јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Higham N. Ч Accuracy and stability of numerical algorithms
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Accuracy and stability of numerical algorithmsјвтор: Higham N. јннотаци€: Treats the behavior of numerical algorithms in finite precision arithmetic, combining algorithmic derivations, perturbation theory, and rounding error analysis and emphasizing software practicalities, with particular reference to LAPACK and MATLAB. Includes historical perspectives, especially on the work of Wilkinson and Turing, with quotations introducing chapters on subjects such as floating point summation, condition number estimation, and the Sylvester equation. Although designed as a reference rather than a text, it includes problems and solutions. Annotation c. by Book News, Inc., Portland, Or.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /„исленные методы /„исленный анализ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1996 оличество страниц: 688ƒобавлена в каталог: 23.02.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Halmos, Paul R. 513q Hamada, Hozumi 54 Hammarling, Sven J. 322 326 327 385 503 Hammel, Stephen M. 32 Hammer, Rolf 487 Hamming, R. W. 57 443 Handy, Susan L. 412 Hansen, Per Christian 146 386 461 Hanson, Richard J. 385 409 410 422 503 Harris, P. M. 32 Harter, Richard 459 Hartfiel, D. J. 146 Harwell Ч Boeing sparse matrix collection 527 Hearon, John Z. 315 Heath, Michael T. 261q 399 Hein, Piet 36q 127q Helvin, Marie 166q Henderson, Harold V. 323 490 Hennessy, John L. 39n 57 Henrici, Peter 32 52 53 67q 84 351 Henson, Van Emden 470 HeronТs formula 50 Heroux, Michael 460 575 Herzberger, Jurgen 486 Hessenberg matrix, determinant of 27Ч28 34 282Ч283 Hessenberg matrix, Gaussian elimination 27Ч28 34 Hessenberg matrix, growth factor for 182 Hewer, Gary 323 Hewlett Ч Packard HP 48G calculator, condition estimator 304 Hewlett Ч Packard HP 48G calculator, exhausting its range and precision 17Ч18 Hidden bit 45 Higham, Desmond J. 32 126 141 149 178 179 195 345q 348 407 441 Higham, Nicholas J. 72 100 141 145 164 165 178 179 195 197 223 225 242 243 248 250Ч253 257 265 272 273 284 295 300 304Ч307 322 324 328 329 354 356 358 384 389 422 440 443 460 461 489 508 574 577 Hilbert matrix 514Ч517 Hilbert matrix, Cholesky factor 515 Hilbert matrix, inverse 515 Hilbert, David 526 Hildebrand, F. B. 33 39q Hocks, Matthias 487 Hodel, A. Scottedward 323 Hodges, Andrew xxvii Hoffman, A. J. 386 Hoffmann, Christoph M. 34 Hoffmann, W. 284 385 Holder inequality 118 119 HomerТs method 104Ч115 HomerТs method for derivatives 106Ч109 HomerТs method for rational function 29 HomerТs method, running error bound 105Ч106 113 Hooper, Judith A. 504 Horn, Roger A. 119 150 310 348 546 551 555 558 580 Horning, Jim 491q Hotelling, Harold 186 187 445 Hough, David 47 509 HoughТs underflow story 509Ч510 Householder transformation 362Ч363 Householder transformation in QR factorization 363Ч364 Householder transformation, aggregated (WY representation) 370Ч371 Householder transformation, block 384 Householder transformation, error analysis 364Ч369 Householder transformation, history of 383 Householder, Alston S. 2 117q 126 160 172 383 410 565 Hull, T. E. 52 61 488 506 530 Huskey, H. D. 188 Hussaini, M. Yousuff 32 Hyman, M. A. 282 HymanТs method 34 282Ч283 287 IBM, ESSL library 448 450 IEEE arithmetic 43 45Ч48 IEEE arithmetic, 46Ч47 492 495 IEEE arithmetic, double rounding 48 63 541 IEEE arithmetic, exception handling 46 493Ч495 IEEE arithmetic, exceptions 4647 IEEE arithmetic, exploiting in software 492Ч495 IEEE arithmetic, extended formats 47 IEEE arithmetic, gradual underflow 47 IEEE arithmetic, implementation using formal methods 59Ч60 IEEE arithmetic, nan 46 492 495 IEEE arithmetic, parameters 41t 45 IEEE arithmetic, recommended auxiliary functions 495 IEEE arithmetic, rounding modes 46 IEEE arithmetic, signed zeros 46 IEEE arithmetic, Standard 754 45 IEEE arithmetic, Standard 854 48 IEEE arithmetic, subnormal numbers 47 495 Ikebe, Yasuhiko 303 305 307 Incertis, F. 512 Index of a matrix 336 Inner product in extended precision 70 Inner product, error analysis 68Ч71 Inner product, reducing constant in error bound 69 Intel Pentium chip, division bug 59 Internet 582 Interval analysis 46 198 485Ч487 Interval analysis, dependencies 485 Interval analysis, fallibility 487 Interval analysis, Gaussian elimination 485Ч486 Interval analysis, super-accurate inner product 486 Interval arithmetic see УInterval analysisФ Inverse iteration 27 Inverse matrix 261Ч287 Inverse matrix in solving Ax = b, stability 262 Inverse matrix, bound using diagonal dominance 167 Inverse matrix, error analysis for Gauss Ч Jordan elimination 277Ч281 Inverse matrix, error analysis for LU factorization 270Ч275 Inverse matrix, error analysis for triangular matrix 265Ч270 Inverse matrix, high accuracy computation of 284 Inverse matrix, left and right residuals 263Ч264 Inverse matrix, perturbation theory 140 Inverse matrix, times for computation on early computers 276t Inverse matrix, triangular, bounds for 159Ч161 Inverse matrix, triangular, error analysis 265Ч270 Inverse matrix, why not to compute 262 Involutary matrix 521 Ipsen, Use C. F. 136 141 147 385 386 Iri, Masao 53 488 Isaacson, Eugene 189 257 Iterative methods see УStationary iterative methodsФ Iterative methods, dates of publication 326t Iterative methods, error analysis 329Ч341 Iterative methods, error analysis, survey of 327Ч329 Iterative methods, stopping criteria 341Ч342 Iterative refinement 30 188 231Ч244 497 Iterative refinement for least squares problem 399Ч403 410 Iterative refinement for Vandermonde system 438Ч440 Iterative refinement in fixed precision 234 Iterative refinement in mixed precision 234 Iterative refinement, backward error analysis 235Ч240 Iterative refinement, behaviour with GEPP 239 Iterative refinement, behaviour with QR factorization 375Ч376 Iterative refinement, condition number estimate from 243 Iterative refinement, forward error analysis 232Ч235 Iterative refinement, LAPACK convergence test 242 Iterative refinement, practical issues 242Ч243 Jacobi method, forward error analysis 332Ч334 Jalby, William 385 Jankowski, M. 94 241 242 Jansen, Paul 486 Jennings, A. 165 Jennings, L. S. 421 Johnson, Charles R. 119 150 287 310 348 546 551 555 558 580 Johnson, Samuel 675 Jones, Mark T. 226 Jones, William B. 507 Jordan canonical form 346Ч348 Jordan, Camille 284 Jordan, T. L. 409 Jordan, Wilhelm 284 Kagstrom, Bo 305 320 322Ч324 Kahan matrix 161 214 Kahan matrix, second smallest singular value 167 Kahan, William M. (Velvel) 1q 29 33 34 46 47 47q 50 50q 59 63Ч65 75 86 92Ч95 98 113 123 126 136 161 165 169q 225 243 486 490 494 496 497 499 501 502 507 Kahaner, David K. 391q Kailath, T. 441 Kala, R. 323 324 Kaniel, S. 226 Karasalo, Ilkka 165 Karatsuba, A. 461 Karlin, Samuel 523 Karlson, Rune 404 413 Karney, David L. 514 525 Karp, A. 195 Karpinski, Richard 56 497 Kate, Tosio 126 Kaufman, Linda 221 225 226 385 Keiper, Jerry B. 36 Keller, Herbert Bishop 189 257 325q Kennedy, Jr., William J. 34 Kenney, Charles S. 301 323 525 Kerr, Thomas H. 225 KielbasinskiAndrzej 84 94 224 242 406 411 418 422 Kincaid, D. R. 503 Kittaneh, Fuad 525 Knight, Philip A. 328 329 354 356 358 460 461 Knuth, Donald E. xxiv 54 57 58 67q 87q 93 94 114 461 491q 520q 526 534 Kocak, Huseyin 32 Koltracht, I. 141 517 Korner, T. W. 465q Kornerup, Peter 54 Kostlan, Eric 518 527 Kovarik, Z. V. 145 Kowalewski, G. 440 Krasny, Robert 505 Kreczmar, Antoni 460 Kreiss matrix theorem 353 Krogh, F. T. 503 Krol, Ed 582 Kronecker product 310 323 Kruckeberg, F. 198 Kubota, Koichi 488 Kuczynski, J. 300 Kuki, H. 60 Kulisch, Ulrich W. 486 487 Kuperman, I. B. 146 La Porte, M. 53 La Touche, Mrs. 87q 88 Laderman, Julian 450 459 Lagrange, Joseph Louis 219 Lancaster, Peter 322 LANCELOT 181 197 Lanczos, Cornelius 490 LAPACK 587Ч589 LAPACK, 500Ч501 LAPACK, block and partitioned LU factorization 258 LAPACK, Cholesky factorization 226Ч227 LAPACK, condition number estimation 294Ч297 306 LAPACK, diagonal pivoting method 227 LAPACK, forward error bound for linear systems 144 LAPACK, iterative refinement 242Ч243 LAPACK, least squares problem 412 LAPACK, LU factorization 192 198Ч199 258 LAPACK, matrix 1-norm estimator 294Ч297 LAPACK, matrix inversion 285 LAPACK, QR factorization 386Ч387 LAPACK, Sylvester equation 324 LAPACK, test matrix generation 527 LAPACK, triangular systems 166 LAPACK, underdetermined system 423 LAPACK, xlamch for determining machine parameters 498 Laratta, A. 421 422 Larson, John L. 488 Larsson, S. 32 Laszlo, Lajos 351 Latin, neoclassic, publishing papers in 470 Laub, Alan J. 301 320 322 323 525 Lauchli, Peter 388 Lawson, Charles L. 385 409 410 422 502 Least significant digit 40 Least squares problem 391Ч413 Least squares problem, augmented system matrix 393 Least squares problem, augmented system matrix, scaling and conditioning of 402 Least squares problem, backward error 404Ч407 413 Least squares problem, constrained 412 Least squares problem, iterative refinement 399Ч403 410 Least squares problem, Longley test problem 410 Least squares problem, modified Gram Ч Schmidt, error analysis 396Ч397 Least squares problem, normal equations, error analysis 397Ч399 Least squares problem, normal equations, versus QR factorization 399 Least squares problem, perturbation theory 392Ч394 Least squares problem, QR factorization, error analysis 395Ч396 Least squares problem, seminormal equations 403Ч404 Least squares problem, weighted 411Ч412 LeBlanc, E. 486 Lee, King 460 Lehmer, D. H. 529 Lehoucq, R. B. 569 Leja ordering 111 113 115 438 Lemeire, Frans 165 Leuprecht, H. 98 Level index arithmetic 53 LeVeque, Randall J. 13 33 Lewis, John G. 33 301 305 527 Li, T. Y. 285 Li, Xiaoye 495 Linear system, large dense, in applications 198 Linear system, perturbation theory 131Ч150 Linear system, practical forward error bounds 143Ч144 Linear system, records for largest solved 199t Linear system, scaling before Gaussian elimination 191Ч192 197Ч198 Linear system, times for solution on early computers 189t Linnainmaa, Seppo 53 83 93 100 504 LINPACK 587 LINPACK, Cholesky factorization of semidefinite matrix 217 LINPACK, condition estimator 297Ч299 305 LINPACK, iterative refinement 242 LINPACK, LU factorization 192 LINPACK, matrix inversion 267 271Ч274 LINPACK, tridiagonal system solution 306 Linz, Peter 100 Linzer, Elliot 470 Liu, Joseph W. H. 224 226 Logarithmic distribution of numbers 51 53 Longley test problem 410 Longley, James W. 410 Lotstedt, Per 412 Lotti, Grazia 456 457 LU factorization 169Ч201 (see also УGaussian eliminationФ) LU factorization for nonsymmetric positive definite matrix 223Ч224 LU factorization of Hessenberg matrix 27Ч28 LU factorization of tridiagonal matrix 184 LU factorization without pivoting, instability of 17 LU factorization, a posteriori stability tests 192Ч194 LU factorization, block see УBlock LU factorizationФ LU factorization, complete pivoting 170 LU factorization, CroutТs method 174 LU factorization, determinantal formulae for factors 172 LU factorization, DoolittleТs method 173Ч174 LU factorization, error analysis 174Ч177 LU factorization, error analysis, history of 186Ч191 LU factorization, existence and uniqueness 171Ч172 LU factorization, growth factor 177Ч183 (see also УGrowth factorФ) LU factorization, loop orderings 195 LU factorization, partial pivoting 170 173 LU factorization, partitioned, error analysis of 248Ч250 LU factorization, perturbation bounds 194 LU factorization, row and column scaling 191Ч192 LU factorization, stability for M-matrix 198 LU factorization, versus CramerТs rule 14Ч15 Lu, Hao 441 Lyapunov equation, backward error 316Ч317
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




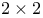 problems, solving
problems, solving