "Legendre equation" Linear differential equations, n linearly independent solutions of 208 786 Linear differential equations, nonhomogeneous 221Ч246 Linear differential equations, nonhomogeneous with constant coefficients 221Ч240 Linear differential equations, nonhomogeneous with nonconstant coefficients 236Ч237 241Ч246 Linear differential equations, nonhomogeneous, definition of 196 Linear differential equations, ordinary point of 570 Linear differential equations, reduction to a system 784Ч785 Linear differential equations, singularity of 570 Linear differential equations, singularity of, irregular 572 Linear differential equations, singularity of, regular 571 Linear differential equations, solution of, by complex variables 230Ч231 Linear differential equations, solution of, by inverse operators 272Ч282 288Ч291 Linear differential equations, solution of, by Laplace transforms 296Ч302 Linear differential equations, solution of, by method of Frobenius 572Ч584 Linear differential equations, solution of, by partial fraction expansion of inverse operators 288Ч291 Linear differential equations, solution of, by polynomial operators 262Ч265 Linear differential equations, solution of, by power series 537Ч546 Linear differential equations, solution of, by reduction of order 242Ч246 Linear differential equations, solution of, by undetermined coefficients 221Ч230 Linear differential equations, solution of, by variation of parameters 233Ч240 Linear differential equations, systems of see "System entries" Linear differential equations, Tschebyscheff 589 Linear differential equations, uniqueness theorem for see "Existence and uniqueness theorems" Linear independence of functions 205 775-Comment 777-5 Linear independence of solutions 781-Comment 64.15 Linear independence, definition of 205 Linear property of inverse operators 296 Linear property of Laplace transformation 295 Linear property of polynomial operators 253 Linearization of first order systems 424Ч438 Lipschitz condition 731 734 764 766 Liquid, flowing through an orifice 183 Liquid, rotating in a cylinder 193Ч194 Logarithmic decrement 356 Maclaurin series 535 Magnification ratio 363 Mass, variable 191Ч193 Mathematical induction 250 Mean, law of the 731 Method of Frobenius 572 see Method of reduction of order 242Ч246 Method of undetermined coefficients 221Ч230 Method of variation of parameters 233Ч240 Milne method for second order equation 710Ч711 Milne method for system of two first order equations 703 Milne method for third order equation 712-4 Milne method for y'=f(x,y) 684Ч689 Milne method, comment on error in 688Ч689 Modulated amplitude 345 Modulus of elasticity 385 Modulus, Young's 385 Moment of force 381 Moment of inertia 381 Moment, bending 384 Momentum, angular 472 Motion of a complex system 189Ч191 Motion of a particle in space see "Particle in motion in space subject to a central force" Motion of a particle on a circle 316Ч317 Motion of a particle on a straight line 138Ч166 314Ч316 Motion of a projectile 463Ч465 Motion, damped, forced 359Ч364 Motion, damped, free (damped harmonic) 348Ч353 Motion, forced, damped 359Ч364 Motion, forced, undamped 338Ч342 Motion, free, damped (damped harmonic) 348Ч353 Motion, free, undamped see "Simple harmonic motion" Motion, horizontal 160Ч162 Motion, inclined 164Ч166 Motion, period of 318 333 351 477 Motion, planetary 491Ч492 Motion, stable 339 Motion, steady state 361 Motion, transient 361 Motion, undamped, forced 338Ч342 Motion, undamped, free see "Simple harmonic motion" Motion, unstable 340 Multiplicity of solutions 28Ч31 Mutual inductance 454 n-parameter family of solutions, definition of 30 n-parameter family of solutions, finding a differential equation from an 31Ч33 Natural (undamped) frequency 318 319 Neutral surface 384 Newton's first law of motion 138 Newton's interpolation formulas 663Ч671 Newton's interpolation formulas, backward 669 Newton's interpolation formulas, error in 670 671 Newton's interpolation formulas, forward 667 Newton's law of universal gravitation 491 Newton's proof of inverse square law 494Ч495 Newton's second law motion 138 459 Nonhomogeneous linear equation, definition of 196 Nonlinear equations, existence and uniqueness theorem for 765Ч767 Nonlinear equations, numerical solution of see "Numerical methods" Nonlinear equations, reduction to a system 766Ч767 Nonlinear equations, series solution of 562Ч567 see Normal, coordinates 444 Normal, frequencies 443 Number, complex 197 Number, pure imaginary 197 Number, real 197 Numerical methods 631Ч718 Numerical methods for a second order equation 707Ч711 712-3 715Ч718 Numerical methods for a system of three first order equations 726-2 Numerical methods for a system of two first order equations 702Ч706 723Ч726 Numerical methods for a third order equation 712-4 Numerical methods for first order equation y'=f(x,y) 632Ч658 681-6 684Ч688 690Ч701 713Ч715 Numerical methods, Adams' 681 712-3 Numerical methods, choosing size of h 691Ч692 Numerical methods, continuing 632 Numerical methods, corrector 632 Numerical methods, decreasing h 692Ч694 Numerical methods, difference tables 660 662 663 670 Numerical methods, errors see "Error" "Errors" Numerical methods, fifth degree polynomial 676 678 691 703 Numerical methods, finite differences 659Ч661 Numerical methods, fourth degree polynomial 681-2 Numerical methods, illustrative example and summary 694Ч701 Numerical methods, improvement of polygonal method 641Ч643 Numerical methods, increasing and reducing h 692Ч694 Numerical methods, Milne see "Milne method" Numerical methods, Newton's interpolation formulas 663Ч671 Numerical methods, Newton's interpolation formulas, backward 669 Numerical methods, Newton's interpolation formulas, forward 667 Numerical methods, perturbation theory 713Ч718 Numerical methods, perturbation theory, first order equation 713Ч715 Numerical methods, perturbation theory, second order equation 716Ч718 Numerical methods, Picard's see "Picard's method of successive approximations" Numerical methods, polygonal 632Ч638 Numerical methods, polynomial interpolation see "Polynomial interpolation" Numerical methods, reducing and increasing h 692Ч694 Numerical methods, Runge Ч Kutta see "Runge Ч Kutta formulas" Numerical methods, series 645Ч652 Numerical methods, Simpson's rule 677 678 684 Numerical methods, sixth degree polynomial 677 Numerical methods, starting methods 632 see Numerical methods, summary and an example 694Ч701 Numerical methods, Taylor series 645Ч652 Numerical methods, third degree polynomial 676 678 Numerical methods, three-eighths rule 681 Numerical methods, trapezoidal rule 675 678 682 Numerical methods, Weddle's rule 677 678 691 703 Oceanic pressure 186Ч188 Operator, differential 251 see "Polynomial Order of a differential equation 21 Order of a homogeneous function 57 58 Ordinary differential equation, definition of 20 Ordinary point of a linear differential equation 570 Ordinary point of y'=f(x,y) 43 744Ч747 Orifice, flow through an 183 Orthogonal trajectory in polar coordinates 118 Orthogonal trajectory in rectangular coordinates 117 Orthogonal, definition of, functions 602 Orthogonal, property of Bessel functions 622 Orthogonal, property of Laguerre polynomials 630 Orthogonal, property of Legendre polynomials 602Ч604 Oscillator, harmonic 323Ч329 377 Output of a system 341 360 372 Overdamped 349 Parabolic reflector 759Ч760 Parameters, number of 30 Parameters, variation of 233Ч240 Parasite problem 447Ч451 Partial differential equation, meaning of 20 Partial fraction expansion 283Ч284 Partial fraction expansion of inverse operators 287 289 Particle in motion in space subject to a central force 470Ч496 521Ч522 Particle, force inversely proportional to cube of distance 521Ч522 Particle, force inversely proportional to square of distance 481Ч488 494 Particle, force inversely proportional to square of distance, determining constants of integration 484Ч486 Particle, force inversely proportional to square of distance, energy considerations 487Ч488 Particle, force inversely proportional to square of distance, planetary motion 491Ч492 Particle, force proportional to distance 476Ч479 Particle, Kepler's laws 492 Particle, law of conservation of angular momentum 471Ч472 Particle, law of conservation of energy 475 Particle, moves in plane, proof that particle 470Ч471 Particle, moving in a circle 316Ч317 Particle, moving in a plane see "Particle in motion in space subject to a central force" Particle, moving in rotating tube 380 Particle, moving on a straight line 138Ч166 314Ч316 Particle, period of 477 492 Particle, satisfies law of conservation of angular momentum 471Ч472 Particle, satisfies law of conservation of energy 475 Particle, special central force problem 521Ч522 Particle, sweeps out equal areas in equal times, proof that particle 472 Particular solution of a differential equation 33Ч37 Particular solution of a differential equation, definition of 35 Pendulum, actual period of 333 Pendulum, amplitude of 328 Pendulum, period independent of amplitude 334-34 Pendulum, simple 327Ч329 Pendulum, weight of wire not negligible 331-29 Perigee 490 Period 318 477 Period, actual, of a simple pendulum 333 Period, damped 351 Perturbation method 713Ч718 Perturbation method, first order equation 713Ч715 Perturbation method, second order equation 715Ч718 Phase and phase angle 318 Picard's method of successive approximations 720Ч726 Picard's method of successive approximations for a system of three first order equations 726-9 Picard's method of successive approximations for a system of two first order equations 723Ч726 Picard's method of successive approximations for first order equations 720Ч723 Plane analytic geometry, a review of 62Ч63 Plane motion of a particle see "Particle in motion in space subject to a central force" Plane motion of a projectile 463Ч465 Planetary motion 491Ч492 Point, singular 43 744Ч747 Polar form of a complex number 199 Polygonal method 632Ч638 Polygonal method, an improvement of 641Ч643 Polygonal method, comment on errors in 636Ч638 Polynomial interpolation 661Ч684 Polynomial interpolation, Adams' 681 712-3 Polynomial interpolation, error in 670Ч671 679 Polynomial interpolation, fifth degree polynomial 676 678 679 Polynomial interpolation, function 662 Polynomial interpolation, Newton's, (backward) formulas 669 Polynomial interpolation, Newton's, (forward) formulas 667 Polynomial interpolation, Simpson's rule 675 678 679 684 Polynomial interpolation, sixth degree polynomial 677 Polynomial interpolation, third degree polynomial 676 678 679 Polynomial interpolation, three-eighths rule 681 Polynomial interpolation, trapezoidal rule 675 678 679 682 Polynomial interpolation, Weddle's 677 678 679 Polynomial operators 251Ч265 Polynomial operators of order n 251 Polynomial operators, algebraic properties of 255Ч259 Polynomial operators, associative law of addition 256 Polynomial operators, associative law of multiplication 257 Polynomial operators, commutative law of addition 256 Polynomial operators, commutative law of multiplication 258 Polynomial operators, definition of 251 Polynomial operators, distributive law of multiplication 258 Polynomial operators, exponential shift theorem for 260 Polynomial operators, exponential shift theorem for, corollaries to 261 Polynomial operators, factoring of 258 Polynomial operators, linear property of 253 Polynomial operators, P(D)y, definition 252 Polynomial operators, P(D+a), definition 259 Polynomial operators, product of h(x) by 256 Polynomial operators, product of two 257 Polynomial operators, solution of linear equations by 262Ч265 Polynomial operators, solution of systems of linear equations by 398Ч417 Polynomial operators, sum of two 255 Polynomials, Hermite 607 Polynomials, Laguerre 625Ч630 Polynomials, Legendre 597Ч605 Polynomials, Tschebyscheff 589 Potential 473 Potential, energy 329 473 Power series see "Series" "Solution Pressure, atmospheric and oceanic 186Ч188
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 ,
, 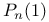 ,
,