|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Stewart G.W. Ч Matrix algorithms. Volume 2: Eigensystems |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Moon, Y.S. 236
More, J.J. 265
Morgan, R.B. 296 345
Multiple eigenvalue 2
Multiple eigenvalue, algebraic multiplicity 4 6 12
Multiple eigenvalue, geometric multiplicity 6 12
Multiset 2
Murray, F.J. 203
Nash, S. 24
Newton, I. 418
Newton-based methods 381
NewtonТs method 395
NewtonТs method, application to eigenproblem 418Ч419
NewtonТs method, derivation by perturbation expansion 395Ч396
NewtonТs method, history 418
NewtonТs method, relation to Rayleigh quotient method 418
NewtonТs method, relation to the QR algorithm 403 418Ч419
Nielsen, C.P. 201
Nilpotent matrix 12Ч13
Nonnormal matrix 71
Norm 25 36
Norm and spectral radius 31Ч33 36
Norm,  -norm 26 27 -norm 26 27
Norm, 1-norm 26 27
Norm, 2-norm, and Frobenius norm 27
Norm, 2-norm, and largest singular value 205
Norm, 2-norm, matrix norm 27
Norm, 2-norm, of orthonormal matrix 27
Norm, 2-norm, properties 27
Norm, 2-norm, unitary invariance 27
Norm, 2-norm, vector norm 26
Norm, absolute norm 28
Norm, absolute norm, examples 28
Norm, compatable norm 36
Norm, consistent norm 29 36
Norm, consistent norm, consistent vector norm 29Ч30
Norm, consistent norm, construction by similarities 30
Norm, consistent norm, examples 29
Norm, equivalence of norms 30
Norm, Euclidean norm 26
Norm, family of norms 26
Norm, Frobenius norm 26
Norm, Frobenius norm, and 2-norm 27
Norm, Frobenius norm, and singular values 205
Norm, Frobenius norm, trace characterization 26
Norm, Frobenius norm, unitary invariance 27
Norm, limitations 28 33 35Ч36 43
Norm, matrix norm 25
Norm, operator norm 27
Norm, rounding a matrix 28
Norm, spectral norm see УNorm 2-normФ
Norm, subordinate norm 27
Norm, triangle inequality 26
Norm, unitarily invariant norm 27
Norm, vector norm 26
Normal matrix 14
Normal matrix, eigenvalues 14
Normal matrix, eigenvectors 14
Nour-Omid, B. 347 380
Null space 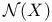 424 424
Nullity [null(A)] 424
Oettli, W. 70
Olsen, J. 419
Operation count, application of a plane rotation 91
Operation count, Arnoldi process 304
Operation count, balancing 108
Operation count, band tridiagonalization 189
Operation count, basic QR step in Hessenberg QR algorithm 92
Operation count, bidiagonal QR step 220
Operation count, complex arithmetic 86Ч87
Operation count, deflation by inspection 107
Operation count, divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition 185
Operation count, divide-and-conquer algorithms 181Ч182
Operation count, eigenvectors of a triangular matrix 102
Operation count, explicit shift Hessenberg QR algorithm 100
Operation count, Householder reduction to Hesssenberg form 86
Operation count, Householder-matrix product 82
Operation count, hybrid QRD-SVD algorithm 226
Operation count, implicit double shift QR step 123
Operation count, implicit tridiagonal QR step 167
Operation count, implicitly restarted Arnoldi 320Ч323
Operation count, inertia of a tridiagonal matrix 192
Operation count, Jacobi Ч Davidson method 409
Operation count, Krylov Ч Schur restarting 329
Operation count, Lanczos recurrence 308
Operation count, QZ algorithm 150Ч152
Operation count, reduction to bidiagonal form 217
Operation count, reduction to Hessenberg-triangular form 147
Operation count, reduction to tridiagonal form 162
Operation count, spectral decomposition updating 179Ч181
Operation count, WilkinsonТs algorithm for S/PD eigenproblem 232
Orthogonal similarity see УUnitary similarityФ
Osborne, E.E. 112
Ostrowski, A.M. 36 71
Overflow see УExponent exceptionФ
Paige, C.C. 237 280 296 315 366
Parlett, B.N. 24 169 170 228 265 279 295 296 346 347 365 367 379 380
Pencil see УGeneralized eigenvalue problemФ
Pentadiagonal matrix 186
Perturbation theory see УEigenpairФ УEigenvalueФ УEigenvectorФ УGeneralized УHermitian УRelative УSimple УSingular УS/PD
Peters, G. 418 420
Petrov method see УRayleigh Ч Ritz methodФ
Plane rotation 88 111
Plane rotation and Wilkinson diagrams 91
Plane rotation in the (i,j)-plane 88
Plane rotation, application 89Ч91
Plane rotation, application, operation count 91
Plane rotation, application, pre- and postmultiplication 91
Plane rotation, exponent exception 89
Plane rotation, generation 89
Plane rotation, introducing a zero into a 2-vector 88
Plane rotation, introducing a zero into a matrix 88Ч89
Plane rotations, GivensТ method 170
Positive definite matrix 425
Positive semidefinite matrix 425
Powell, M.J.D. 70
Power method 56 69Ч70 266 381
Power method, assessment 66
Power method, choice of starting vector 58 60
Power method, convergence 57
Power method, convergence criteria 60Ч62
Power method, deflation 70
Power method, effects of rounding error 65
Power method, implementation 64
Power method, Markov chain 69
Power method, normalization 59
Power method, operation counts 58Ч59
Power method, rate of convergence 58
Power method, Rayleigh quotients 63
Power method, shifting 64 70
Power method, with two vectors 381Ч382
Prager, W. 70
Primitive Ritz vector see УRayleigh Ч Ritz methodФ
Principal vector see УJordan canonical formФ
Projector 427
Proper value 24
Pseudospectrum 36Ч37
qd-algorithm 110
QL algorithm see УQR algorithmФ
QR algorithm 1 24 55 394 396 УHessenberg УQZ УSubspace УTridiagonal
QR algorithm as factorization of a polynomial 76
QR algorithm, convergence 111
QR algorithm, convergence, alternate shifts 75
QR algorithm, convergence, cubic 75
QR algorithm, convergence, error bounds for a QR step 73Ч74
QR algorithm, convergence, multiple eigenvalues 75
QR algorithm, convergence, quadratic 75
QR algorithm, convergence, unshifted algorithm 77Ч80
QR algorithm, history 110
QR algorithm, impracticality on a full matrix 80Ч81
| QR algorithm, QL algorithm 111 113 169 170
QR algorithm, QR step 71
QR algorithm, Rayleigh quotient shift 73
QR algorithm, relation to inverse power method 72Ч73 111
QR algorithm, relation to NewtonТs method 403 418Ч419
QR algorithm, relation to power method 72 77 111
QR algorithm, shifted 71
QR algorithm, unshifted 77Ч80
QR algorithm, unshifted, convergence to Schur decomposition 78Ч79
QR algorithm, unshifted, disorder in eigenvalues 79
QR algorithm, unshifted, equimodular eigenvalues 80
QR algorithm, unshifted, implications for the shifted algorithm 80
QR algorithm, unshifted, rates of convergence 80
QR algorithm, variants (RQ, QL, LQ) 111 113 169 170 418
QR algorithm, Wilkinson shift 75
QR decomposition 426Ч427
QR decomposition and QR algorithm 110
QR step see УQR algorithmФ
Quasi-triangular matrix 115
Quasi-triangular matrix, computing eigenvectors 126Ч128
QZ algorithm 147Ч148 156
QZ algorithm, 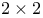 blocks 155 blocks 155
QZ algorithm, choice of double shift 148
QZ algorithm, computation of eigenvectors 155
QZ algorithm, deflation 150 153
QZ algorithm, eigenvalues only 152
QZ algorithm, operation count 150Ч152
QZ algorithm, QZ step 148Ч152
QZ algorithm, real shifts 156
QZ algorithm, stability 152
QZ algorithm, starting the double shift 148
QZ algorithm, treatment of infinite eigenvalues 153Ч155 156
Rank 424
Raphson 418
Rational Krylov transformation 342Ч344 347
Rational Krylov transformation, no free lunch 343Ч344
Rational Krylov transformation, potential instability 343
Rayleigh (J.W. Strutt) 70 295
Rayleigh quotient 47 63 70
Rayleigh quotient and optimal residuals 70
Rayleigh quotient for generalized eigenvalue problem 136 138
Rayleigh quotient for subspaces 252
Rayleigh quotient in Arnoldi decomposition 301
Rayleigh quotient in Krylov decomposition 309
Rayleigh quotient in Lanczos decomposition 306
Rayleigh quotient method 69 71 396
Rayleigh quotient method, quadratic convergence 69
Rayleigh quotient method, relation to NewtonТs method 418
Rayleigh quotient shift see УQR algorithmФ
Rayleigh quotient, accuracy of 260
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method 252 280 381 396
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method and Lanczos algorithm 348
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method as a generalized eigenvalue problem 283
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, choosing a primitive Ritz basis 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, convergence 284 295
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, convergence, Hermitian matrix 286Ч288
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, convergence, residual 289
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, convergence, Ritz blocks and bases 288
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, convergence, Ritz value 285Ч287
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, convergence, Ritz vector 286Ч287
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, convergence, uniform separation condition 287
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, exact eigenspace 281
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, failure 282Ч283
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Galerkin method 295Ч296
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, general procedure 281
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method 293 me
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, history 295
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, oblique 283
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, optimal residual 284
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, orthogonal 284
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Petrov method 295Ч296
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, primitive Ritz basis 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, primitive Ritz vector 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, projection method 295
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, residual bound 288
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Ritz basis 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Ritz block 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Ritz pair 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Ritz space 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Ritz value 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Ritz vector 282
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, separation condition 283
Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, two levels of approximation 280Ч281
Real matrix, eigenvectors 5Ч6
Real matrix, perturbation of simple eigenvalue 38
Real Schur form 113 126 128
Real Schur form in subspace iteration 391
Real Schur form, computation by double shift QR algorithm 123Ч126
Real Schur form, computation by Householder transformation 115
Real Schur form, computing eigenvectors 126Ч128
Refined Ritz vector 289 295Ч296
Refined Ritz vector, computation 291Ч292
Refined Ritz vector, computation, basic algorithm 291
Refined Ritz vector, computation, compared with Ritz vector 291
Refined Ritz vector, computation, cross-product algorithm 291Ч292 296
Refined Ritz vector, computation, from Krylov decomposition 314
Refined Ritz vector, convergence 289Ч290
Refined Ritz vector, use of Rayleigh quotient 290
Reid, J.K. 156
Reinsch, C. 113
Relative and structured perturbation theory 54
Relative error 28
Relative error in eigenvalues 43 231
Relative error, normwise 28
Representation of symmetric matrices 159
Representation of symmetric matrices in two-dimensional arrays 159
Representation of symmetric matrices, packed storage 159
Residual 61
Residual, backward error 61 70 253 265
Residual, computation in the inverse power method 66Ч67
Residual, convergence testing 62 195Ч196
Residual, optimal 63 252 264
Resolvent 247
Reverse communication 345
Rigal, J.L. 380
Right eigenpair 2
Ritz pair see УRayleigh Ч Ritz methodФ
Ritz, W. 295
Rounding unit  27 27
Row orientation see УColumn- and row-oriented algorithmsФ
Ruhe, A. 23 295 347 367 379 380
Rutishauser, H. 110 203 394 395
S/PD generalized eigenproblem 157 229
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, B-orthogonality 230
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, banded problems 235
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, ChandrasekaranТs method 235
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, congruence transformation 229
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, diagonalization by congruences 229
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, eigenvalue 230
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, eigenvalue, condition number 231
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, eigenvalue, ill conditioned 231
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, eigenvalue, projective representation 231
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, eigenvalue, well conditioned eigenvalues not determined to high relative accuracy 231
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, eigenvector 230
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, generalized shift and invert transformation 370
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, ill-conditioned B 233Ч235
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, ill-conditioned B, use of pivoted Cholesky decomposition of B 234
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, ill-conditioned B, use of spectral decomposition of B 234
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, no infinite eigenvalues 230
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, perturbation theory 231 234Ч235
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, product problem (AB) 235
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, S/PD pencil 229
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, WilkinsonТs algorithm 231Ч233 235
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, WilkinsonТs algorithm, computation of  232Ч233 232Ч233
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, WilkinsonТs algorithm, operation count 232
S/PD generalized eigenproblem, WilkinsonТs algorithm, storage and overwriting 232
Saad, Y. 23 279 280 295 344Ч347
scalar 421
Schnabel, R.B. 418
Schur decomposition 1 10Ч12 24 55 71
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -norm
-norm 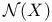
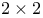 blocks
blocks 
