Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Higham N. — Accuracy and stability of numerical algorithms
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Accuracy and stability of numerical algorithmsАвтор: Higham N. Аннотация: Treats the behavior of numerical algorithms in finite precision arithmetic, combining algorithmic derivations, perturbation theory, and rounding error analysis and emphasizing software practicalities, with particular reference to LAPACK and MATLAB. Includes historical perspectives, especially on the work of Wilkinson and Turing, with quotations introducing chapters on subjects such as floating point summation, condition number estimation, and the Sylvester equation. Although designed as a reference rather than a text, it includes problems and solutions. Annotation c. by Book News, Inc., Portland, Or.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Численные методы /Численный анализ /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1996Количество страниц: 688Добавлена в каталог: 23.02.2005Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
64 500—501 205 218 69 74 46—47 492 495 352 3M method 450 461 505 3M method, error analysis 458—459 Aasen, Jan Ole 226 Aasen’s method 226 229 Abdelmalek, Nabih N. 385 410 Abramowitz, Milton 35 Absolute error 4 Absolute norm 119 Accuracy versus precision 7 33 ACRITH 486 Acton, Forman S. 35 203q 285 Adams, Duane A. 113 Aggarwal, Vijay B. 84 Ahac, Alan A. 198 Ahlberg, J. H. 167 Aitken extrapolation 101 Aitken, A. C 383 Albers, Donald J. 513 n Alefeld, Goltz 486 Alexopolous, Aristides G. 54 Allen, Jr., Richard C. 84 Almacany, Montana 425 q Alternating directions method 477 Aluru, Srinivas 459 Alvarado, Fernando L. 165 Amato, James J. 323 Ames, William F. 32 Amodio, Pierluigi 197 Anda, Andrew A. 385 Anderson, E. 289 q Anderson, T. W. 527 Ando, T. 196 Approximation theory, references for rounding error analysis 32 Arioli, Mario 143 304 328 343 410 411 421 422 Arnold, William F. 323 Ashenhurst, R. L. 489 Asplund, Edgar 305 Atanasoff, John V. 151 q Augment precompiled 486 504 506 Augmented system matrix 393 Augmented system matrix, scaling and conditioning 402 Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) 56 189t 195 343 Automatic differentiation 488 Automatic error analysis 473—490 (see also “Interval analysis; running error analysis”) Automatic error analysis, condition estimation 480—481 Automatic error analysis, solving a cubic 483—484 Automatic error analysis, Strassen’s inversion method 481—482 Automatic error analysis, using direct search optimization 474—477 Axelsson, Owe 343 Babuska, Ivo 100 Bachelis, Boris 61 Backward error 7—8 Backward error analysis in differential equations 33 Backward error analysis, development by Wilkinson 33—34 189 Backward error analysis, motivation 7 Backward error analysis, not a panacea 1q Backward error analysis, purpose 71—72 203 Backward error, componentwise 134 141 Backward error, componentwise relative 134 Backward error, componentwise, evaluating 143 Backward error, definition 7 Backward error, least squares problem 404—407 413 Backward error, linear system, Oettli — Prager theorem 135 Backward error, linear system, Rigal — Gaches theorem 14 132 Backward error, Lyapunov equation 316—317 Backward error, mixed forward-backward error 8 Backward error, norm wise relative 132 Backward error, normwise 132 Backward error, preserving symmetric structure 149 406—407 Backward error, structured 141 Backward error, Sylvester equation 313—316 Backward error, underdetermined system 419 423 Backward stability, componentwise 142 Backward stability, definition 8 Backward stability, normwise 142 Bai, Zhaojun 322 352 527 Bailey, David H. 448 460 461 471 482 491q 505 Baksalary, J. K. 323 324 Ballester, C. 441 Banded matrix, growth factor 183 Bane, Susanne M. 461 Bank, Randolph E. 257 Bareiss, E. H. 53 191 Bargmann, V. 186 Barlow, Jesse L. 33 51 53 191 193 301 385 411 412 Barnett, S. 323 Barone, John L. 391q 410 Barrett, Geoff 59 Barrlund, Anders 194 198 224 Bartels — Stewart method 311—313 Bartels, R H. 312 Bartels, Sven G. 141 304 441 Barwell, Victor 226 Bauer, F. L. 57 83 119 126 139 146 148 149 191 284 551 Bauer’s scaling theorem 139 146 Beam, Richard M. 527 Beaton, Albert E. 391q 410 Bell, E. T. 281 q Bellman, Richard 324 Benford, Frank 51 Benoit, Commandant 224 Benschop, N. F. 327 Berman, Abraham 147 579q 580 Bhatia, Rajendra 322 382 Bilinear noncommutative matrix multiplication algorithm 449—450 Bilinear noncommutative matrix multiplication algorithm, error analysis 456—457 Binary-decimal conversion 61—62 Bini, Dario 441 456 457 Birkhoff, Garrett 32 281 483 Bischof, Christian H. 299 301 370 384 Bit 60 Bj0rstad, Petter 461 Bjorck, Ake 83 242 361q 379 385 386 388 397 399 400 402 403 409—411 422 423 434 436 441 570 Blanch, G. 507 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms) 586—587 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms), fast level 3 460 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms), level 2 extended precision extension 506 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms), xnrm2 (2-norm) 502—503 510—511 Bliss, B. 488 Block algorithm, advantages of 245 q Block algorithm, definition 246 Block diagonal dominance 251—255 257 Block diagonal dominance and block LU factorization 252—255 Block diagonal dominance, definition 251 Block LU factorization 246—259 Block LU factorization, computation 247 Block LU factorization, definition 246 Block LU factorization, error analysis 250—257 Block LU factorization, existence and uniqueness 247 Block LU factorization, stability for (point) diagonally dominant matrix 255 Block LU factorization, stability for block diagonally dominant matrix 251—255 Block LU factorization, stability for block tridiagonal matrix 258 Block LU factorization, stability for symmetric positive definite matrix 255—257 Blue, James L. 502 Bodewig, E. 188 Bohlender, Gerd 98 Bohte, Z. 183 Boley, Daniel 243 Bollen, Jo A. M. 328 Bondeli, S. 525 Boros, T. 441 Borwein, J. M. 491q Borwein, P. B. 491q Bowden, B. V. 203q Bowdler, H. J. 196 Boyd, David W. 291 293 304 Boyle, Jeff 51 Brent, Richard P. 51 162 164 448 451 453 460 486 504 508 Briggs, William L. 470 Brightman, Tom 60 Brown, W. S. 498 501 Brunet, Marie-Christine 53 488 Buchan, John 62q Buchanan, James L. 165 Buchholz, W. 60 Bukhberger, B. 305 Bulirsch, R 83 84 190 Bunch — Kaufman factorization 221—223 Bunch — Parlett factorization 219—220 Bunch, James R 141 146 149 219—221 225 226 231q Buoni, John J. 198 Burgmeier, James W. 84 Businger, Peter A. 146 193 410 Butcher, J. C 100 Byers, Ralph 305 320 323 324 353 567 BYTE 60 Caffney, John 520 Calculator, displaying words on 37 Calve, M. P. 32 Calvetti, D. 440—442 Calvin (and Hobbes) 473q Campbell, S. L. 337 Campbell-Kelly, Martin 245q Cancellation 10—11 30 Cancellation in summation 91 543 Cancellation of rounding errors 21—26 Cancellation, not a bad thing 11 Canuto, Claudio 32 Cao, Wei-Lu 305 Caprani, Ole 100 Cardano, Geronimo 483 Carr III, John W. 57 Carter, Russell 496 Cauchy matrix 516—517 Cauchy matrix, inverse 516 Cauchy matrix, LDU factors 516—517 Cauchy — Schwarz inequality 119 Cauchy, Augustin-Louis 516 Cayley, Arthur 446 CELEFUNT 499 Chaitin-Chatelin, Francoise 53 358 488 Chan, Raymond H. 471 Chan, Tony F. 13 33 146 147 386 Chandrasekaran, Shivkumar 136 141 386 Chang, Xiao-Wen 225 Chaos, references for rounding error, analysis 32 Chartres, Bruce A. 190 Chatelin, Francoise see “Chaitin-Chatelin Francoise” Chebyshev spectral differentiation matrix 346 355 Choi, Man-Duen 513q 526 Cholesky factorization 204 Cholesky factorization, computation of 205 Cholesky factorization, conditions for success in floating point 208—209 Cholesky factorization, error analysis 205—209 Cholesky factorization, existence and uniqueness 204 Cholesky factorization, perturbation bounds 209—210 Cholesky factorization, semidefinite matrix, complete pivoting 211 Cholesky factorization, semidefinite matrix, computation of 210—211 Cholesky factorization, semidefinite matrix, error analysis 214—218 Cholesky factorization, semidefinite matrix, existence and uniqueness 210 Cholesky factorization, semidefinite matrix, perturbation theory 211—214 Cholesky factorization, semidefinite matrix, termination criteria 217—218 Cholesky, Andre-Louis 224 Chopping 57 Christiansen, S0ren 146 Chu, Eleanor 193 Chu, King-wah Eric 323 Cipra, Barry A. 32 Circulant matrix 468 Circulant preconditioned 471 Circulant system, error analysis for solution by FFT 468—470 CLAPACK 588 Clasen, B.-L 284 Clenshaw, C. W. 32 53 113 Cline, Alan K. 289q 297 299 411 480 Cline, R. E. 422 Clinger, William D. 61 Cody, Jr., William J. 39q 54 55 59 60 495 497 499 504 Cohen, A. M. 180 522 Colon notation 2—3 Companion matrix 525—526 Companion matrix, singular values 525—526 Comparison matrix 157 Compensated summation 92—97 Complete pivoting 170 Complete pivoting, early use of 196 Complete pivoting, fallacious criticism of 200 Complete pivoting, growth factor 180—181 197 Complete pivoting, growth factor, conjecture proved false 181 Complex arithmetic, error analysis 78—80 84 Complex number, division without overflow 503—504 509 Complex number, square root of 36 Componentwise relative error 5 Concus, P. 257 Condition number of function 9 Condition number of linear system, componentwise 135 Condition number of linear system, normwise 133 Condition number of rectangular matrix 392 Condition number of square matrix 121—123 126 Condition number of summation 100 Condition number, distance to singularity and 123 126 140 Condition number, estimation 289—308 Condition number, estimation for tridiagonal matrices 301—303 Condition number, estimation, counterexamples 289q 294—296 299 304 305 Condition number, estimation, counterexamples by direct search 480—481 Condition number, estimation, incremental 301 Condition number, estimation, LAPACK estimator 294—297 480—481 Condition number, estimation, probabilistic methods 300—301 Condition number, estimation, UNPACK estimator 297—299 Condition number, general theory 33 Condition number, Hadamard 281 287 Condition number, minimizing by scaling 136—139 146 Condition number, Skeel’s 135 Conjugate gradient method 328 329 341 Conte, Samuel D. 190 Continued fraction, algorithms and error analysis 507 Continued fraction, evaluating in IEEE arithmetic 492—493 Continued fraction, running error bound 85 Convergent matrix 348 Conversion, binary-decimal 61—62 Cooley, James W. 470 Coomes, Brian A. 32 Coonen, Jerome T. 59 495 Cope, J. E. 145 Coppersmith, Don 448 Corless, Robert M. 32 Corm, Andrew R. 299 Correct significant digits 4—5 32 Cortes, Joaquin 197 Cottle, Richard W. 224 Cox, M. G. 32 Cramer’s rule, (instability of 14—15 34 37 Cray computers, adoption of IEEE arithmetic 49 Cray computers, arithmetic on 39q 495 Cray computers, puzzling results from Cray Y-MP and Cray 2 496—497 Cray computers, UNICOS library 448 450 Crout, Prescott D. 195 Crout’s method 174 Cryer, Colin W. 180 181 196 CS decomposition 388 408 Cubic equation, Newton’s method 489—490 Cubic equation, stability of explicit formulae for roots 483—484
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



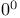 , definition
, definition  problems, reliable solution of
problems, reliable solution of 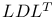 factorization
factorization 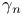 (error constant), definition
(error constant), definition  (IEEE arithmetic)
(IEEE arithmetic)  -pseudospectral radius
-pseudospectral radius