|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Stewart G.W. Ч Matrix algorithms. Volume 2: Eigensystems |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, depth of the recursion 183 185
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, error analysis 201
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, generalities 181Ч182
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, operation count 185
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, recursive vs. direct approach 183
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, stability 183
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, the effects of deflation 185
Divide-and-conquer algorithm for the spectral decomposition, unsuitability for graded matrices 183
Divide-and-conquer algorithms 181Ч182
Dominant eigenpair 31
Dominant eigenvalue 31
Dominant eigenvalue, defective 34
Dominant eigenvector 31
Dominant eigenvector, power method 56
Donath, W.E. 280 367
Dongarra, J.J. 23 201
Duff, I.S. 395
Eigenbasis see УEigenspaceФ
Eigenblock see УEigenspaceФ
Eigenpair 2 24
Eigenpair, complete system 7 me
Eigenpair, diagonal matrix 3
Eigenpair, dominant 31 me
Eigenpair, eigenvalue 2
Eigenpair, eigenvector 2
Eigenpair, left 2
Eigenpair, normalization 2
Eigenpair, perturbation theory, first-order 45Ч46 53
Eigenpair, perturbation theory, rigorous bounds 46Ч47 53
Eigenpair, real matrix 5Ч6
Eigenpair, right 2
Eigenpair, simple 8
Eigenpair, singular matrix 3
Eigenpair, triangular matrix 3
Eigenspace 22 115 240 247
Eigenspace, deflation 243
Eigenspace, deflation, nonorthogonal 243
Eigenspace, eigenbasis 127 242
Eigenspace, eigenblock 242
Eigenspace, eigenpair 242
Eigenspace, eigenpair, behavior under similarity transformations 242
Eigenspace, eigenpair, left 242
Eigenspace, eigenpair, orthonormal 242
Eigenspace, eigenpair, right 242
Eigenspace, examples 240
Eigenspace, existence 242
Eigenspace, left 242
Eigenspace, left, as orthogonal complement of right eigenspace 243
Eigenspace, nonuniqueness 244
Eigenspace, representation by a basis 240Ч241
Eigenspace, representation of A with respect to a basis 241
Eigenspace, residual 251 334Ч335
Eigenspace, residual bounds for eigenspaces of Hermitian matrices 262Ч263 265
Eigenspace, residual bounds for eigenvalues of Hermitian matrices 254 263Ч264 265
Eigenspace, residual, backward error 253 265
Eigenspace, residual, optimal 252 264
Eigenspace, simple 244 me
Eigenvalue 2 (see also УEigenpairФ УHermitian УSimilarity
Eigenvalue, algebraic multiplicity 4 6 12
Eigenvalue, block triangular matrix 5
Eigenvalue, characteristic equation 4 me
Eigenvalue, characteristic polynomial 4 me
Eigenvalue, continuity 37Ч38
Eigenvalue, defective 7 me
Eigenvalue, diagonal matrix 3
Eigenvalue, dominant 31 me
Eigenvalue, EisnerТs theorem 38 52
Eigenvalue, geometric multiplicity 6 12
Eigenvalue, GerschgorinТs theorem 39 me
Eigenvalue, Hermitian matrix 13
Eigenvalue, history and nomenclature 23Ч24
Eigenvalue, multiple 2 me
Eigenvalue, nilpotent matrix 12Ч13
Eigenvalue, normal matrix 14
Eigenvalue, perturbation theory 52
Eigenvalue, perturbation theory, condition 48 me
Eigenvalue, perturbation theory, derivatives 47
Eigenvalue, perturbation theory, first-order 45Ч46 53
Eigenvalue, perturbation theory, rigorous bounds 46Ч47 53
Eigenvalue, perturbation theory, simple eigenvalue 38
Eigenvalue, simple 8
Eigenvalue, singular matrix 3
Eigenvalue, skew Hermitian matrix 14
Eigenvalue, triangular matrix 3
Eigenvalue, unitary matrix 14
Eigenvector 2 (see also УEigenpairФ УHermitian УSimilarity
Eigenvector, complete system 7 me
Eigenvector, computing eigenvectors 100
Eigenvector, diagonal matrix 3
Eigenvector, dominant 31 me
Eigenvector, Hermitian matrix 13
Eigenvector, history and nomenclature 23Ч24
Eigenvector, left 4
Eigenvector, left and right 44 52Ч53
Eigenvector, normal matrix 14
Eigenvector, normalization 2
Eigenvector, null space characterization 6
Eigenvector, perturbation theory, condition 48Ч50 me
Eigenvector, perturbation theory, first-order 45Ч46 53
Eigenvector, perturbation theory, rigorous bounds 46Ч47 53
Eigenvector, real matrix 5Ч6
Eigenvector, right 4
Eigenvector, simple 8
Eigenvector, singular matrix 3
Eigenvector, triangular matrix 3
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix 195Ч200 202
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, attaining a small residual 196Ч197
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, convergence 198Ч200
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, limitations of the algorithm 200
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, loss of orthogonality 197
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, orthogonalization 197Ч198
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, orthogonalization, Gram Ч Schmidt algorithm 198
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, orthogonalization, tradeoffs in clustering 200
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, residual 195Ч196
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, solution of inverse power equation 200
Eigenvectors of a symmetric band matrix, starting vector 200
Eisenstat, S.C. 201 228 419
Eisner, L. 52 111
EisnerТs theorem 38 52 285
EISPACK, 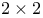 blocks in QZ algorithm 156 blocks in QZ algorithm 156
EISPACK, eigenvalues by bisection 202
Elementary reflector see УHouseholder transformationФ
Ericsson, T. 347 379 380
Exchanging eigenblocks 326Ч328 345Ч346
Exchanging eigenblocks, stability 328
Exponent exception, computing bidiagonal QR shift 223
Exponent exception, computing inertia 193
Exponent exception, eigenvector computation 102
Exponent exception, implicit double shift 119
Exponent exception, plane rotation 89
Factorization 67
Fernando, K.V. 228
Filter polynomial 317 345
Filter polynomial in Arnoldi method 317
Filter polynomial in Lanczos algorithm 352 365
Filter polynomial, Chebyshev polynomial 317 365
Filter polynomial, Leja points 365
Filter polynomial, Ritz values as roots 317
FischerТs theorem 41
fl (floating-point evaluation) 27
Flam (floating-point add and multiply) 58
Flam (floating-point add and multiply) in complex arithmetic 86Ч87
Flrot 91
Fokkema, D.R. 346
Francis, J.G.F. 110Ч112 128 170
Fraysse, V. 380
Freund, R.W. 296
Frobenius norm see УNormФ
Gaches, J. 380
Galerkin method see УRayleigh Ч Ritz methodФ
| Gaussian elimination 157
Gaussian elimination and inertia 191
Gaussian elimination, band matrix 200
Generalized eigenvalue problem 129 296
Generalized eigenvalue problem, background 155
Generalized eigenvalue problem, characteristic polynomial 133
Generalized eigenvalue problem, chordal distance 138 155
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenpair 130
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenpair, left 130
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenpair, perturbation of 136Ч137
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenpair, right 130
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvalue 130
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvalue, algebraic multiplicity 133
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvalue, condition 140
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvalue, first-order expansion 137
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvalue, perturbation bound 140
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvalue, projective representation 134 231
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvector 130
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvector, condition 143
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvector, first-order expansion 141Ч142
Generalized eigenvalue problem, eigenvector, perturbation bound 142Ч143
Generalized eigenvalue problem, equivalence transformation 131
Generalized eigenvalue problem, equivalence transformation, effect on eigenvalues and eigenvectors 132
Generalized eigenvalue problem, generalized Schur form 132 me
Generalized eigenvalue problem, generalized shift-and-invert transform 368 me
Generalized eigenvalue problem, Hessenberg-triangular form 144Ч147 me
Generalized eigenvalue problem, infinite eigenvalue 131
Generalized eigenvalue problem, infinite eigenvalue, algebraic multiplicity 133
Generalized eigenvalue problem, infinite eigenvalue, condition 140
Generalized eigenvalue problem, nonregular pencils 130Ч131
Generalized eigenvalue problem, pencil 130
Generalized eigenvalue problem, perturbation theory 136 155 eigenpairФ УGeneralized eigenvalueФ УGeneralized eigenvectorФ)
Generalized eigenvalue problem, QZ algorithm 147Ч148 me
Generalized eigenvalue problem, Rayleigh quotient 136 138
Generalized eigenvalue problem, real generalized Schur form 143 me
Generalized eigenvalue problem, reduction to ordinary eigenproblem 134 368Ч369
Generalized eigenvalue problem, regular pair 131
Generalized eigenvalue problem, regular pencil 131
Generalized eigenvalue problem, residual 369
Generalized eigenvalue problem, residual, backward error 369 380
Generalized eigenvalue problem, right and left eigenvectors 135
Generalized eigenvalue problem, shifted pencil 134Ч135
Generalized eigenvalue problem, simple eigenvalue 133
Generalized eigenvalue problem, Weierstrass form 132
Generalized Schur form 55 132 155
Generalized Schur form, order of eigenvalues 133
Generalized Schur form, real generalized Schur form 143
Generalized shift-and-invert transform 368 379Ч380
Generalized shift-and-invert transform, bounding the residual 370
Generalized shift-and-invert transform, matrix-vector product 369
Generalized shift-and-invert transform, S/PD pencils 370
Generalized singular value decomposition 236Ч237
Generalized singular value decomposition, computation via the CS decomposition 236Ч237
Generalized singular value decomposition, relation to the S/PD eigenproblem 236
Geometric multiplicity see УEigenvalueФ
Gerschgorin, S.A. 52
GerschgorinТs theorem 39 52 193
GerschgorinТs theorem, diagonal similarities 40Ч41
GerschgorinТs theorem, Gerschgorin disks 39
Givens rotation 170 (see also УPlane rotationФ)
Givens, W. 170 201
Goldstine, H.H. 203
Golub, G.H. 23 24 201 227 264 367
Graded matrix 108 113 200
Graded matrix and balancing 110
Graded matrix and the QR algorithm 108Ч110
Graded matrix, bidiagonal QR algorithm 227Ч228
Graded matrix, JacobiТs method 203
Graded matrix, types of grading 108
Gram Ч Schmidt algorithm 198 303
Gram Ч Schmidt algorithm, B variants 372
Gram Ч Schmidt algorithm, gsreorthog 198 304
Gram Ч Schmidt algorithm, modified 307 359
Grcar, J.F. 365
Greek-Latin equivalents 421
Grimes, R.G. 367
Gsreorthog see УGram Ч Schmidt algorithmФ
Gu, M. 201 228
Gutknecht, M.H. 367
Hadamard, M.J. 110
Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra 112
Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra, balancing for eigenvalue computations 112
Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra, eigenvalues by bisection 202
Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra, eigenvectors by the inverse power method 202
Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra, JacobiТs method 203
Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra, S/PD eigenproblem 235
Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra, singular value decomposition 227
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method 293 296 411
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, computation 293Ч294
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, computation, from Krylov decomposition 314Ч315
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, computation, Hermitian matrix 294
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, computation, ordinary eigenproblem 294
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, computation, Rayleigh quotient 294
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, exact eigenspace 293
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, generalized eigenvalue problem 296
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, harmonic Ritz pair 292
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Hermitian matrix 296
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, Rayleigh quotient preferred to harmonic Ritz value 294 336
Harmonic Rayleigh Ч Ritz method, screening of spurious eigenpairs 293
Hermitian matrix see УSymmetric matrixФ
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue 13 52
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue, condition 42Ч43
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue, FischerТs theorem 41
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue, Hoffman Ч Wielandt theorem 43
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue, interlacing theorem 42
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue, min-max characterization 41
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue, perturbation 42
Hermitian matrix, eigenvalue, principal submatrix 42
Hermitian matrix, eigenvector 13
Hermitian matrix, residual bounds for eigenspaces 262Ч263 265
Hermitian matrix, residual bounds for eigenvalues 254 263Ч264 265
Hermitian matrix, sep 51
Hermitian matrix, special properties 157
Hessenberg form 81
Hessenberg form of a symmetric matrix 158
Hessenberg form, Householder reduction 83Ч88 110Ч111
Hessenberg form, Householder reduction, accumulating transformations 86
Hessenberg form, Householder reduction, first column of the accumulated transformation 87
Hessenberg form, Householder reduction, operation count 86
Hessenberg form, Householder reduction, overwriting original matrix 87
Hessenberg form, Householder reduction, stability 87 111
Hessenberg form, implicit Q theorem 116 me
Hessenberg form, nonorthogonalreduction 111
Hessenberg form, uniqueness of reduction 116
Hessenberg form, unreduced 116 me
Hessenberg QR algorithm, ad hoc shift 100 105
Hessenberg QR algorithm, applying transformations to deflated problems 95Ч96
Hessenberg QR algorithm, basic QR step 92Ч94
Hessenberg QR algorithm, basic QR step, operation count 92
Hessenberg QR algorithm, basic QR step, stability 94
Hessenberg QR algorithm, complex conjugate shifts 115
Hessenberg QR algorithm, deflation 94Ч95 112
Hessenberg QR algorithm, deflation, aggressive deflation 105Ч106 112 123
Hessenberg QR algorithm, deflation, applying transformations to deflated problems 95Ч96
Hessenberg QR algorithm, deflation, double shift algorithm 123
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals 94Ч95
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, 2x2 blocks 129
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, backward stability 94
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, deflation 123
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, double shift algorithm 123Ч126
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, normwise criterion 94Ч95
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, operation count 123
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, QR step 120Ч123
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, relative criterion 95
Hessenberg QR algorithm, detecting negligible subdiagonals, stability 126
Hessenberg QR algorithm, explicit shift algorithm 98Ч100
Hessenberg QR algorithm, explicit shift algorithm, convergence 98Ч100
Hessenberg QR algorithm, explicit shift algorithm, eigenvalues only 100
Hessenberg QR algorithm, explicit shift algorithm, operation count 100
Hessenberg QR algorithm, explicit shift algorithm, searching for negligible subdiagonal elements 96Ч97
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



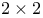 blocks in QZ algorithm
blocks in QZ algorithm