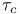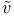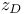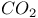 laser 76 77 307—313 539—540 laser 76 77 307—313 539—540
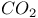 laser cross section of 290 laser cross section of 290
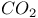 laser pressure broadening of 128—129 163 166—167 laser pressure broadening of 128—129 163 166—167
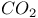 laser pulse amplification in 337 laser pulse amplification in 337
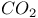 laser transient response of 314—316 laser transient response of 314—316
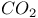 laser with unstable resonators 863—864 885—887 890 laser with unstable resonators 863—864 885—887 890
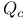 see “Cavity Q value” see “Cavity Q value”
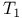 see “Longitudinal relaxation time” see “Longitudinal relaxation time”
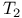 see “Dephasing” “Dephasing “Transverse see “Dephasing” “Dephasing “Transverse
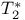 168—171 168—171
 transitions 136—140 transitions 136—140
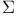 see “Transition cross section” see “Transition cross section”
 transitions 136—141 transitions 136—141
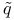 parameter see “Gaussian beam parameter parameter see “Gaussian beam parameter 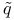 ” ”
ABCD matrices see “Ray matrices Complex
Aberrated laser beams 706—711 (see also “Multimode optical beams”)
Absorbing media 283 (see also “Saturable absorbers”)
Absorption cross section see “Transition cross section”
Absorptive bistability see “Bistable optical systems’
Acoustic transitions 198 (see also “Nonradiative transitions” “Phonon “Phonon
Acoustooptic Q switch see “Q switches”
Active mode locking 1041—1103
Active mode locking autocorrelation measurements of 1081—1082
Active mode locking chirp in 1067 1069—1071
Active mode locking circulating gaussian pulse analysis of 1062—1067 1077—1079
Active mode locking coupled-mode analysis of 1087—1092 1096—1098
Active mode locking detuning effects in 1084—1086 1088
Active mode locking etalon effects in 1071—1073
Active mode locking experimental results for 1050 1052 1070—1073 1081—103 1096 1099—1100
Active mode locking FM laser operation 1057
Active mode locking FM mode locking 1069—1071 1083—1084 1095 1100
Active mode locking general description of 1056—1061
Active mode locking harmonic 1060 1073—1074
Active mode locking higher-order solutions for 1069
Active mode locking homogeneous versus inhomgeneous 1059
Active mode locking modulator polarization term 1089—1091 1092—1095
Active mode locking pre-lasing 1082—1083
Active mode locking synchronously pumped 1058—1059
Active mode locking time and frequency description of 1041—1055
Active mode locking time-domain analysis of 1061—1067
Active mode locking transient buildup of 1075—1081 1083—1084
Adaptive optics 709 711 912
Adiabatic rapid passage 1263 (see also “Coherent transients”)
Adjoint modes 848—849 (see also Linear operators Orthogonality”)
Adler equation 1143 1147—1149
Airy disk pattern 679 728—729
Ammonia maser 74
Amplification coefficient see “Laser amplification”
Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) 547—557
Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) and lifetime shortening 552
Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) and mirrorless lasers 547—557
Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) in regenerative cavity 445 451—454
Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) in semiconductor lasers 445 463—464 “Superradiant
Amplifier saturation see «Saturation”
Amplitude modulation of lasers see “Laser amplitude modulation”
Anomalous dispersion see “Dispersion”
Antenna theorem 672
Antiresonant-ring interferometer 1126—1127 (see also “Interferometers”
Aperture diffraction and relay imaging 739—740 742
Aperture diffraction by annular apertures 736 737
Aperture diffraction by circular aperture 727—743
Aperture diffraction by rectangular aperture 712—727
Aperture diffraction by single slit 716—723
Aperture diffraction from arbitrary apertures 740—742
Aperture diffraction of gaussian beams 667—668 731—734 742
Aperture diffraction on-axis intensity 725—726 731
Aperture diffraction special properties of circular apertures 736—738 (see also “Diffraction effects”)
Aperture diffraction, Airy disk pattern 728—729
Aperture shaping see “Apodization” “Soft “Tapered
Apodization 578—580 710 711
ASE see “Amplified spontaneous emission”
Astigmatic optical systems 597 616—617 647 “Ray “Ray
Asymptotic analysis see “Unstable optical resonators”
Atomic absorption lines 19—22
Atomic energy levels 6—18
Atomic linewidth see Line-broadening effects Linewidths”
Atomic phase shift effects 271—272 275
Atomic rate equations 24—28 37 176—220 228 497—510
Atomic rate equations and blackbody-stimulated transitions 188—190 195—196
Atomic rate equations for four-level system 245—248
Atomic rate equations for magnetic-dipole transition 1249—1256
Atomic rate equations for multiple-energy-level systems 211—220
Atomic rate equations for three-level system 248—250
Atomic rate equations for two-level system 255
Atomic rate equations low- and high-frequency approximations to 218—219
Atomic rate equations transient solutions of 208 218 256 257—263
Atomic rate equations validity of 225—227 (see also “Cavity rate equations” “Coupled “Rabi
Atomic responses, quantum description of 137—142
Atomic responses, sinusoidal steady-state 111—112 (see also “Classical electron-oscillator model” “Rabi susceptibility”)
Autocorrelation techniques 1081—1082 1122—1123
Available power, from laser amplifier 299—5102
Available power, from laser oscillator 480—481
Axial mode beating, in Q-switched lasers 1034—1036 1046 “Mode
Axial modes 41—42 432—440 1041—1054
Axial modes for transient signals 1045
Axial modes in dispersive cavity 436
Axial modes versus transverse modes 569 (see also “Modes” “Optical
Axicons, in unstable resonators 908—912
B integral 385—386
Babinet’s principle 736
Backscattering effects, on laser oscillators 530 534 1163 1170
Backscattering effects, on unstable resonators 906—908 912
Bandwidth, for atomic absorber 284
Bandwidth, for single-pass laser amplifier 281—282 284
Beam distortion see “Aberrated laser beams” “Multimode
Beam scalloping 654 822 “Lensguides”)
Beat frequency 317—318 471—472 575 765—766 767 1163
Bessel functions 45 727—729 742 1097—1100
Bethe small-hole coupling theory 939
Bilinear transformation 680 785
Biorthogonality 847 849—850 853—854 “Orthogonality”)
Birefringent couplers, for variable-reflectivity resonators 920—922
Bistable optical systems 538—546
Blackbody radiation 187—195
Blackbody-stimulated transitions 188—190 195—196
Bloch equations, derivation of 1236—1237 1243
Bloch equations, large-signal solutions of 1257—1266
Bloch equations, longitudinal 1240—1242
Bloch equations, longitudinal solutions for 1249—1256
Bloch equations, Rabi flopping behavior of 1259—1263
Bloch equations, rotating-wave approximation in 1247—1248
Bloch equations, saturation behavior of 1251—1255
Bloch equations, transient solutions of 1257—1262
Bloch equations, transverse 1237—1240
Bloch equations, transverse solutions for 1243—1249
Bloch vector, in superradiant emission 549
Bloembergen three-level maser 74—75
Bohr magneton 1218 1229
Boltzmann ratio 76 202—203
Boltzmann’s principle 27—28 35
Boltzmann’s principle for degenerate levels 154
Boundary waves see “Edge waves”
Brewster windows 63
Canonical form, for Huygen’s integral 805—811
Canonical form, for ray matrix 813
Canonical form, for unstable resonator 867—874
Canonical form, for variable-reflectivity resonator 913—922
Carbon dioxide laser see “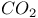 laser” laser”
Carnot cycle 71
Cascade pumping 251
Cassegrainian telescope 863
Cavity decay time see “Cavity lifetime”
Cavity dumping 975—980 (see also “Laser amplitude modulation”
Cavity equation see “Cavity rate equation” “Laser
Cavity frequencies see “Optical resonator frequencies”
Cavity frequency pulling see “Frequency pulling effects”
Cavity lifetime 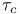 429—430 492 429—430 492
Cavity mode density see “Mode density”
Cavity mode number p 499—501 502—505
Cavity modes see “Optical resonator modes”
| Cavity Q value 429—430 (see also “Cavity lifetime”)
Cavity rate equation 497—510
Cavity rate equation derivation of 497—505 (see also “Atomic rate equations” “Coupled
Chaos, in lasers 545—546
Chemical lasers 175
Chirp 333—334 345—348 356
Chirp due to self-phase modulation 382—383
Chirp in FM mode-locked lasers 1067—1071
Chirp in spatial frequency domain 707—708
Chirp radar 347—348 350—351
Circle diagram, for stable resonators 748—749
Circuit analogs see “Equivalent-circuit models”
Circular polarization, of electric-dipole transition 136—141 144—145 149
Circular polarization, of magnetic-dipole transition 1246—1248 1255
Clamping of population inversion 515—520
Classical electron-oscillator model 80—89 113—117 227—228
Classical electron-oscillator model collision broadening of 93—94
Classical electron-oscillator model power transfer to 177—178
Classical electron-oscillator model two- and three-dimensional 149
Classical magnetized top model 1228—1236
Classical magnetized top model equation of motion for 1231
Classical magnetized top model precession of 1231—1232 (see also “Magnetic dipole transitions”)
Cleaved-coupled-cavity lasers 528
Coherence 23 28 33—35 49—60 66—67 547
Coherence brightening 555—556 (see also “Amplified spontaneous emission”)
Coherence in stimulated transitions 28
Coherence spatial 43 55—57 67
Coherence temporal 54—55 66—67
Coherent pulse effects see “Coherent transients”
Coherent transients 237—341 547 1257—1263
Colliding-pulse mode locking see “Passive mode locking”
Collimated beam propagation 55—56 669—670
Collimated Presnel number 806—808 870
Collins chart 680—681
Collision rate, in real gases 99
Collisions and collision broadening 90—97 127—130 134
Collisions and collision broadening elastic versus inelastic 200 1196
Collisions and collision broadening in classical electron-oscillator mode 93—94
Collisions and collision broadening in real atoms 99
Collisions and collision broadening velocity-changing 1196 (see also “Dephasing” “Pressure
Complex ABCD matrix see “Complex ray matrices”
Complex gaussian ducts see “Ducts”
Complex gaussian pulse shape 107—109 169 331—335
Complex gaussian pulse shape in laser mode-locking theory 1062
Complex lorentzian lineshape 107—109 169 1245
Complex paraxial resonators 815—857
Complex paraxial resonators analysis of 815—819
Complex paraxial resonators complex stable and unstable resonators 828—829
Complex paraxial resonators eigensolutions for 815—819
Complex paraxial resonators higher-order modes 821—822 836—837
Complex paraxial resonators multielement 841—846
Complex paraxial resonators perturbation-stable 817—818
Complex paraxial resonators perturbation-unstable 831—834 836—837
Complex paraxial resonators real and geometrically stable 820—822 841
Complex paraxial resonators real and geometrically unstable 822—828
Complex paraxial resonators round-trip phase shifts 835—836
Complex paraxial resonators self-consistent 816
Complex paraxial resonators standing-wave versus traveling-wave 838—840
Complex paraxial resonators types of modes in 819
Complex paraxial resonators with intracavity telescopes 842—845
Complex paraxial wave optics 777—814
Complex paraxial wave optics and complex Hermite-gaussian beams 782—785 798—804
Complex paraxial wave optics and gaussian apertures 786—792
Complex paraxial wave optics and gaussian ducts 790—792 793—797
Complex paraxial wave optics Huygen’s integral for 777—782 792—797 805—811
Complex radius of curvature 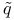 see “Gaussian beam parameter see “Gaussian beam parameter 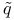 ” ”
Complex ray matrices 786—792 797
Complex ray matrices and gaussian apertures 786—788 (see also “Complex paraxial wave optics”)
Complex source point 638
Complex spot size 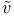 see “Hermite-gaussian see “Hermite-gaussian 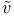 parameter” parameter”
Confined modes see “Complex paraxial resonators”
Confocal parameter 669 674
Confocal resonator 438—439 751—756 759—760 771 873—874
Confocal resonator diffraction losses of 770—774
Confocal resonator resonance frequencies of 763
Cornu spiral 717—718
Coupled cavity-atomic rate equations 505—510
Coupled cavity-atomic rate equations derivation of 505—510
Coupled cavity-atomic rate equations for laser Q switching 1008
Coupled cavity-atomic rate equations for laser spiking 958—964 970
Coupled cavity-atomic rate equations for passive Q switching 1024 (see also “Atomic rate equations” “Cavity
Coupled-mode analysis see “Active mode locking” “Unstable
Coupled-mode equations 1087—1092 1096—1098
Critical slowing 544
Cross section, for atomic transitions see “Transition cross section”
Cross section, for collisions see «Collisions”
Cross-modulation effects 318 1095
Cross-relaxation effects 1195—1199
Cross-saturation effects see “Mode competition effects” “Saturation”
Damping, coherent versus incoherent 100
Damping, nonradiative 83—84
Damping, of classical electron oscillator 82—83
Damping, radiative 83 (see also “Line-broadening effects” “Relaxation” “Spontaneous
Decay see “Damping Energy
Decibel (definition of) 280
Degeneracy factors 115 153—157 190 208—210
Degeneracy, of atomic energy levels 115 185—186 256 287—288
Degenerate optical resonators 845
Delta function see “Dirac delta function”
Dephasing in Bloch equations 1239—1240
Dephasing of classical oscillator model 93—96
Dephasing of electric-dipole transitions 90—99 127—130 134
Dephasing of magnetic-dipole precession 1237—1240 1255—1256
Dephasing time 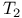 93—96 210 222—223 308—309 “Dephasing” “Transverse 93—96 210 222—223 308—309 “Dephasing” “Transverse
Dephasing, by collisions 90—95
Dephasing, by dipolar coupling 93
Dephasing, by FM modulation 98—99 100—101
Dephasing, by thermal vibrations 93 99
Dephasing, plus applied signals 97—98
Dephasing, versus energy decay 133—134 (see also “Collisions” “Transverse
Derivative spectroscopy 109 135
Detailed balance 193—194
Detuning effects 1084—1086 (see also “Active mode locking”)
Dicke superradiance see “Superradiant emission”)
Diffraction effects 277 635 698—743
Diffraction effects circular versus other apertures 736—738
Diffraction effects from arbitrary apertures 740—741
Diffraction effects on gaussian beams 667—668 731—734 “Numerical
Diffraction losses see “Optical resonators”
Diode lasers see “Semiconductor lasers”
Dipolar coupling 93 131—132
Dipole matrix element see “Transition matrix element”
Dirac delta function 340
Dirac delta function Fresnel integral as 717—718
Dirac delta function lorentzian line as 163
Dispersion and cavity frequency pulling 468
Dispersion anomalous 389
Dispersion in inhomogemeous transitions 1192—1194 1209—1210
Dispersion in optical fibers 357—358
Dispersion in optical materials 356—357
Dispersion in resonant atomic systems 351—355 376
Dispersion in resonant cavities 436—437
Dispersion in wave-propagating systems 335—339
Dispersion length 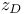 356—358 356—358
Dispersion nonlinear 375—386
Dispersion parameter D 356—357
Dispersive bistability see “Bistable optical systems”
Dispersive pulse broadening 356—358 388—392
Dispersive pulse broadening in optical fibers 357—358 388—392
Dispersive pulse broadening in optical materials 356—357
Doppler broadening 157 159 160—161 1184—1186
Doppler shift, from moving grating 706
Doppler shift, from moving mirror 986—987 1069
Double-pulsing in passively mode-locked lasers 1114—1115
Double-pulsing in Q-switched lasers 1020—1021
Ducting, in focusing media see “Ducts”
Ducts definition of 584
Ducts gaussian beams in 652—656
Ducts Huygens’ integral for 793—794
Ducts ray matrix for 534—592
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



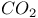 laser
laser 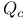
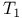
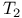
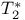
 transitions
transitions 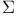
 transitions
transitions 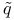 parameter
parameter