јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Winterbone D.E. Ч Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Advanced thermodynamics for engineersјвтор: Winterbone D.E. јннотаци€: Although the basic theories of thermodynamics are adequately covered by a number of existing texts, there is little literature that addresses more advanced topics. In this comprehensive work the author redresses this balance, drawing on his twenty-five years of experience of teaching thermodynamics at undergraduate and postgraduate level, to produce a definitive text to cover thoroughly, advanced syllabuses.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /“ермодинамика, статистическа€ физика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 378ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.10.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
8 101 105 acetylene 185 217 300 Acid rain 286 Activation energy 279Ч285 311 Activity coefficient 353 Adiabatic combustion 187Ч205 Adiabatic compressibility 115 Adsorption, gas molecules 294 Air 152 159 Air standard cycle 71 189 208 Air, composition 159 Air-fuel ratio 30Ч31 186Ч188 225 265Ч272 292 Air-fuel ratio, lean(weak) 186 223 245 265Ч272 301 Air-fuel ratio, rich 186 222 224 245 252 265Ч272 301 Air-fuel ratio, stoichiometric 186 216Ч217 233 267 269 299 Alcohols 185 213 217 Alkanes 138 185 217 Alkenes 185 217 Amagat's Law 121Ч122 Ammonia 296 Amount of substance 7 100 158Ч159 172Ч177 189 196Ч205 219Ч259 268 275 319 348 Annular combustion chamber 313 Aqueous solution 347Ч353 Argon 159 Aromatics 217 Arrhenius equation 279 294 299 311 Atmospheric nitrogen 159 Atomic nitrogen 242Ч245 273 282 Atomic oxygen 164 242Ч245 273 282Ч284 Atomic weight 158 Atomisation 211 Atomisation energy 208Ч215 Availability 13Ч36 64 359 Availability balance 27Ч36 Availability transfer 29 Availability, change of 18 22Ч29 Availability, closed system 18 27Ч30 Availability, effect of change of entropy 32 Availability, effect of change of volume 30 Availability, effect of combustion 30Ч34 Availability, flow 21 35 Availability, loss of 13Ч36 Availability, molar 15 Availability, non-flow 15 18 30 Availability, open system 34Ч36 Availability, rate of change 29 35 Availability, reaction 31 40Ч41 Availability, specific 15 19 27Ч29 Availability, steady flow 21 35 Availability, work 29 Available energy 21Ч26 36 67 Avogadro's hypothesis 159 Avogadro's number 340 347 Barrel swirl (tumble) 307 Baruah 268 Beattie Ч Bridgeman equation 128 Bejan 85 Benson 164 benzene 202 209Ч210 217 225 Benzoic acid 215 Bertholet equation 129 Binary cascade cycle 137 Boiler 276 291 Boiling point 137 Boltzmann constant 340 Bond energy 40 182 187 208Ч217 291 348 Bond energy, atomisation energy 209Ч217 Bond energy, dissociation energy 209Ч217 Bond energy, minimum potential energy 208Ч211 Bosch Smoke Number 287 Boyle's law 121Ч122 Bradley 303 Brake thermal efficiency 304 Branching reactions 295Ч296 Bronchial irritants 286 Bunsen burner 297 305 Butane 135Ч136 185 192 217 296 Calorific value 64 Calorific value, higher 188Ч205 Calorific value, lower 188Ч205 Carbon dioxide 9 40 135 139Ч140 159 164 168 182Ч205 209 211 218Ч275 292 345 Carbon monoxide 1 9 40 159 164 168 184Ч192 218Ч275 285 288 296 300 Carbon particulates 285 287 312 Carbon-12 158Ч159 192 Carbon/hydrogen ratio 185 224 270 272 Carnot cycle 21 65 68 85 89 Carnot efficiency 65Ч82 85Ч96 345 Cascade 137 Cascade, binary cycle 137 Cascade, ternary cycle 137 Catalytic converters 288 Cetane 217 Cetane number 311 Chain reaction 295Ч296 Charles' law 121Ч122 Chemical bonds 187 208Ч217 354 Chemical composition 186Ч188 196Ч206 229Ч238 245Ч257 265Ч285 Chemical equilibrium 218Ч257 Chemical kinetics 8 194 245 265 275 276Ч289 295 299 306 chemical potential 7 8 100 165 220Ч231 319 332 334Ч337 349Ч353 Chemical potential, standard 227Ч230 Chemical reaction 185Ч285 Chemical structure of fuels 208Ч217 Chemistry, combustion 184Ч187 208Ч217 Chlorine 351 Clapeyron equation 117 Clausius equation of state 123 Clausius inequality 14 Clausius Ч Clapeyron equation 115 117 Closed system 5Ч7 13Ч21 27Ч34 218 Coal 185 Coefficient of expansion 114 123Ч125 144 Coefficient of performance 137Ч138 Cold utility 47Ч60 Combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) 47 92 287 Combined cycle heat engine 92Ч96 137 Combustion 182Ч313 Combustion chamber 307Ч313 Combustion systems, diesel 309Ч312 Combustion systems, gas turbine 312Ч313 Combustion systems, spark ignition 307Ч309 Combustion with heat transfer 194 199 Combustion with work transfer 194 Combustion zones, gas turbine 313 Combustion, adiabatic 187Ч274 Combustion, chemistry 184Ч187 208Ч217 Combustion, constant pressure 193 202 312 Combustion, constant volume 193 196 199Ч202 233Ч238 245Ч257 267Ч275 Combustion, diffusion 291 Combustion, energy equation 188Ч205 245Ч257 Combustion, exergy change 40 Combustion, heat release 208 312 Combustion, heterogeneous 183 292 305Ч306 Combustion, homogeneous 183 292 296Ч305 Combustion, incomplete 195 204 233Ч238 245Ч257 Combustion, initiation 304Ч305 310 Combustion, laminar 183 296Ч302 Combustion, multi-phase 183 Combustion, non-premixed 183 305Ч306 309Ч313 Combustion, premixed 292Ч305 307Ч309 Combustion, rich mixture 186 195 202Ч205 224 233Ч238 252Ч254 267Ч274 Combustion, single-phase 183 Combustion, speed of 297Ч304 Combustion, three dimensional 183 Combustion, turbulent 183 302Ч303 Combustion, two-dimensional 183 Combustion, weak mixture 186 200 223 245Ч252 267Ч274 Combustion, zero-dimensional 183 Composite diagram 55 60 Composite temperature - heat load diagram 51 57 Compressibility, adiabatic 115 Compressibility, factor 129 Compressibility, isentropic 115 Compressibility, isothermal 114Ч115 125 Compression coefficient 129 Compression, isentropic 15Ч18 24Ч25 65Ч82 Compressor 24Ч25 76Ч82 Concentration component 319 Concentration gradient 316 332 335 360 Concentration, molar 277Ч284 Condenser 69Ч76 Conductance, heat transfer 92Ч95 Conduction of electricity 318 322Ч332 Conduction of heat 317 319Ч332 Conjugate fluxes 319Ч342 Conjugate forces 319Ч342 copper 347Ч351 Copper sulfate 347Ч351 Corresponding states, law of 125Ч129 Coulombic forces 348 Counterflow heat exchanger 37Ч40 coupled equations 316Ч342 Coupled processes 319Ч342 Coupling matrix 319Ч342 Critical isotherm 125Ч127 Critical point 124Ч131 135 Critical point, water 126 135 Critical pressure 124 135 140 Critical temperature 124 135 146 Critical volume 124 Cross-coupling 316Ч342 Crude oil 184 Current, electric 316 322Ч332 347Ч361 Current, electric, density 321Ч332 Cycle calculations 30Ч34 48 69Ч82 Cycle efficiency 69Ч82 Cycles, air standard 71 189 208 Cycles, bottoming 34 Cycles, Carnot 21 65 68 85 89 Cycles, Diesel 68 Cycles, endo-reversible 65Ч82 85Ч96 Cycles, gas turbine, see Joule Cycles, internally reversible 65Ч82 85Ч96 Cycles, irreversible 65Ч82 Cycles, Joule 68 76Ч82 Cycles, Otto 30Ч34 68 267 Cycles, Rankine 69Ч76 79 Cycles, reversible 65 Cycles, Stirling 85 Cyclone separator 288 Dalton Principle 172 Damkohler 302 Daniell cell 345Ч351 Datum pressure, also standard pressure 164 228Ч229 de Groot 333 dead state 14Ч43 65Ч82 Dead state, pressure 14Ч43 Dead state, temperature 14Ч43 65Ч82 Debye theory 162 Deflagration 183 296Ч305 Delocalised electrons 210 Desorption, gas molecules 294 Destruction of availability 24Ч29 39Ч41 Detonation 183 296 309 Diatomic 184 Diesel cycle 68 Diesel engine 309Ч312 Diesel oil 217 Dieterici equation of state 129 Diffuser 313 Diffusion 175 294 319 332Ч339 359 Diffusion, burning 287 305Ч306 311 Diffusion, flames 291 297 305Ч306 Diffusivity mass 298 332Ч342 Diffusivity, thermal 298 303 332Ч342 Dilution zone 313 Direct injection engines 309Ч312 Dissociation 7 182 194Ч195 265Ч275 Dissociation energy 208Ч210 214 Dissociation, degree of 218Ч259 Dissociation, effect of pressure 239Ч240 Dissociation, effect of temperature 239Ч241 Dry ice (carbon dioxide) 139 Dryness fraction (quality) 137 150 Dufour effect 332Ч338 Dynamic equilibrium 218 222 349 Eddy diffusivity 302 Efficiency at maximum power 85Ч96 Efficiency, cycle 64Ч82 Efficiency, fuel cell 357Ч359 Efficiency, isentropic 22Ч25 30Ч34 69Ч82 Efficiency, overall 64 Efficiency, rational 65Ч82 154 359 Efficiency, thermal 17 64Ч82 85Ч96 292 355 Electrical cells 346Ч351 Electrical conduction 316 323Ч332 345Ч361 Electrical flow 323Ч332 Electrochemical potential 349Ч361 Electrode 346Ч351 Electrostatic precipitator 288 Elementary reaction 278 End gas 309 Endoreversible heat engine 85Ч96 Endothermic reaction 184 256 273Ч275 295 energy equation 5Ч6 14Ч15 27 34 58 86 143 189Ч205 233Ч257 347Ч349 Energy equation, steady flow 58 89 143 189Ч205 Energy equation, unsteady flow 34 Energy, available 13Ч36 Energy, Gibbs see Gibbs energy Energy, Helmholtz see Helmholtz energy Energy, internal 5Ч9 13Ч34 37Ч40 100Ч118 160Ч178 187Ч205 245Ч257 Energy, potential 1Ч4 Energy, unavailable 6 21Ч22 26 37 67 80 Engine, combustion systems 307Ч313 Engine, diesel 276 286Ч287 291 305 309Ч312 Engine, irreversible 65 Engine, petrol see spark-ignition Engine, reversible 5 17 21 26 65 85Ч96 Engine, spark-ignition 208 276 291 304 307Ч309 Engine, stratified charge 305 Enthalpy 6Ч9 22Ч25 34Ч36 40Ч43 100Ч118 141Ч154 160Ч175 187Ч205 245Ч257 Enthalpy coefficients of gases 167Ч170 Enthalpy of formation 65 187Ч205 209Ч217 241Ч242 Enthalpy of products 188Ч205 245Ч257 Enthalpy of reactants 188Ч205 245Ч257 Enthalpy of reaction 40Ч41 64 187Ч217 355Ч361 Enthalpy, molar 160 165 174 Enthalpy, specific 160 337 Enthalpy-temperature diagram 188Ч205 entropy 3Ч7 19Ч43 64Ч82 91 100Ч118 162Ч178 218Ч221 316Ч342 Entropy change 3 19 23 28 37 39 117 348 Entropy change due to mixing 175Ч178 229Ч231 Entropy creation 3Ч4 317Ч322 333 336 Entropy flow 5 317Ч322 Entropy flux 321Ч336 Entropy generation see creation Entropy mixtures 175Ч178 229Ч231 Entropy of transport 324Ч332 Entropy production see creation Entropy, ideal gas 23Ч25 77Ч82 162 165Ч166 Entropy, maximum 4 319 Environment 23 see Equation of constraint 227 Equations of state 121Ч131 158Ч159 Equations of state, Beattie Ч Bridgeman 128 Equations of state, Bertholet 129 Equations of state, Dieterici 129 Equations of state, ideal gas 105Ч107 110 121Ч123 144 159Ч178 195Ч205 233Ч238 Equations of state, perfect gas see also ideal gas 15Ч19 30Ч34 76Ч82 Equations of state, van der Waals' gas 123Ч128
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



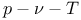 diagram
diagram