|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Straumann N. — General relativity and relativistic astrophysics |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Laws of physics in external gravitational fields 89ff
Leibniz rule 10 30
Lense — Thirring effect see also “Precession of gyroscope” 263 265
Levi — Civita connection 58
Levi — Civita connection, local expression of 58
Lie algebra of vector fields 17 71
Lie derivative 21 24 71
Lie derivative, local coordinate expression of 25 71
Lie derivative, of metric tensor 139
Lie transport 115 124—125
Light rays deflection of 86
Light rays deflection of measurements of 180—181
Light rays deflection of, by the solar corona 181—182
Light rays deflection of, in a Schwarzschild metric 178ff
Light rays in geometrical optics 103
Light rays puths of 90
Linear connection see “Affine connection”
Linearized Bianchi identities 214
Linearized Einstein tensor 214
Linearized field equations 215 217—218
Linearized field, multipole expansion of 226ff
Linearized Ricci tensor 214 217
Linearized Riemann tensor 223
Linearized theory gravitational waves in 220ff
Linearized theory of gravity 214ff
Local basis of one-forms 21
Local basis of vector fields 21
Local coordinate neighborhood 4
Local coordinate systems 12 118—119
Local flow of vector field 21
Local inertial system 83 89 147
Local Lorentz transformation 147 151
Local one-parameter group 22
Local reference frames 111ff
Locally finite covering 43
Lorentz gauge condition 102
Lorentz invariance, local 151
Lorentz manifold 88
Lorentz manifold, spherically symmetric see also “Manifolds Pseudo-Riemannian” 88
Lorentz transformation 147
Lorentz transformation, local 147 151
Magnetic dipole radiation see also “Pulsars” 352
Magnetic fields conservation of magnetic flux 350
Magnetic fields determined with cyclotron line 348—349
Magnetic fields diffusion time 350
Magnetic fields influence on neutron star cooling 319
Magnetic fields matter in strong magnetic fields 358—360
Magnetic fields of neutron stars 348—349 353
Magnetic fields rapid dissipation 350
Magnetic fields reconnection 350
Magnetic fields relativistic magnetohydro-dynamics 351—352
Magnetosphere of pulsar 355—358
Manifold 4ff
Manifold  -compact 4 -compact 4
Manifold (pseudo-)Riemannian 20
Manifold differentiable 6
Manifold dimension of 12
Manifold flat 68
Manifold locally flat 4
Manifold open 5
Manifold orientable 36
Manifold oriented 36
Manifold paracompact 4
Manifold product 8
Manifold Schwarzschild — Kruskal 196
Manifold sub- 7
Manifold topological 4 12
Mappings and tensor fields 22
Mappings coordinate representation of 6
Mappings differentiable 6
Mappings of class 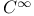 56 56
Mass function for binary systems 382
Material derivative 432
Matter in strong magnetic fields 358—360
Matter in strong magnetic fields, ground-state energy of hydrogen atom 360
Maximal mass of neutron stars 300
Maximal mass of neutron stars, for realistic equations of state 298
Maximal mass of neutron stars, model independent bounds 299 305
Maxwell's equations 93
Maxwell's equations, as variational equations 144
Maxwell's equations, characteristics of 165
Maxwell's equations, conformal invariance of 94
Mean free path and diffusion constant 343
Mean free path of neutrino during supernova formation 342
Mean free path of neutrino in neutron star 307
Measure-valued one-form 45
Mechanics of binary systems 374—376 382—383
Mechanics of binary systems, mass function 382
Mechanics of binary systems, motion of test particle 375
Mechanics of binary systems, motion of test particle, equilibrium positions 375
Mechanics of binary systems, motion of test particle, equipotential surfaces 375
Mechanics of binary systems, motion of test particle, inner Lagrange point 376
Mechanics of binary systems, motion of test particle, Jacobi integral 375
Mechanics of binary systems, motion of test particle, nature of critical points 376
Mechanics of binary systems, motion of test particle, Roche lobe 376
Mechanics of binary systems, Navier — Stokes equation in corotating system 376
Mechanics of binary systems, velocity curve 383
Melting temperature of ion lattice 310
Metric conformally flat 134—135
Metric connection 57 63
Metric Lorentzian 88
Metric physically equivalent 139
Metric pseudo-Riemannian 19
Metric raising and lowering indices with 59
Metric Riemannian see also “Kerr-Newman metric; Post-Newtonian approximation; Schwarzschild metric; Weak field approximation” 19
Mini-black holes 369
Mobius strip 36
Motion of a test body see “Test body”
Moving frame see also “Tetrad field” 61
Multilinear forms 27
Multilinear mapping, associated to tensor field 19
Multilinear mapping, associated to tensor field, differential forms 29
Multipole expansion of linearized field 226ff
Naked singularity 365
Navier — Stokes equation nonrelativistic 434
Navier — Stokes equation relativistic 426 440
Neutral current interaction 313
Neutral current interaction, and neutrino scattering 342
Neutral current interaction, effect in pair annihilation 335—336
Neutral current interaction, effective four-fermion interaction 314 342
Neutrino emission from neutron stars gradient of neutrino luminosity 307
Neutrino emission from neutron stars influence of superfluidity 318
Neutrino emission from neutron stars modified Urea rate 314—316
Neutrino emission from neutron stars modified Urea reactions 313
Neutrino emission from neutron stars neutrino pair bremsstrahlung 313
Neutrino emission from neutron stars neutrino transparency 307
Neutrino emission from neutron stars nucleon pair bremsstrahlung 313
Neutrino emission from neutron stars pion condensate  -decay 317 -decay 317
Neutrino emission from neutron stars suppression of Urea reactions see also “Cooling of neutron stars” 313
Neutrino emission from supernovae 305
Neutrino emission from supernovae neutronization reactions 342
Neutrino emission from supernovae, neutrino trapping 342—344
Neutrino emission from supernovae, thermal reactions see also “Supernova formation; Core collapse” 305 334 345
Neutrino emission of massive stars 334
Neutrino emission of massive stars, important processes 334
Neutrino emission of massive stars, luminosity 333 336
Neutrino emission of massive stars, pair annihilation 334—336
Neutrino opacity 342
Neutrino scattering on heavy nuclei 342—343
Neutrino scattering on neutrons 343
Neutrino stars 297
Neutrino stars Oppenheimer — Volkoff limit for 297
Neutrino trapping 342—344
Neutron stars 280ff
Neutron stars allowed core region 302
Neutron stars and supernovae 281 285 306 346
Neutron stars bounds for muss 189 305
Neutron stars central core 294
Neutron stars cooling of see “Cooling of neutron stars crust” 293—294
Neutron stars cyclotron lines 348—349
| Neutron stars density profile 298
Neutron stars, detailed models 297
Neutron stars, equations of state 297
Neutron stars, Fermi momenta of nucleons 309
Neutron stars, formation 281 285 346
Neutron stars, gross features 285
Neutron stars, historical remarks 285
Neutron stars, hyperons in 294
Neutron stars, ideal n-p-e model 394
Neutron stars, inner fluid 294
Neutron stars, interior 293
Neutron stars, magnetic fields 348—349 353
Neutron stars, mass-radius relation 297
Neutron stars, maximum mass 296 298—299 305
Neutron stars, observations comparison with cooling calculations 318—321
Neutron stars, observations cyclotron lines 348—349
Neutron stars, observations masses 269 379
Neutron stars, observations radii 381
Neutron stars, observations surface temperatures 306
Neutron stars, observations thermal radiation see also “Binary pulsar; Pulsars; X-ray binary bursters; X-ray binary pulsars” 306
Neutron stars, Oppenheimer — Volkoff model 296
Neutron stars, pion condensate 294 316
Neutron stars, quark phase in 294
Neutron stars, relation between surface and interior temperature 308
Neutron stars, specific heat 308 312
Neutron stars, superconductivity in 294 311
Neutron stars, superfluidity in 294 310 318
Neutron stars, temperature profile 308
Neutron stars, thermal energy transport 307
Neutron stars, thermal equilibrium 306—307
Neutron stars, thermodynamic properties 306ff
Neutron stars, uniform density model see also “Accretion; Binary pulsar; Pulsars Superfluidity 290 318
Neutronization see also “Electron capture” 280
Newton vs. Coulomb 327
Newtonian limit 96—97 133
Newtonian limit, potential 126 128
Newtonian limit, theory, comparison with 126
Nonsaturation of gravitational forces heuristic discussion 324
Nonsaturation of gravitational forces rigorous results 325—327
Normal coordinates 50
Nova outbursts 387
Nuclear density 295 310
Nucleon-nucleon interaction BCS pairing 311—312
Nucleon-nucleon interaction in nucleon pair bremsstrahlung 314—315
Nucleon-nucleon interaction Landau interaction 316
Nucleon-nucleon interaction Landau limit 316
Nucleon-nucleon interaction one pion exchange 315
Nucleon-nucleon interaction short range contribution 315
Number density of baryons 289 307
Observer at rest 107
Observer rotation of 120
One parameter group local 22
One parameter group of diffeomorphisms 22
One-forms 19
One-forms, covariant derivative of 53
One-forms, pull back of 19
Opacity 307 408
Opacity Rosseland-mean 408
Opacity, electron scattering 408
Opacity, free-free transitions 408
Orientation and volume forms 36
Orientation induced 44
Orientation of boundary 44
Orientation of manifold 36
Orientation same 36
Oriented atlas 36
Oriented basis of one-forms 39
Oriented manifold 36
Palatini identity 217
Parallel transport 50—51
Parallel transport, path independence of 69
Penrose mechanism 368
Perihelion (periastron) see also “Binary pulsar; Post-Newtonian approximation”
Perihelion (periastron) advance of 176ff 220 258 268
Perihelion (periastron) advance of, of mercury 178
Perturbations adiabatic 291 338
Perturbations eigenvalue equation for 291
Perturbations of thin accretion disks 419
Photodisintegration 280
Photodisintegration, of iron-nickel core 280 337—338
Photospheric boundary conditions 307
Pion condensation 294 316
Pion condensation quasiparticles in presence of 317
Pion condensation, chiral rotation 317
Pion condensation, influence on neutron star cooling 306 318 320
Pion condensation, wave vector 317
Plane waves in the linearized theory 221ff
Plane waves in the linearized theory, polarization states of 222
Plane waves in the linearized theory, polarization tensor of 221
Planetary orbits 273ff
Plasma frequency 310
Poincare lemma 33 40 71
Polarization states of gravitational waves 222
Polarization tensor for the linearized field 221
Polarization vector of electromagnetic waves 101
Positive chart 36
Positive coordinate system 37
Post-Newtonian approximation asymptotic fields 252
Post-Newtonian approximation Christoffel symbols 248
Post-Newtonian approximation equation of motion 255
Post-Newtonian approximation field equations 246
Post-Newtonian approximation gauge conditions for 244 247 251
Post-Newtonian approximation metric 254
Post-Newtonian approximation periastron shift 258
Post-Newtonian approximation precession of gyroscope 261
Post-Newtonian approximation Ricci tensor 245
Post-Newtonian approximation two-body problem 256
Post-Newtonian approximation two-body problem, center of mass in 256
Post-Newtonian approximation two-body problem, Hamilton — Jacobi function of 260
Post-Newtonian approximation two-body problem, Hamiltonian for 257—258
Post-Newtonian approximation two-body problem, solution of 258
Post-Newtonian potentials 247
Post-Newtonian potentials, for system of point particles 254
Post-Newtonian potentials, particle in 249
Post-Newtonian potentials, particle in, Langrangian for 249
Potential effective 174 176
Potential electromagnetic 93ff
Potential gravitational inertial 88
Potential Newtonian 126 128 219
Precession of gyroscope geodesic precession 186ff 263 265
Precession of gyroscope in a gravitational field 111ff 115
Precession of gyroscope in a Schwarzschild field 186ff
Precession of gyroscope in orbit around the Earth 263
Precession of gyroscope in post-Newtonian approximation 261—263
Precession of gyroscope Lense — Thirring effect 263 265
Principle of equivalence 79 81ff 135
Principle of equivalence, ambiguities 95
Principle of equivalence, mathematical formulation 87
Principle of general covariance see “Covariance”
Product manifold 8
Product manifold, differentiable structure of 8
Pseudo-Riemannian manifold 20
Pseudo-Riemannian metric 19
Pseudotensors and three-forms of stress-energy see also “Energy and momentum; Superpotential”
Pseudotensors and three-forms of stress-energy for a plane wave 236—237
Pseudotensors and three-forms of stress-energy for gravitational field 155
Pseudotensors and three-forms of stress-energy Landau — Lifschitz 155—156
Pull back of covariant tensor field 20 22
Pull back of one-form 20
Pulsars see also “Binary pulsar; Crab pulsar; Supernovae”
Pulsars, aligned rotator model 355 357
Pulsars, as rotating neutron stars 352
Pulsars, braking index 353
Pulsars, characteristic age 353
Pulsars, energy in radio pulses 354
Pulsars, gravitational radiation from 354
Pulsars, induced electric fields 355 357
Pulsars, instability of exterior vacuum solution 355—357
Pulsars, light cylinder model 358
Pulsars, magnetic dipole radiation 352—353
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 -compact
-compact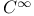
 -decay
-decay